A Crossroads of Cultures: Exploring the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East
Related Articles: A Crossroads of Cultures: Exploring the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Crossroads of Cultures: Exploring the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Crossroads of Cultures: Exploring the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East

The Mediterranean and Middle East, a region spanning from the Iberian Peninsula to the Arabian Peninsula, is a complex tapestry of diverse cultures, histories, and landscapes. Its map, a visual representation of this intricate region, is a powerful tool for understanding its multifaceted nature and the interconnectedness of its people and places.
A Geographic Overview
The Mediterranean Sea, a vast body of water encompassing a diverse array of coastlines, acts as the region’s defining feature. Its shores are home to a mosaic of countries, each with its unique characteristics and historical narratives. To the north, Europe’s southernmost nations, including Spain, Italy, Greece, and Turkey, embrace the Mediterranean’s warmth and influence. To the south, the African continent extends its presence through countries like Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, and Morocco. And to the east, the Middle East, a region steeped in history and tradition, borders the Mediterranean through countries like Israel, Lebanon, Syria, and Cyprus.
Historical Significance
The Mediterranean and Middle East have long been a crossroads of civilizations, witnessing the rise and fall of empires and the development of diverse cultural expressions. From the ancient Egyptians and Greeks to the Romans and Ottomans, countless empires have left their mark on this region, contributing to its rich historical tapestry. The Mediterranean, in particular, served as a vital trade route, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences. This historical legacy is evident in the region’s architectural marvels, ancient ruins, and cultural traditions, which continue to captivate and inspire people across the globe.
Cultural Diversity
The region’s cultural diversity is as profound as its historical significance. From the vibrant mosaic of languages spoken across the region, including Arabic, Turkish, Hebrew, Greek, and Spanish, to the diverse religious beliefs, including Islam, Christianity, Judaism, and other faiths, the Mediterranean and Middle East are a testament to the power of cultural exchange and coexistence.
Geological Features
The region’s landscape is as varied as its cultures. From the rugged mountains of the Atlas range in North Africa to the lush valleys of the Nile River in Egypt, the Mediterranean and Middle East exhibit a diverse array of geological formations. The region is also home to several deserts, including the Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, and the Arabian Desert. These diverse geological features have played a significant role in shaping the region’s history, influencing its agricultural practices, and contributing to its unique cultural identity.
Modern Challenges and Opportunities
The Mediterranean and Middle East face numerous challenges in the modern world, including political instability, economic disparities, and environmental concerns. However, the region also holds immense potential for growth and development, particularly in areas like renewable energy, tourism, and technology. Understanding the region’s complexities, its historical legacy, and its cultural diversity is crucial for finding sustainable solutions to these challenges and unlocking its potential for a brighter future.
Exploring the Map: A Deeper Dive
1. The Mediterranean Sea: A Cradle of Civilizations
The Mediterranean Sea, with its warm waters and strategic location, has played a pivotal role in shaping the region’s history and culture. It served as a major trade route, connecting the ancient world’s most powerful civilizations, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. The sea’s shores are dotted with ancient cities, ports, and archaeological sites, offering glimpses into the region’s rich past.
2. The Middle East: A Region of Ancient Empires and Modern Challenges
The Middle East, with its vast deserts and fertile river valleys, has been home to some of the world’s oldest civilizations. Ancient empires like Mesopotamia, Persia, and the Roman Empire have left an enduring legacy on the region’s cultural landscape. Today, the Middle East is a region of immense geopolitical significance, facing challenges related to political instability, conflict, and economic development.
3. North Africa: A Bridge Between Continents
North Africa, with its diverse landscapes, from the Sahara Desert to the fertile coastal plains, serves as a bridge between the Mediterranean and the African continent. The region’s history is intertwined with both Europe and Africa, reflecting a unique blend of cultures and influences. North African countries are grappling with challenges related to economic development, political stability, and environmental sustainability.
4. The Levant: A Region of Ancient Trade and Modern Conflict
The Levant, a region encompassing countries like Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Israel, has long been a crossroads of civilizations, witnessing the rise and fall of empires and the development of diverse cultural expressions. Its fertile lands have attracted empires and civilizations throughout history, making it a hub of trade and cultural exchange. Today, the Levant is a region marked by conflict and political instability, posing significant challenges to its future.
5. The Iberian Peninsula: A Gateway to the Mediterranean
The Iberian Peninsula, home to Spain and Portugal, serves as a gateway to the Mediterranean. Its history is intricately linked to the region, reflecting a blend of Roman, Islamic, and European influences. The peninsula’s diverse landscapes, from the snow-capped Pyrenees Mountains to the sun-drenched Mediterranean coast, offer a unique blend of cultural and natural beauty.
FAQs About the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East
1. What are the major geographical features of the Mediterranean and Middle East?
The region’s major geographical features include the Mediterranean Sea, the Atlas Mountains, the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, and the Arabian Desert.
2. What are the major languages spoken in the Mediterranean and Middle East?
The region is home to a diverse array of languages, including Arabic, Turkish, Hebrew, Greek, Spanish, and French.
3. What are the major religions practiced in the Mediterranean and Middle East?
The region is home to a diverse range of religions, including Islam, Christianity, Judaism, and other faiths.
4. What are some of the major historical empires that have ruled the Mediterranean and Middle East?
The region has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, including the ancient Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, Ottomans, and Persians.
5. What are some of the major challenges facing the Mediterranean and Middle East today?
The region faces numerous challenges, including political instability, conflict, economic disparities, and environmental concerns.
6. What are some of the major opportunities for growth and development in the Mediterranean and Middle East?
The region holds immense potential for growth and development, particularly in areas like renewable energy, tourism, and technology.
Tips for Understanding the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East
1. Study the region’s history: Understanding the region’s historical context is crucial for comprehending its present-day challenges and opportunities.
2. Explore the region’s cultural diversity: The Mediterranean and Middle East are home to a rich tapestry of cultures, each with its unique traditions, languages, and beliefs.
3. Consider the region’s geopolitical significance: The region plays a crucial role in global affairs, and understanding its political dynamics is essential for understanding its future.
4. Analyze the region’s environmental challenges: The Mediterranean and Middle East face significant environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and climate change.
5. Examine the region’s economic prospects: The region holds immense potential for economic growth and development, particularly in areas like tourism, technology, and renewable energy.
Conclusion
The map of the Mediterranean and Middle East is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s complexities, its historical legacy, and its cultural diversity. It allows us to visualize the interconnectedness of its people and places, appreciate the region’s rich history, and recognize the challenges and opportunities it faces in the modern world. By engaging with the region’s map, we can gain a deeper understanding of its multifaceted nature and contribute to a more informed and nuanced perspective on this vital part of the world.
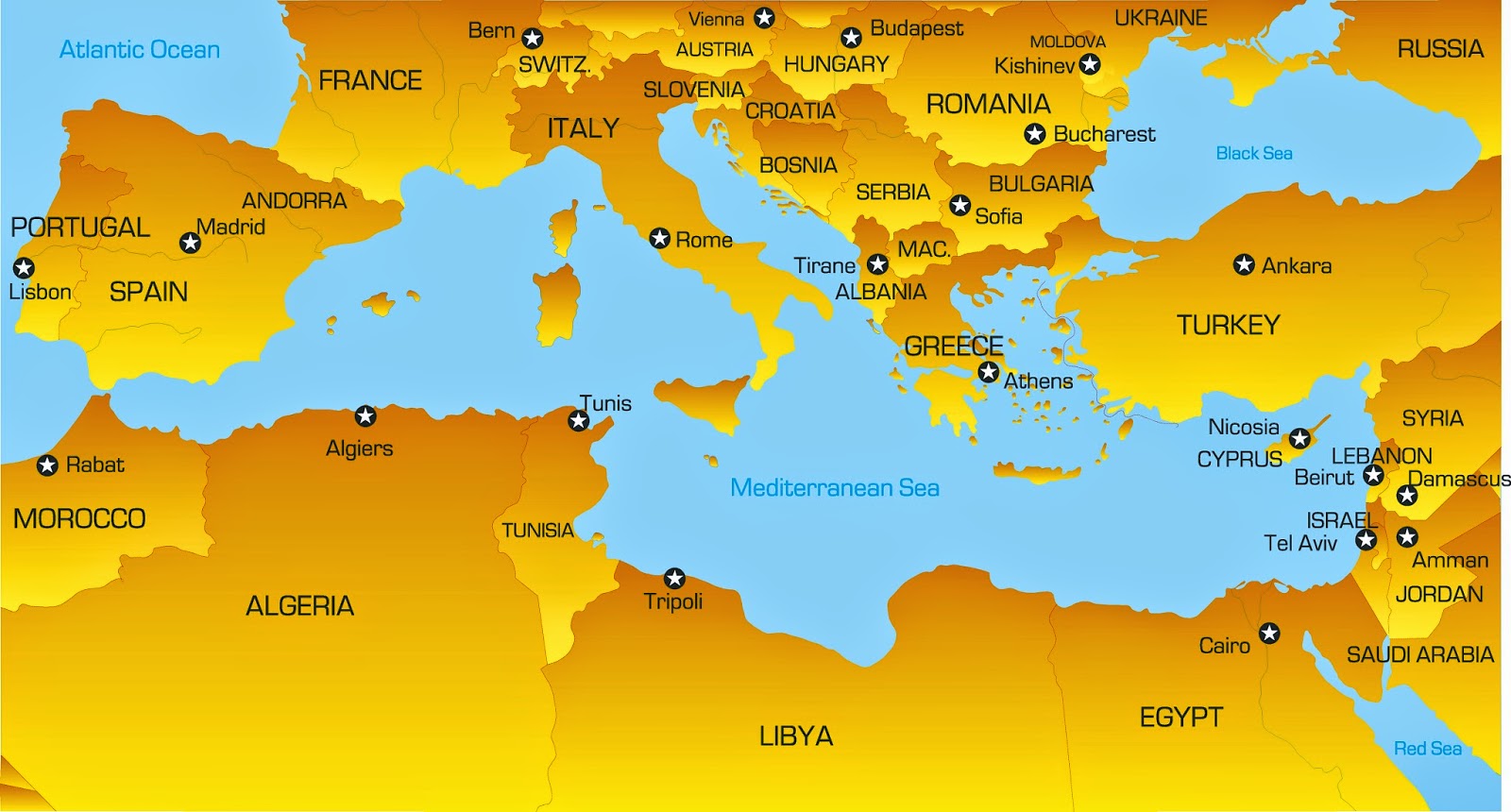


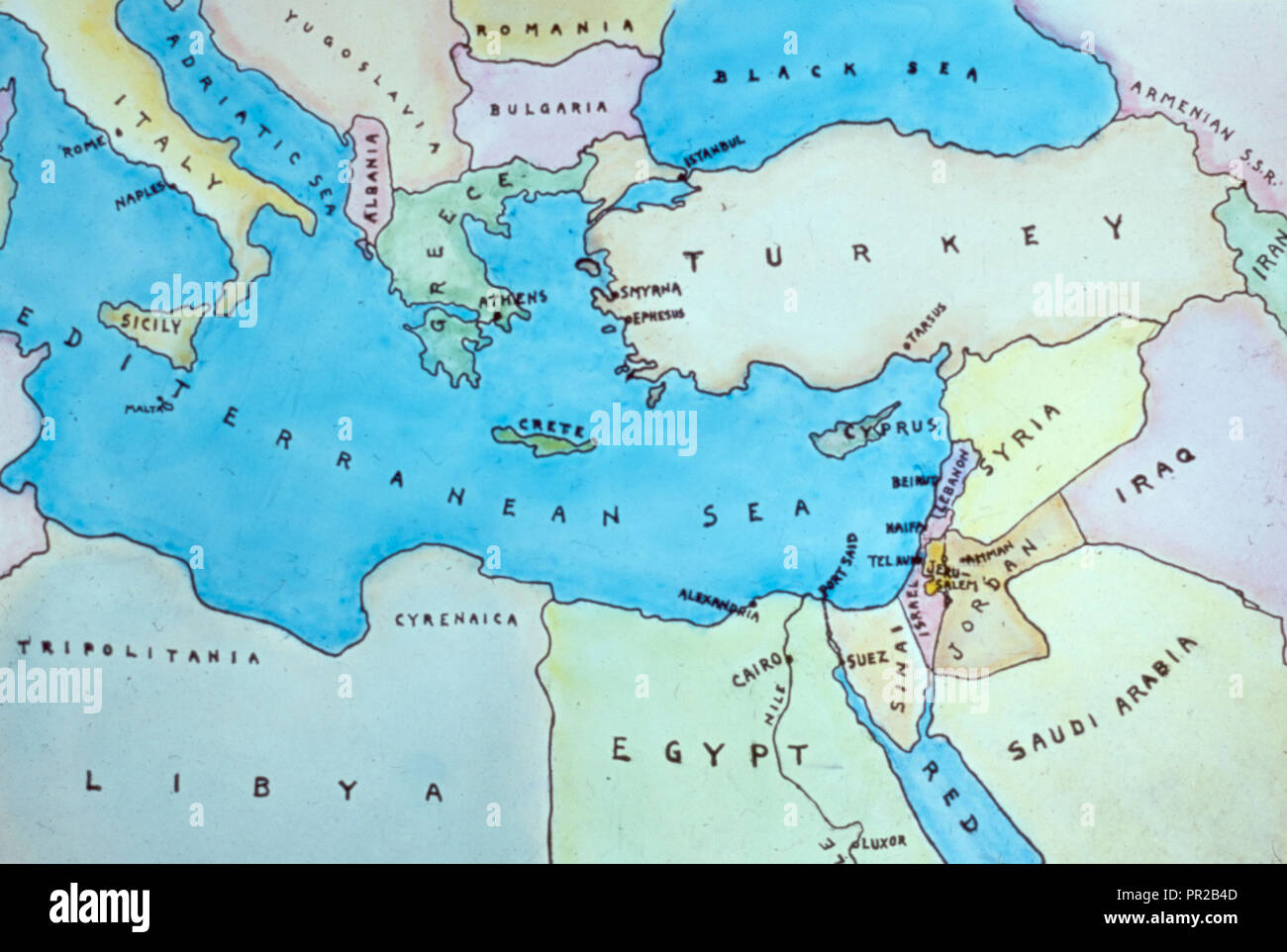
![Map showing the various ethnicities of the Middle East [1500x785] : r](https://i.redd.it/qu6y1k5fy2tx.jpg)
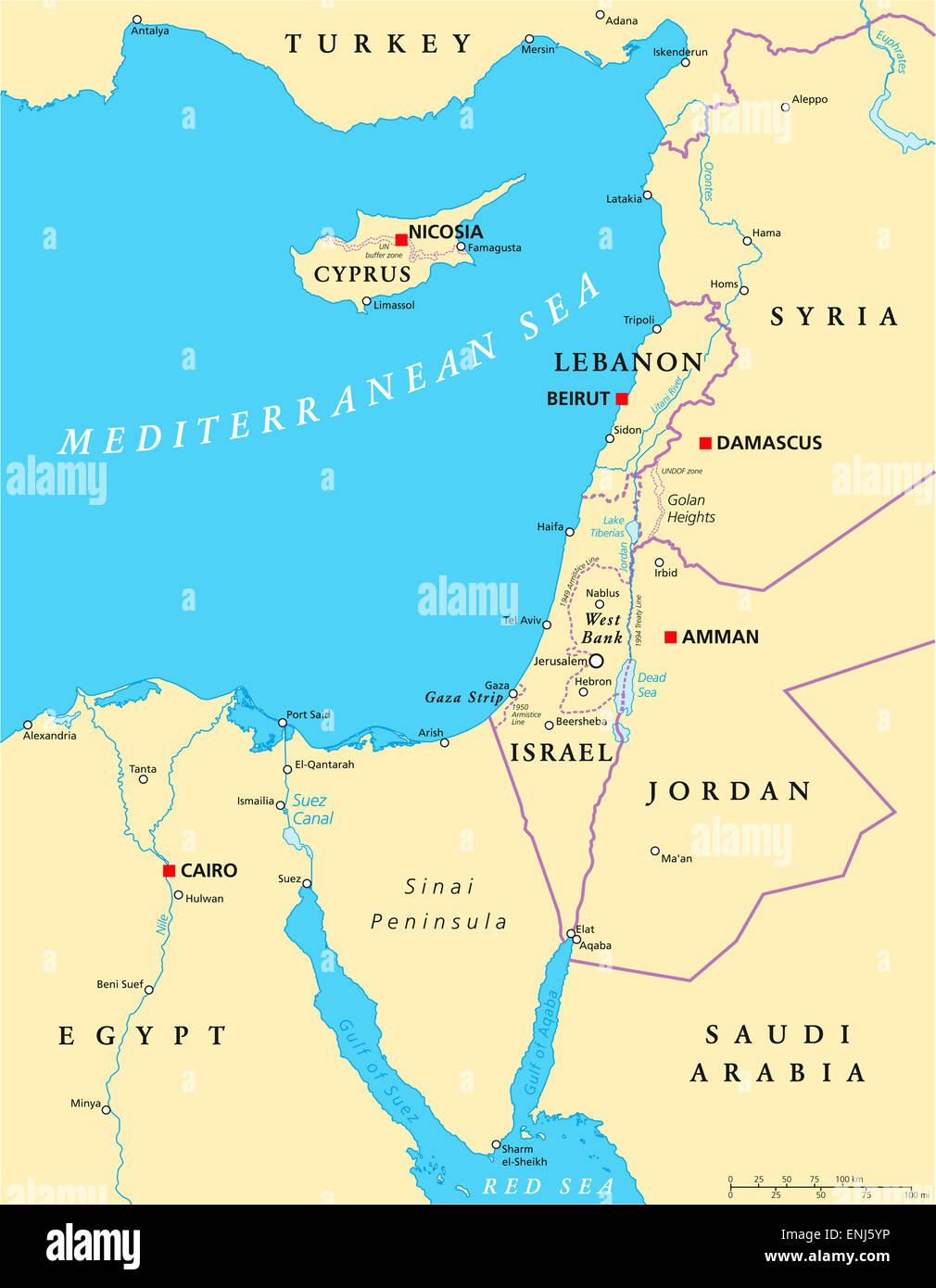


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Crossroads of Cultures: Exploring the Map of the Mediterranean and Middle East. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!