Navigating the Cosmos: Understanding Star Map Coordinates
Related Articles: Navigating the Cosmos: Understanding Star Map Coordinates
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Cosmos: Understanding Star Map Coordinates. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Cosmos: Understanding Star Map Coordinates
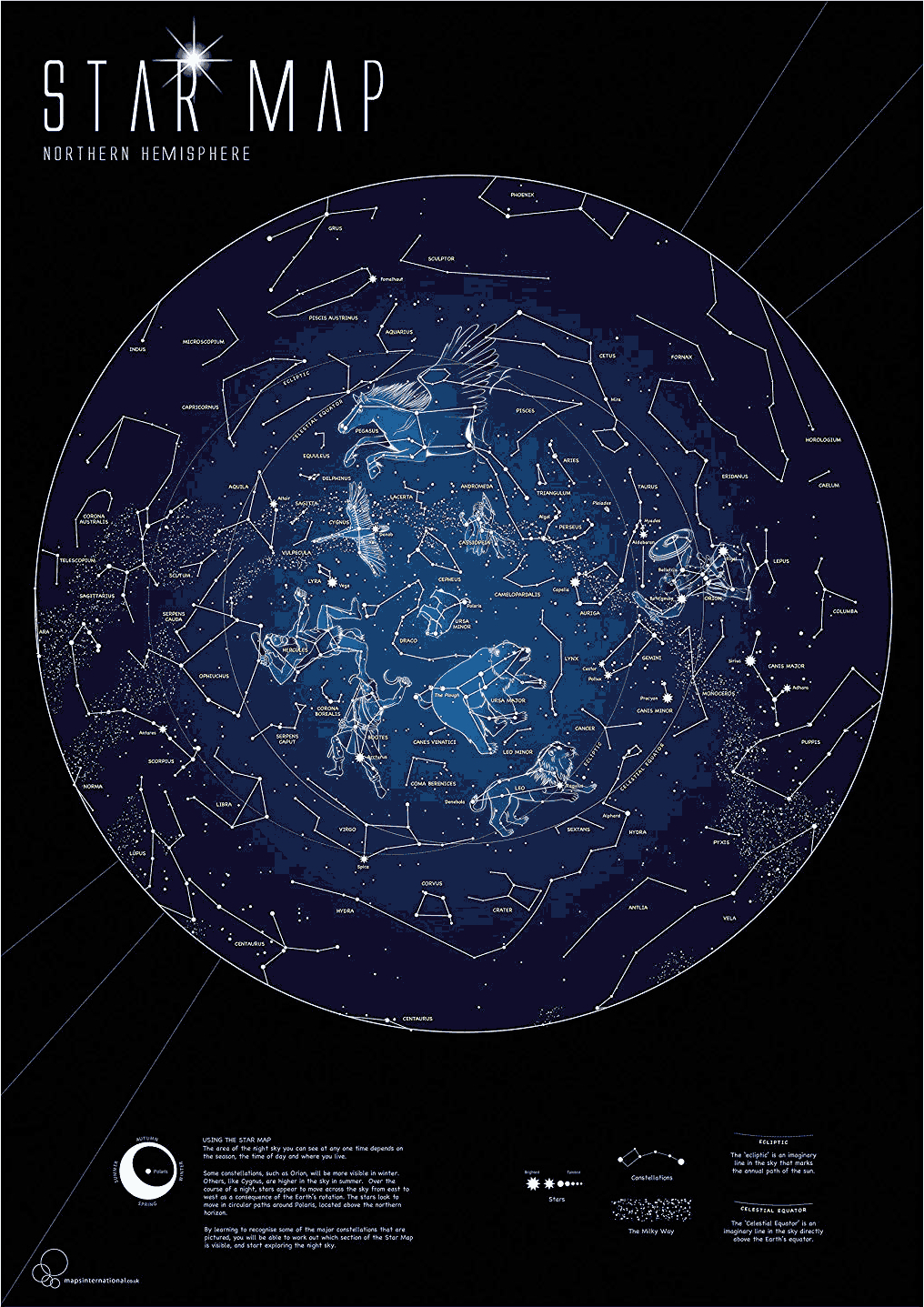
The vast expanse of the night sky, teeming with celestial bodies, has captivated humanity for millennia. From ancient civilizations using constellations for navigation to modern astronomers mapping the universe, our fascination with the stars has driven us to develop sophisticated tools for understanding and exploring the cosmos. Among these tools, star map coordinates stand out as a crucial element for accurately pinpointing and locating celestial objects.
A Framework for Cosmic Navigation:
Star map coordinates, analogous to the latitude and longitude used on Earth, provide a precise system for identifying the position of stars, planets, galaxies, and other celestial objects. This system, based on the celestial sphere, a theoretical sphere surrounding Earth, allows astronomers and stargazers to unambiguously locate and track these objects, regardless of their location on Earth.
The Celestial Sphere: A Conceptual Framework
Imagine a giant sphere, with Earth at its center. This sphere, known as the celestial sphere, encompasses the entire universe as seen from Earth. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool, not a physical entity, but it serves as a fundamental framework for understanding the positions of celestial objects.
Declination: Celestial Latitude
Similar to latitude on Earth, declination (Dec) measures the angular distance of a celestial object north or south of the celestial equator, the projection of Earth’s equator onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees, ranging from +90° at the celestial north pole to -90° at the celestial south pole, with 0° representing the celestial equator.
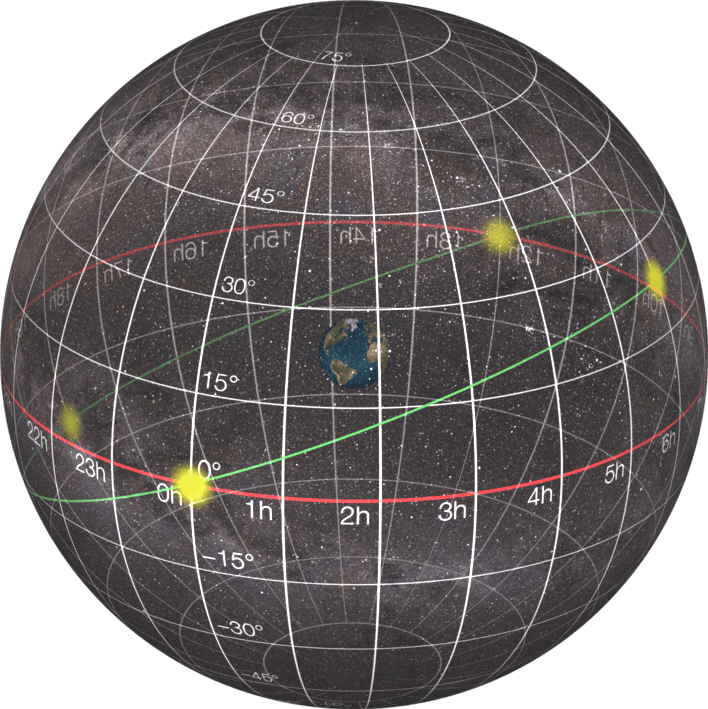
Right Ascension: Celestial Longitude
Right ascension (RA), analogous to longitude on Earth, measures the angular distance of a celestial object eastward along the celestial equator from the vernal equinox, a specific point where the Sun crosses the celestial equator moving northward. Right ascension is measured in hours, minutes, and seconds, with 24 hours corresponding to a full circle of the celestial equator.
The Importance of Star Map Coordinates:
The use of star map coordinates is paramount in various astronomical and scientific endeavors, including:
- Precise Object Identification: Star map coordinates provide a unique identifier for each celestial object, allowing astronomers to unambiguously reference and track them.
- Telescope Targeting: Astronomers use star map coordinates to direct telescopes towards specific objects of interest, enabling detailed observation and study.
- Satellite Tracking: Space agencies rely on star map coordinates to track the positions of satellites orbiting Earth, ensuring safe operations and communication.
- Spacecraft Navigation: Spacecraft utilize star map coordinates for navigation and orientation in the vast expanse of space.
- Astrophysics Research: Star map coordinates play a crucial role in astrophysical studies, enabling researchers to analyze the distribution and movement of celestial objects, furthering our understanding of the universe.
- Amateur Astronomy: Even amateur astronomers benefit from star map coordinates. Star charts, using these coordinates, help locate celestial objects for observation and enjoyment.
Understanding Star Map Coordinates: A Practical Example
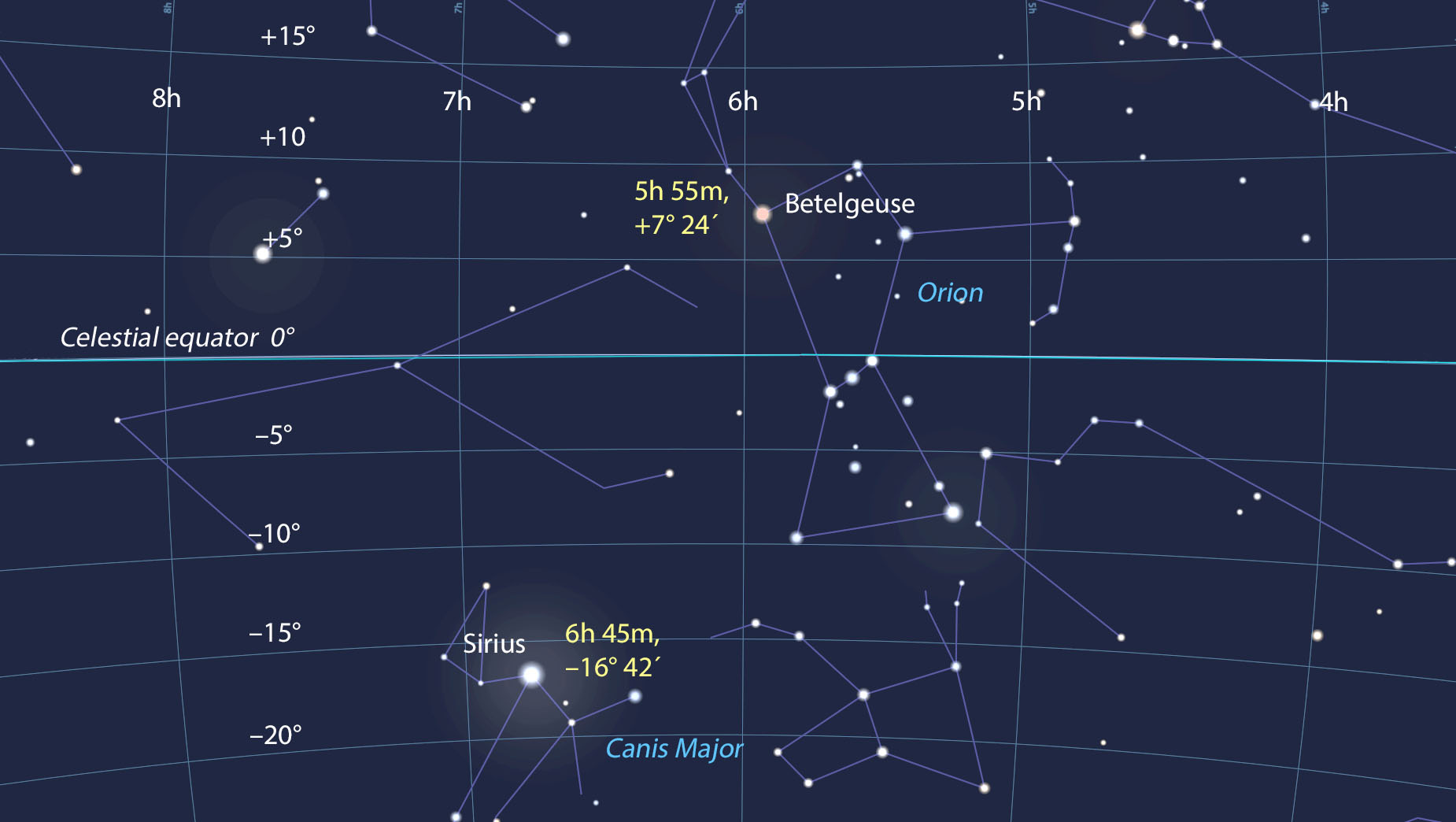
Let’s consider the bright star Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Its coordinates are:
- Right Ascension: 06h 45m 08.9s
- Declination: -16° 42′ 58"
These coordinates indicate that Sirius is located approximately 6.75 hours east of the vernal equinox and 16.7 degrees south of the celestial equator. This information allows astronomers and stargazers to pinpoint Sirius’s location in the night sky with remarkable precision.
FAQs Regarding Star Map Coordinates:
Q: What are the different coordinate systems used in astronomy?
A: While the equatorial coordinate system (using right ascension and declination) is most commonly used, other systems exist, including:
- Horizontal Coordinates: Using altitude and azimuth, these coordinates are specific to a particular location and time.
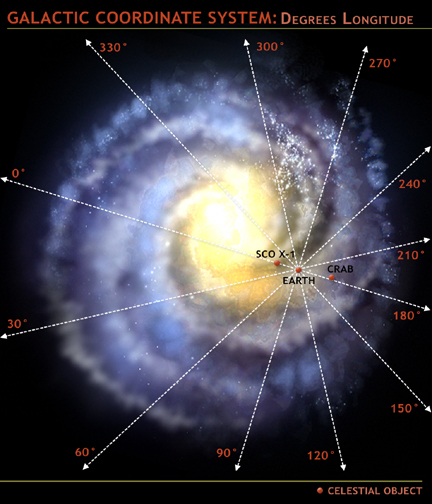
- Galactic Coordinates: Using galactic longitude and galactic latitude, these coordinates are centered on the Milky Way galaxy.
Q: How are star map coordinates determined?
A: Astronomers use precise instruments like telescopes and satellite observations to measure the positions of celestial objects. These measurements are then converted into star map coordinates using complex mathematical calculations.
Q: Can star map coordinates change over time?
A: Due to the Earth’s precession, a slow wobble in its axis, star map coordinates change very gradually over long periods. This change is accounted for in astronomical calculations.
Q: How can I use star map coordinates to find celestial objects?
A: Star charts, planetarium software, and online tools can help you locate celestial objects using their star map coordinates. Many smartphone apps also provide interactive star maps with search functionality based on coordinates.
Tips for Using Star Map Coordinates:
- Use reliable sources: Consult reputable star charts, planetarium software, or online databases for accurate star map coordinates.
- Consider your location and time: Remember that the position of celestial objects changes depending on your location and the time of observation.
- Practice: Familiarize yourself with star map coordinates and practice locating objects in the night sky.
- Start with bright stars: Begin by finding bright stars with well-known coordinates, then gradually expand your search to fainter objects.
Conclusion: Guiding Our Exploration of the Cosmos
Star map coordinates are a fundamental tool for navigating the cosmos, providing a precise and consistent system for locating celestial objects. From astronomers studying the universe to amateur stargazers exploring the night sky, these coordinates play a vital role in our understanding and appreciation of the vastness and wonder of the cosmos. As we continue to explore the universe, star map coordinates will remain an indispensable instrument, guiding our exploration and revealing the secrets of the celestial realm.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Cosmos: Understanding Star Map Coordinates. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!