Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding Japan’s Earthquake Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding Japan’s Earthquake Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding Japan’s Earthquake Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding Japan’s Earthquake Map

Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the volatile Ring of Fire, is renowned for its stunning landscapes and vibrant culture. However, beneath its surface lies a constant reminder of the Earth’s dynamic nature: a complex network of fault lines that regularly generate earthquakes. This geological reality has shaped the country’s history, culture, and infrastructure, necessitating a deep understanding of its seismic activity.
Decoding the Earthquake Map: A Window into Japan’s Geological Past and Present
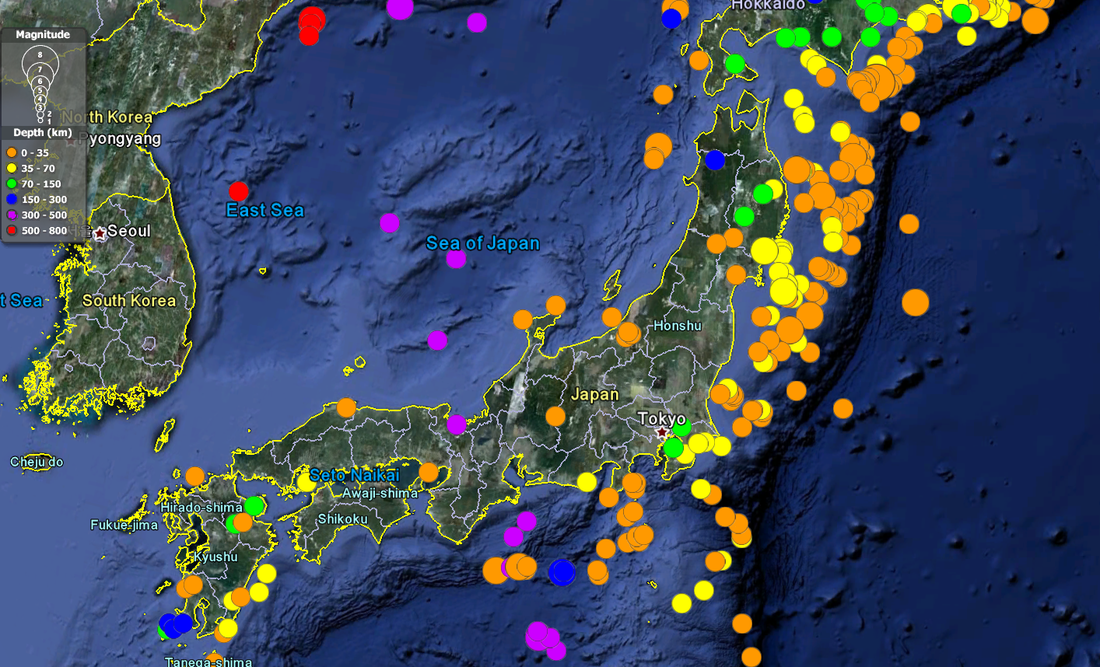
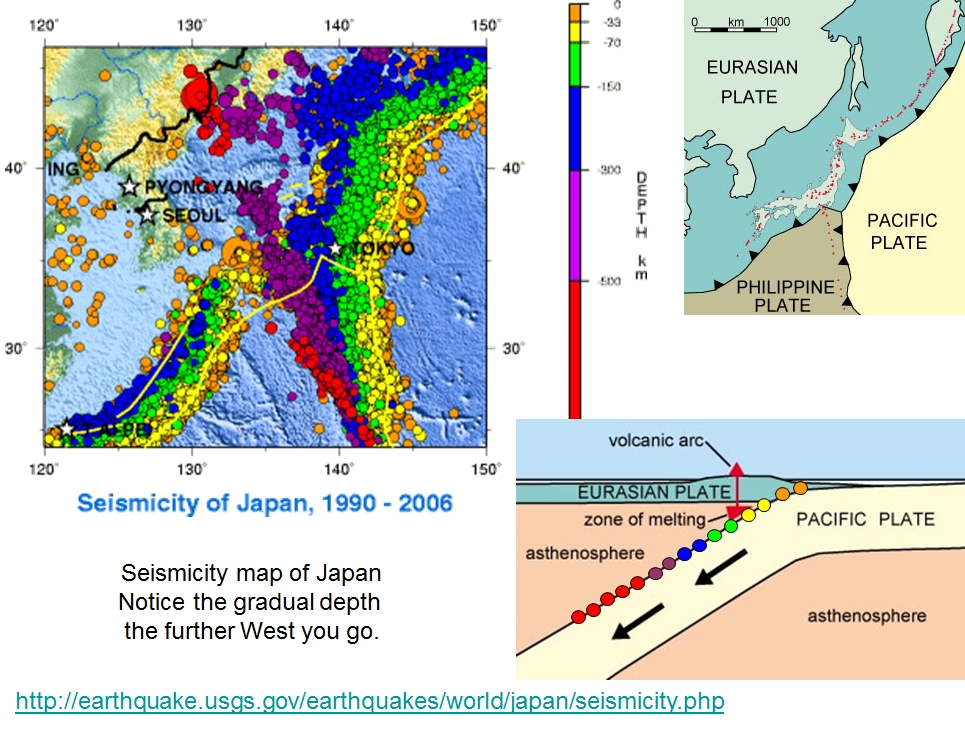
Japan’s earthquake map is a powerful tool, providing a visual representation of the country’s seismic history and ongoing activity. It showcases the locations of past earthquakes, the magnitude of their tremors, and the distribution of active fault lines. This map is not just a static representation of past events; it’s a dynamic tool for understanding the ongoing geological processes that shape Japan’s landscape and influence its future.
The Ring of Fire: A Global Hotspot of Seismic Activity
Japan’s vulnerability to earthquakes stems from its location within the Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped region encircling the Pacific Ocean. This zone is characterized by intense volcanic and tectonic activity, where multiple tectonic plates collide and grind against each other. The Pacific Plate, the Philippine Sea Plate, and the Eurasian Plate converge near Japan, creating a complex interplay of forces that generate earthquakes.
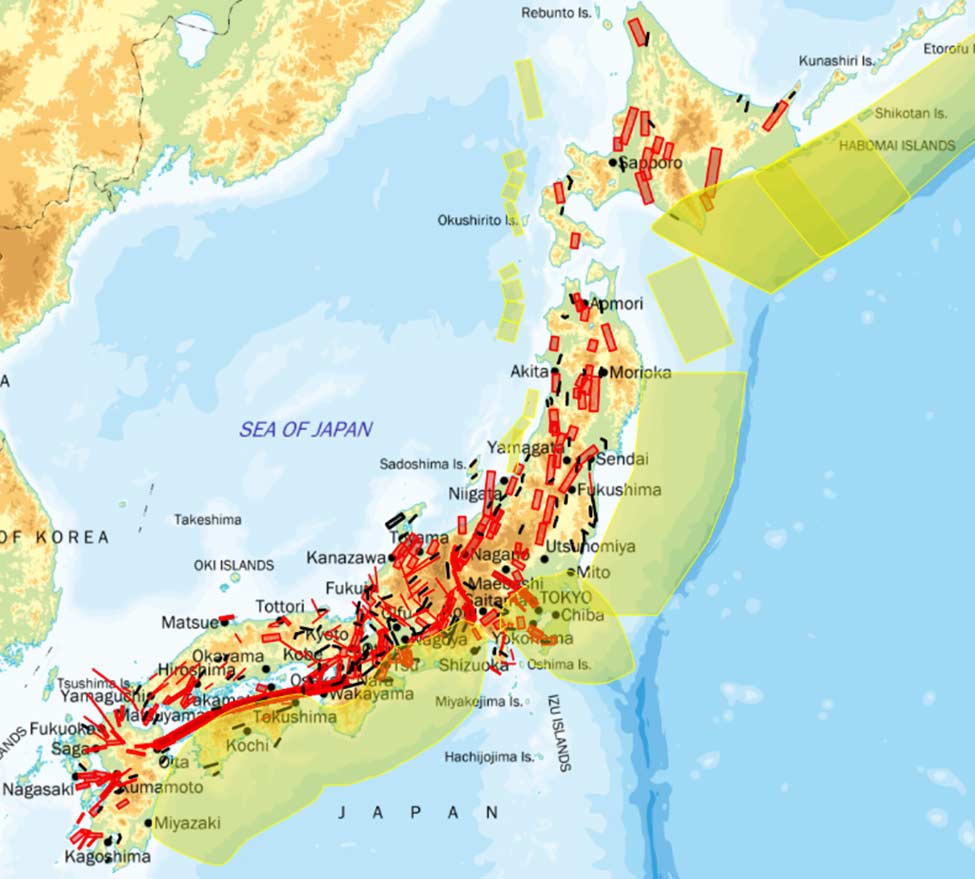
Fault Lines: The Epicenters of Seismic Activity
The earthquake map highlights the intricate network of fault lines that crisscross Japan. These fault lines represent zones of weakness in the Earth’s crust, where tectonic plates move and interact. The movement along these fault lines can cause sudden shifts and releases of energy, resulting in earthquakes.
Magnitude and Intensity: Understanding the Impact of Earthquakes
The earthquake map often uses color gradients to represent the magnitude and intensity of past earthquakes. Magnitude refers to the amount of energy released during an earthquake, while intensity describes the perceived shaking and damage at a particular location.
The Importance of Earthquake Maps: A Tool for Preparedness and Mitigation
The earthquake map serves as a crucial tool for disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts in Japan. By analyzing historical seismic data and understanding the distribution of active fault lines, scientists and engineers can:
- Identify high-risk areas: The map helps pinpoint regions most susceptible to earthquakes, allowing for targeted infrastructure development and emergency response planning.
- Develop building codes: Knowledge of earthquake activity informs the development of stricter building codes and regulations, ensuring structures can withstand seismic forces.
- Implement early warning systems: The map plays a crucial role in the development and deployment of earthquake early warning systems, providing precious seconds for people to take cover and minimize casualties.
- Educate the public: The map helps educate the public about earthquake risks, fostering awareness and promoting responsible behavior during seismic events.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Human Impact of Earthquakes
While the earthquake map provides a technical overview of seismic activity, it’s crucial to remember the human impact of earthquakes. These natural disasters can cause:
- Loss of life: Earthquakes can result in widespread destruction, leading to fatalities and injuries.
- Infrastructure damage: Buildings, bridges, roads, and other infrastructure can be severely damaged or destroyed, disrupting transportation and essential services.
- Economic losses: Earthquakes can cause significant economic damage, impacting businesses, industries, and the overall economy.
- Social disruption: Earthquakes can disrupt daily life, leading to displacement, power outages, and communication disruptions.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Japan’s Earthquake Map
1. What is the most significant earthquake recorded in Japan’s history?
The Great Tohoku Earthquake of 2011, with a magnitude of 9.0, is considered the most powerful earthquake to hit Japan in recorded history. It triggered a devastating tsunami, causing widespread destruction and claiming thousands of lives.
2. How often do earthquakes occur in Japan?
Japan experiences thousands of earthquakes annually, with smaller tremors occurring almost daily. The frequency and intensity of earthquakes vary depending on the location and geological activity.
3. What are the areas most vulnerable to earthquakes in Japan?
The Pacific coast of Japan, particularly the Tohoku region and the Kanto Plain, are considered high-risk areas due to the convergence of tectonic plates.
4. How can I stay safe during an earthquake?
During an earthquake, it’s essential to:
- Drop, Cover, and Hold On: Seek shelter under a sturdy table or desk, covering your head and neck.
- Stay away from windows and heavy objects: These can pose a significant danger during shaking.
- Evacuate if necessary: Follow evacuation orders from authorities and move to a safe location.
5. How can I learn more about earthquake preparedness in Japan?
Local authorities, government agencies, and educational institutions offer resources and information on earthquake preparedness. It’s essential to stay informed about local safety guidelines and emergency procedures.
Tips for Understanding and Using Japan’s Earthquake Map
- Explore interactive maps: Utilize online interactive earthquake maps that offer detailed information, including historical data, real-time updates, and risk assessments.
- Consult with local experts: Seek guidance from seismologists, geologists, and emergency response professionals for a deeper understanding of the map’s significance and implications.
- Stay informed: Regularly check for updates on earthquake activity and follow official sources for reliable information.
Conclusion: A Constant Reminder of Nature’s Power
Japan’s earthquake map is more than just a visual representation of seismic activity; it’s a vital tool for understanding the country’s geological reality and mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes. By embracing the knowledge gleaned from the map and implementing appropriate preparedness measures, Japan continues to navigate the challenges posed by its dynamic tectonic environment. The map serves as a constant reminder of the power of nature and the importance of resilience in the face of adversity.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding Japan’s Earthquake Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!