Navigating the Political Landscape of Southern Africa: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape of Southern Africa: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape of Southern Africa: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape of Southern Africa: A Comprehensive Guide
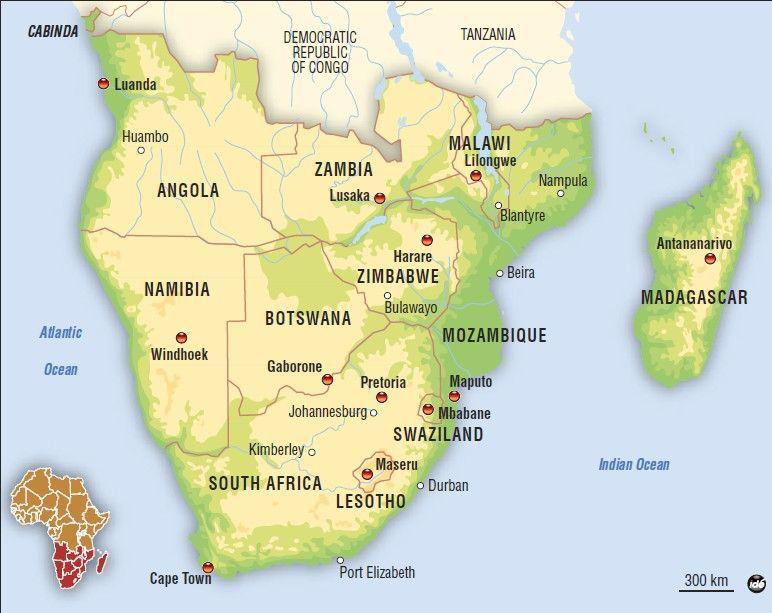
Southern Africa, a region brimming with diverse cultures, languages, and landscapes, also boasts a complex and dynamic political map. Understanding this intricate tapestry of nations and their relationships is crucial for grasping the region’s history, current affairs, and potential future trajectories. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed exploration of the political landscape of Southern Africa, offering insights into its individual countries, regional organizations, and the interconnectedness that defines the region.
A Mosaic of Nations: Examining the Individual States
Southern Africa comprises a diverse array of nations, each with its own unique history, political system, and challenges. Understanding the individual states is essential for appreciating the broader regional dynamics:
-
Angola: Emerging from a long civil war, Angola has transitioned to a multi-party democracy, though challenges remain in terms of political stability and economic diversification.
-
Botswana: A shining example of democratic governance and economic success, Botswana has achieved political stability and significant economic growth through its diamond resources.
-
Eswatini: A constitutional monarchy, Eswatini faces challenges in terms of political reform and economic development, with a focus on diversifying its economy beyond agriculture.
-
Lesotho: Encircled by South Africa, Lesotho’s political landscape is marked by frequent changes in government, with a focus on addressing poverty and unemployment.
-
Malawi: A multi-party democracy, Malawi grapples with poverty, corruption, and political instability, with a focus on improving governance and economic development.
-
Mozambique: Emerging from a protracted civil war, Mozambique is undergoing a period of political transition, with a focus on economic diversification and addressing poverty.
-
Namibia: A relatively stable democracy, Namibia faces challenges in terms of economic inequality and dependence on South Africa, with a focus on diversifying its economy and addressing poverty.
-
South Africa: The region’s economic powerhouse, South Africa faces challenges in terms of inequality, unemployment, and crime, with a focus on addressing these issues and promoting social justice.
-
Zambia: A multi-party democracy, Zambia faces challenges in terms of economic diversification and corruption, with a focus on promoting good governance and economic development.
-
Zimbabwe: A nation grappling with political and economic challenges, Zimbabwe faces a complex political landscape marked by authoritarian rule and economic instability.
Regional Cooperation: The Importance of Collective Action
Beyond individual nations, Southern Africa is characterized by regional cooperation, which plays a vital role in fostering stability, promoting economic growth, and addressing shared challenges. Key regional organizations include:
-
The Southern African Development Community (SADC): Established in 1980, SADC comprises 16 member states and aims to promote economic growth, regional integration, and political stability.
-
The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA): A regional economic bloc with 21 member states, COMESA aims to promote trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
-
The African Union (AU): A continental organization with 55 member states, the AU promotes peace, security, and development across the African continent, with a focus on addressing shared challenges and fostering cooperation.
Challenges and Opportunities: Shaping the Future of Southern Africa
Southern Africa faces a range of challenges, including:
-
Poverty and Inequality: Despite economic growth in some countries, poverty and inequality remain significant challenges, hindering social development and creating social unrest.
-
Political Instability: Political instability, including conflict, corruption, and authoritarian rule, undermines good governance, economic development, and regional cooperation.
-
Climate Change: The region is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including drought, floods, and rising sea levels, threatening food security, water resources, and economic stability.
-
HIV/AIDS: While progress has been made in combating HIV/AIDS, the pandemic continues to impact the region, affecting public health, economic development, and social well-being.
However, alongside these challenges, Southern Africa also presents significant opportunities:
-
Economic Growth: The region boasts abundant natural resources, including minerals, agriculture, and tourism, offering potential for economic growth and development.
-
Regional Integration: Increased regional cooperation through organizations like SADC can facilitate trade, investment, and infrastructure development, fostering economic growth and stability.
-
Technological Advancements: Technological advancements, particularly in areas like renewable energy, agriculture, and communication, offer potential for innovation and economic transformation.
-
Youth Population: The region’s growing youth population represents a demographic dividend, offering potential for human capital development and economic progress.
FAQs: Exploring the Political Landscape
Q: What are the major political ideologies present in Southern Africa?
A: Southern Africa exhibits a diverse range of political ideologies, including:
-
Democracy: Many countries in the region have transitioned to multi-party democracies, with varying levels of political stability and economic development.
-
Authoritarianism: Some countries, particularly Zimbabwe, have experienced authoritarian rule, characterized by limited political freedoms and centralized power.
-
Socialism: While not widely prevalent, socialist ideas have influenced some political parties and movements, emphasizing social justice and economic equality.
Q: How has the political map of Southern Africa evolved over time?
A: The political map of Southern Africa has undergone significant transformations, shaped by:
-
Colonialism and Independence: The region’s political landscape was heavily influenced by colonial rule, leading to a period of decolonization and the emergence of independent nations.
-
Civil Wars and Conflicts: Several countries, including Angola, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe, experienced prolonged civil wars and conflicts, shaping their political systems and economic development.
-
Political Transitions: Some countries have experienced significant political transitions, moving from authoritarian rule to multi-party democracies, while others have witnessed periods of instability and political upheaval.
Q: What are the major challenges to regional integration in Southern Africa?
A: Regional integration in Southern Africa faces several challenges, including:
-
Political Instability: Political instability in some countries can hinder regional cooperation and economic integration.
-
Economic Inequality: The disparity in economic development between countries can create barriers to trade, investment, and cooperation.
-
Lack of Infrastructure: Limited infrastructure development, including transportation and communication networks, can hinder regional integration and economic growth.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Southern Africa
-
Engage with News and Media: Stay informed about current events and political developments in the region through reliable news sources and media outlets.
-
Explore Academic Research: Access academic journals, research papers, and reports on Southern Africa’s political landscape to gain deeper insights into the region’s complexities.
-
Visit the Region: Direct experience through travel and interaction with people from different countries can provide valuable perspectives on the political landscape and its diverse cultures.
-
Engage in Discussions: Participate in discussions, forums, and online communities focused on Southern Africa to exchange ideas and perspectives on the region’s political dynamics.
Conclusion: A Region in Transition
The political map of Southern Africa is a dynamic and complex landscape, reflecting the region’s diverse history, challenges, and opportunities. Understanding the individual nations, regional organizations, and interconnectedness that define the region is essential for grasping its current affairs and potential future trajectories. While the region faces significant challenges, including poverty, inequality, and political instability, it also presents opportunities for economic growth, regional integration, and technological advancement. By fostering cooperation, promoting good governance, and addressing shared challenges, Southern Africa can build a more prosperous and stable future for its people.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape of Southern Africa: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!