Navigating the World in 1750: A Map of Empires, Trade, and Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the World in 1750: A Map of Empires, Trade, and Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World in 1750: A Map of Empires, Trade, and Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World in 1750: A Map of Empires, Trade, and Exploration

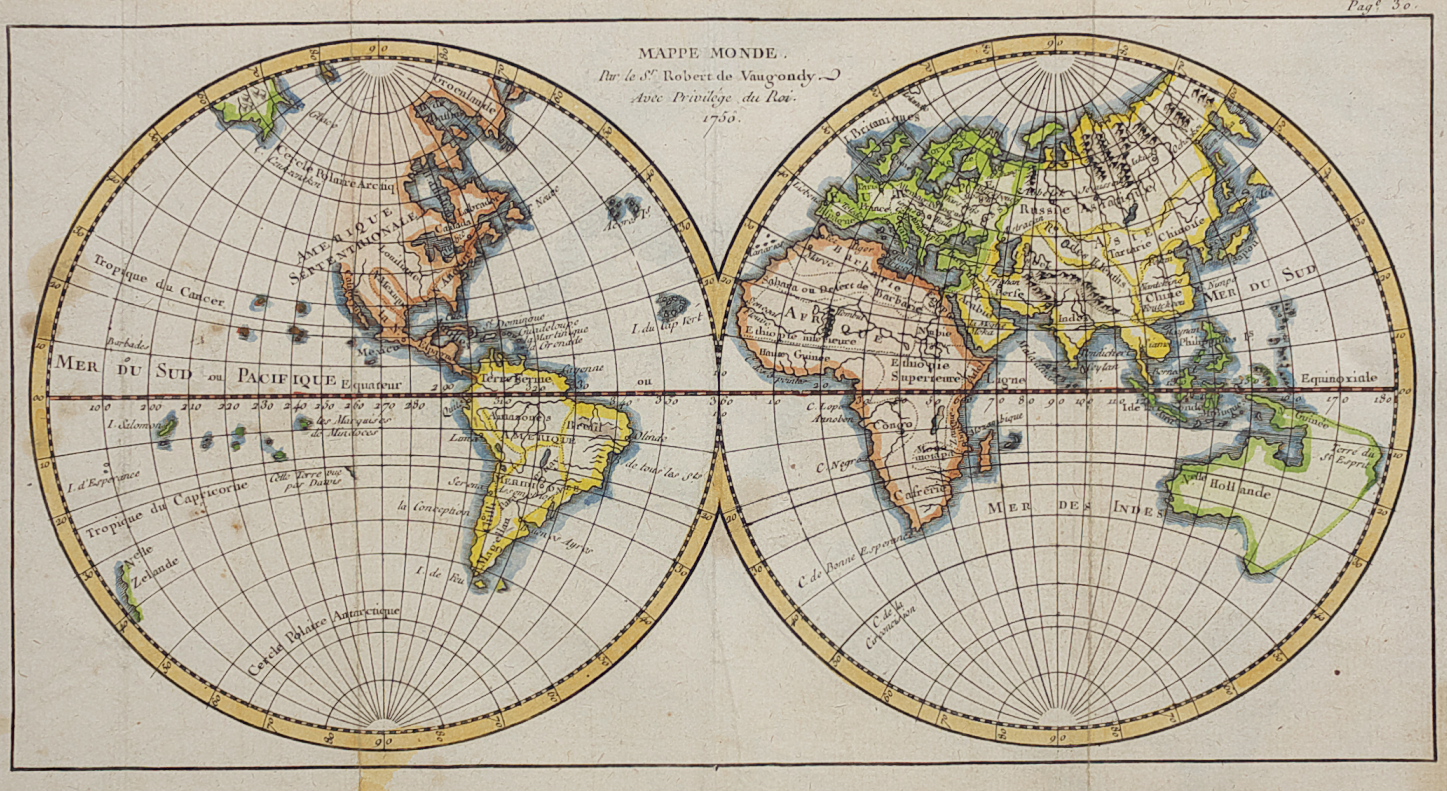
The year 1750 marks a pivotal moment in human history. The Age of Exploration was in full swing, empires were expanding across continents, and global trade networks were evolving at an unprecedented pace. This era, often referred to as the "Early Modern Period," is vividly reflected in the world maps of the time, offering a unique window into the geopolitical landscape and the prevailing understanding of the globe.
A Shifting Global Order:
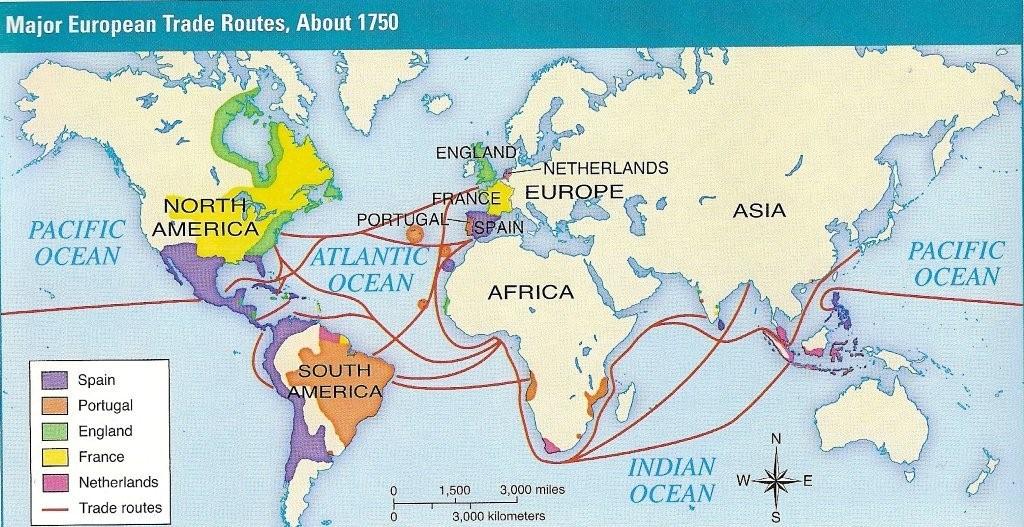
The world map of 1750 reveals a complex tapestry of empires and territories, each vying for dominance and influence. European powers, fueled by advancements in navigation and maritime technology, had carved out vast colonial possessions across the Americas, Africa, and Asia. The British Empire, with its burgeoning colonies in North America and India, was rapidly expanding its reach, while the French Empire held sway over vast territories in North America, the Caribbean, and India.
The Spanish Empire, though facing challenges, still maintained significant holdings in the Americas, while the Portuguese Empire controlled territories in South America, Africa, and Asia. The Dutch Empire, known for its prowess in trade and exploration, held colonies in the East Indies and South Africa. These European empires, through trade, conquest, and colonization, reshaped the global order, leaving a lasting impact on the political, economic, and cultural landscape.
The Rise of Global Trade:
The world map of 1750 also highlights the burgeoning global trade networks that were connecting different parts of the world. The Atlantic slave trade, a brutal system of forced labor, fueled the growth of European economies, while the transatlantic trade in goods such as sugar, tobacco, and cotton facilitated the exchange of commodities and ideas.
The East India Company, a powerful British trading corporation, established a vast network of trade routes across Asia, bringing goods such as spices, textiles, and tea to Europe. These trade networks, while enriching European nations, also had significant implications for the societies they touched, often leading to social and economic upheaval in colonized regions.
Mapping the Unknown:
While European powers had a relatively good understanding of the continents of Europe, Asia, and Africa, vast portions of the world remained unexplored and uncharted. The map of 1750 reflects this uncertainty, with vast swathes of the Pacific Ocean, the Arctic, and the interior of Africa still marked as "terra incognita."
Explorers and cartographers were constantly venturing into these unknown territories, striving to map new lands, discover new routes, and expand the boundaries of geographical knowledge. The quest for exploration, fueled by scientific curiosity and the pursuit of wealth, shaped the world map of the time and laid the foundation for future discoveries.
Beyond the Lines:
The world map of 1750, while offering a valuable snapshot of the geopolitical landscape, is also a reminder of the limitations of cartography. The map represents a European-centric perspective, often neglecting the diverse cultures, languages, and societies that existed beyond the reach of European influence.
It is crucial to acknowledge the inherent biases and omissions present in maps, recognizing that they are not objective representations of reality but rather products of the historical context in which they were created.
The Importance of Understanding the World Map of 1750:
The world map of 1750 serves as a powerful tool for understanding the interconnectedness of the world and the historical forces that shaped it. By studying this map, we can gain insights into:
- The Rise of Global Empires: The map reveals the territorial ambitions of European powers and their impact on the global political order.
- The Evolution of Trade Networks: The map highlights the importance of trade in the 18th century and the role it played in connecting different parts of the world.
- The Exploration of the Unknown: The map showcases the frontiers of geographical knowledge and the ongoing quest to explore and map the globe.
- The Limits of Cartography: The map emphasizes the limitations of cartography and the need to acknowledge the biases and perspectives that inform mapmaking.
FAQs about the World Map of 1750:
1. What are some of the key features of the world map of 1750?
The world map of 1750 features a complex tapestry of empires, with European powers holding significant colonial possessions across the Americas, Africa, and Asia. It also highlights the burgeoning global trade networks that were connecting different parts of the world.
2. What were some of the major empires depicted on the world map of 1750?
The major empires depicted on the world map of 1750 included the British Empire, the French Empire, the Spanish Empire, the Portuguese Empire, and the Dutch Empire.
3. What were some of the key trade routes depicted on the world map of 1750?
The world map of 1750 highlights the transatlantic trade routes, the East India Company’s trade network across Asia, and the Atlantic slave trade.
4. What were some of the areas of the world that remained unexplored in 1750?
Vast portions of the Pacific Ocean, the Arctic, and the interior of Africa remained unexplored and uncharted in 1750.
5. What are some of the limitations of the world map of 1750?
The world map of 1750 is a product of its time and reflects a European-centric perspective. It often neglects the diverse cultures, languages, and societies that existed beyond the reach of European influence.
Tips for Studying the World Map of 1750:
- Focus on the Major Empires: Identify the territories controlled by the major empires of the time and understand their influence on the global political order.
- Analyze the Trade Routes: Trace the key trade routes depicted on the map and understand their significance in the global economy.
- Consider the Unexplored Areas: Identify the areas that remained unexplored in 1750 and consider the motivations behind the quest for exploration.
- Recognize the Biases: Acknowledge the inherent biases and limitations of the map and consider the perspectives that are not represented.
Conclusion:
The world map of 1750 offers a fascinating glimpse into a pivotal period in human history, a time of global empires, expanding trade networks, and the exploration of new frontiers. By studying this map, we can gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of the world and the historical forces that shaped it. However, it is important to remember that maps are not objective representations of reality but rather products of their time and place. By recognizing the limitations of cartography and considering the biases and perspectives that inform mapmaking, we can gain a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of the world we inhabit.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World in 1750: A Map of Empires, Trade, and Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!