The Female Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Internal Anatomy
Related Articles: The Female Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Internal Anatomy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Female Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Internal Anatomy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Female Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Internal Anatomy

Understanding the intricate workings of the female body is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. This article provides a detailed overview of the internal organs, their functions, and their interconnectedness, offering a comprehensive guide to female anatomy.
The Internal Landscape: A Map of Essential Organs
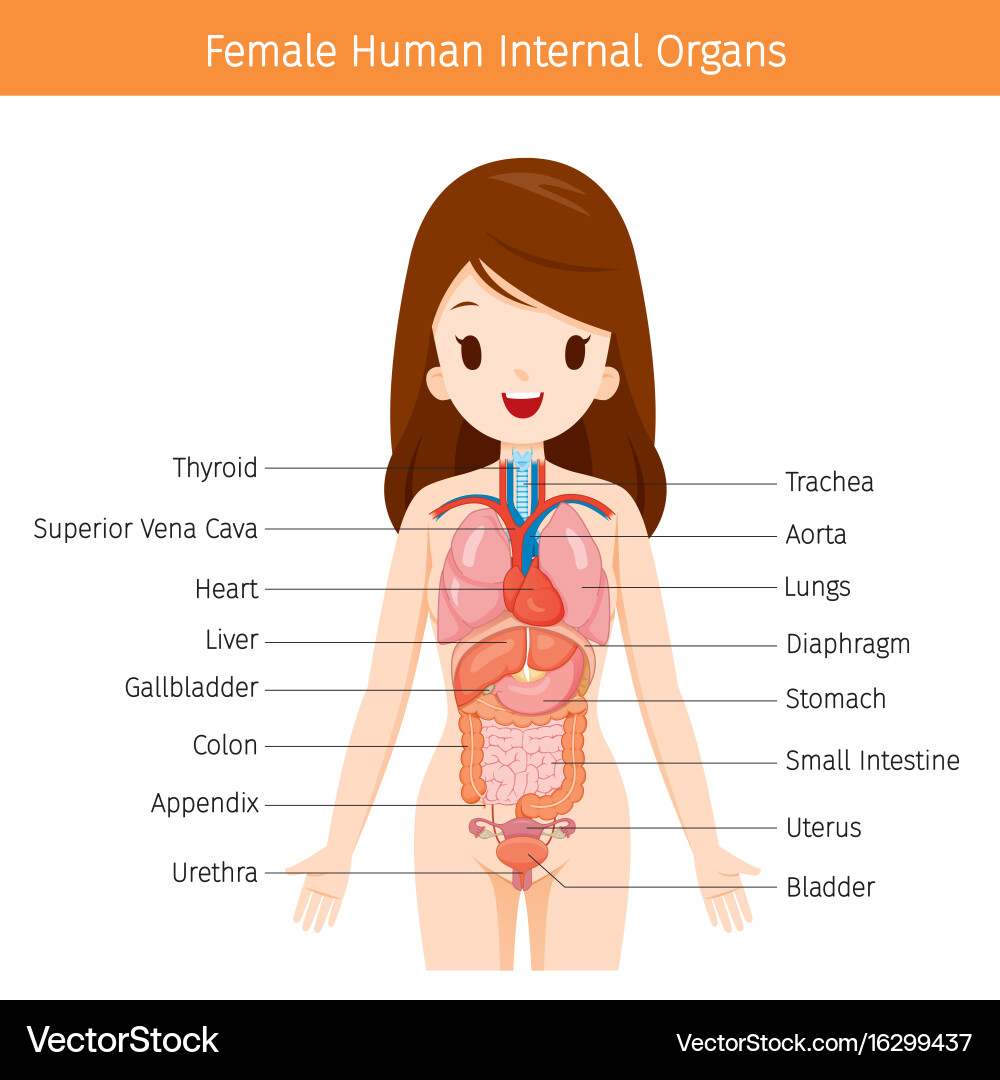
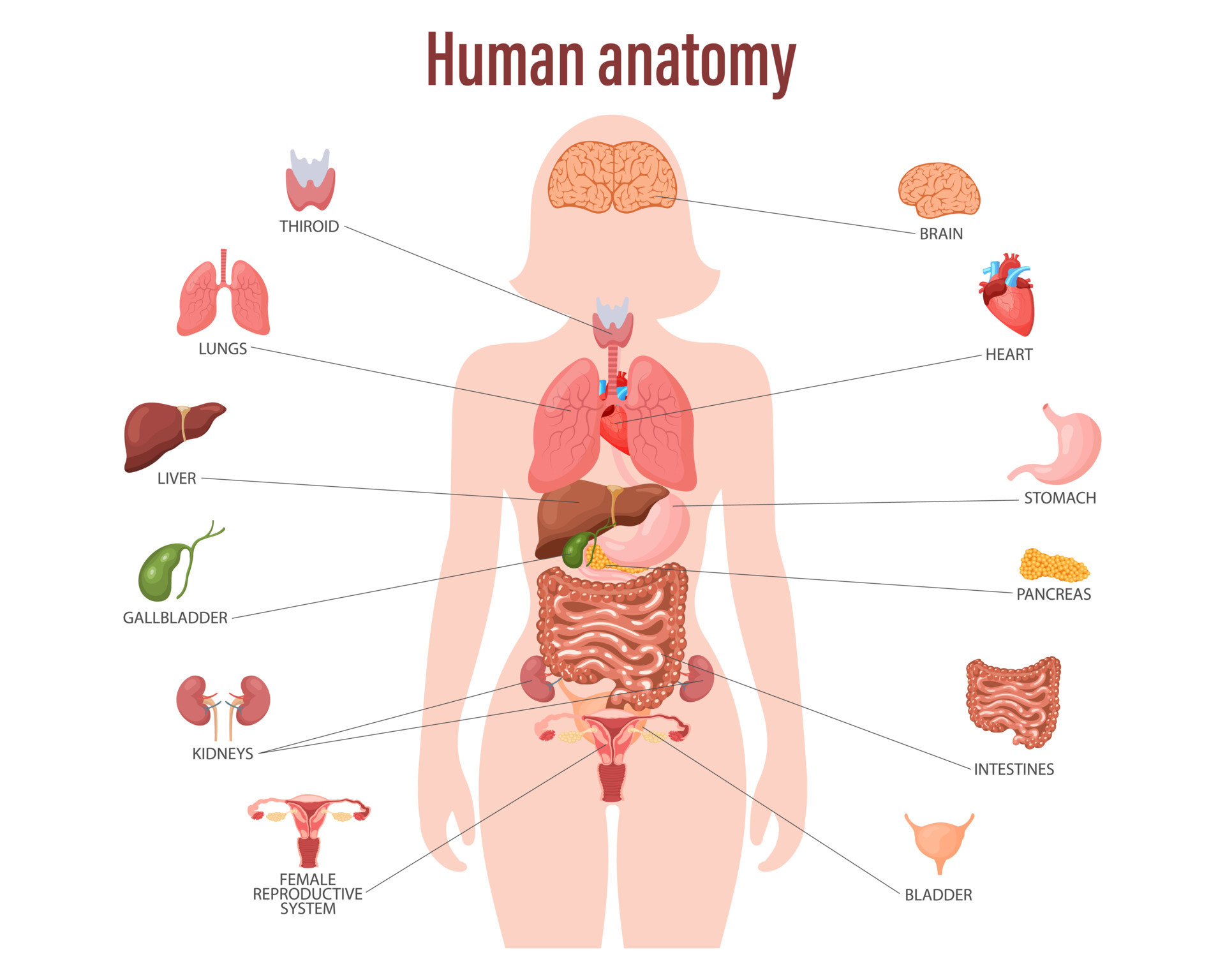
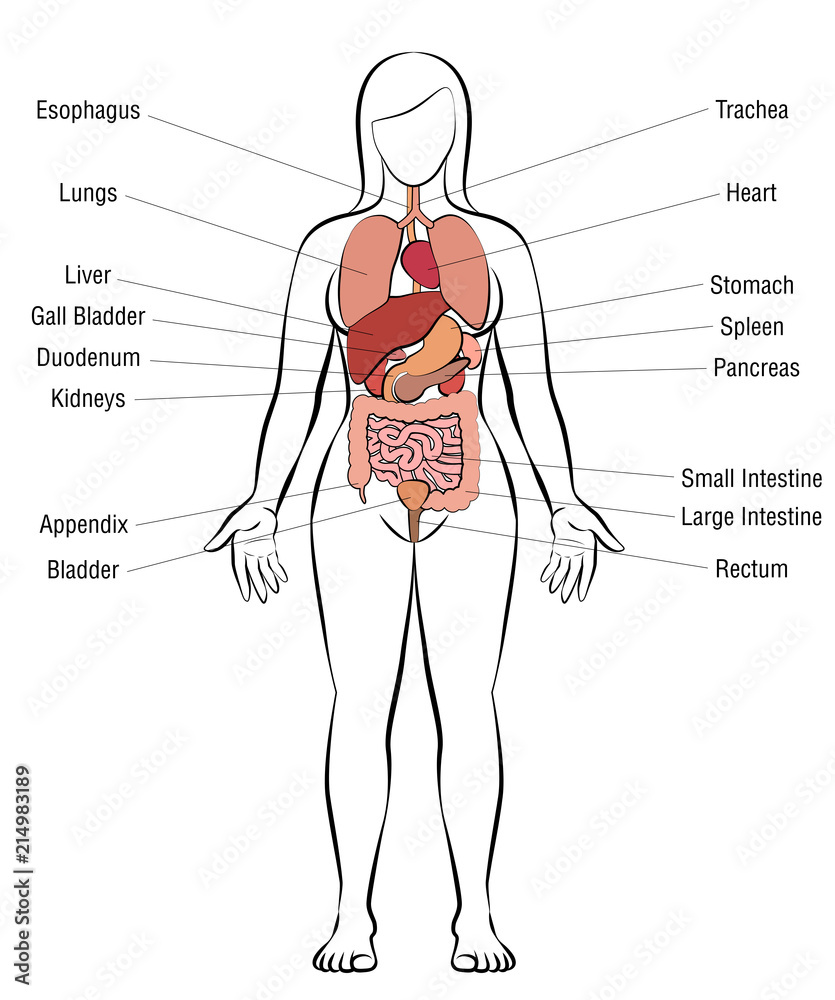
The female body houses a complex network of organs, each playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health and facilitating vital bodily functions. Here’s a breakdown of the key internal organs and their respective functions:
1. The Reproductive System:
- Ovaries: These almond-shaped organs are responsible for producing eggs (ova) and secreting hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and play a vital role in fertility.
- Fallopian Tubes: These slender tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, transporting eggs during ovulation and serving as the site of fertilization.
- Uterus: This muscular organ, shaped like an upside-down pear, is where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus.
- Cervix: This lower portion of the uterus connects to the vagina and acts as a barrier, protecting the uterus from infections.
- Vagina: This muscular canal serves as the birth canal and also provides a pathway for menstrual blood to exit the body.
2. The Urinary System:
- Kidneys: These bean-shaped organs filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
- Ureters: These tubes carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: This muscular sac stores urine until it is eliminated from the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
3. The Digestive System:
- Stomach: This muscular organ mixes food with digestive juices and acids, breaking it down into smaller particles.
- Small Intestine: This long, coiled tube further digests food and absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Large Intestine: This shorter, wider tube absorbs water and electrolytes from waste products, forming solid stool.
- Rectum: This final portion of the large intestine stores feces until it is eliminated from the body.
- Anus: This opening at the end of the digestive tract allows for the elimination of waste products.
4. The Respiratory System:
- Lungs: These two spongy organs are responsible for gas exchange, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
- Trachea: This tube carries air from the nose and mouth to the lungs.
- Bronchi: These tubes branch off from the trachea and carry air to the lungs.
5. The Circulatory System:
- Heart: This muscular organ pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products.
- Blood Vessels: These tubes carry blood throughout the body, including arteries, veins, and capillaries.
6. The Endocrine System:
- Pituitary Gland: This gland, located in the brain, secretes hormones that regulate other glands and control growth and development.
- Thyroid Gland: This gland, located in the neck, secretes hormones that regulate metabolism.
- Adrenal Glands: These glands, located near the kidneys, secrete hormones that regulate stress response and blood pressure.
- Pancreas: This gland, located near the stomach, secretes hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
7. The Nervous System:
- Brain: This organ controls thought, emotion, and behavior.
- Spinal Cord: This bundle of nerves carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
Understanding the Interconnections
These organs are not isolated entities but work together in a complex and coordinated manner to ensure the body functions optimally. For instance, the reproductive system relies on hormones produced by the endocrine system, while the digestive system provides nutrients essential for the growth and development of the reproductive organs.
Importance and Benefits of Understanding Female Anatomy
A thorough understanding of female anatomy offers numerous benefits:
- Empowered Health Decisions: Knowledge of the body’s workings empowers women to make informed decisions about their health, including preventive measures, lifestyle choices, and seeking appropriate medical care.
- Enhanced Self-Awareness: Understanding the functions and interconnections of different organs fosters a deeper appreciation for the body’s complexity and promotes a sense of self-awareness and well-being.
- Improved Communication with Healthcare Professionals: A clear understanding of anatomical terms and functions facilitates better communication with healthcare providers, leading to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
- Enhanced Sexual Health: Knowledge of the reproductive system, including its functions and potential issues, promotes informed choices and safer sexual practices.
- Increased Awareness of Potential Health Risks: Understanding the location and functions of various organs allows women to identify potential health risks and take proactive steps to mitigate them.
FAQs on Female Anatomy
Q: What are the most common health issues affecting women?
A: Common health issues affecting women include menstrual irregularities, reproductive system infections, breast cancer, heart disease, and osteoporosis.
Q: How can I maintain good reproductive health?
A: Maintaining good reproductive health involves regular gynecological checkups, practicing safe sex, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Q: What are some tips for understanding female anatomy?
A:
- Consult Reliable Resources: Utilize reputable medical websites, textbooks, and educational materials to learn about female anatomy.
- Visual Aids: Explore anatomical diagrams and illustrations to visualize the location and structure of internal organs.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult a healthcare professional for personalized information and guidance on female anatomy.
- Engage in Open Conversations: Discuss anatomical topics with healthcare providers or trusted friends and family members to gain further insights and clarify any questions.
Conclusion
The female body is a remarkable and complex system, with each organ playing a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Understanding the functions and interconnections of these organs empowers women to make informed decisions about their health, engage in open communication with healthcare professionals, and promote a deeper appreciation for their own bodies. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of female anatomy, women can cultivate a more empowered and fulfilling relationship with their health and well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Female Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Internal Anatomy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!