The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation
Related Articles: The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation
- 3.1 Unveiling the Battlegrounds: A Geographical Perspective
- 3.2 Unraveling the Historical Narrative: A Visual Guide to Understanding the War
- 3.3 Beyond the Battlefields: The Lasting Legacy of the Mexican War
- 3.4 FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Mexican War Map
- 3.5 Tips: Using a Mexican War Map Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of the Mexican War Map
- 4 Closure
The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation

The Mexican War, a tumultuous period in North American history spanning from 1846 to 1848, reshaped the political and geographical landscape of the continent. The conflict, sparked by territorial disputes and simmering tensions over the annexation of Texas, left a lasting imprint on the United States, Mexico, and the future of the West. Understanding this complex historical event requires a comprehensive understanding of its geographical context, which is best visualized through the lens of a Mexican War map.
Unveiling the Battlegrounds: A Geographical Perspective
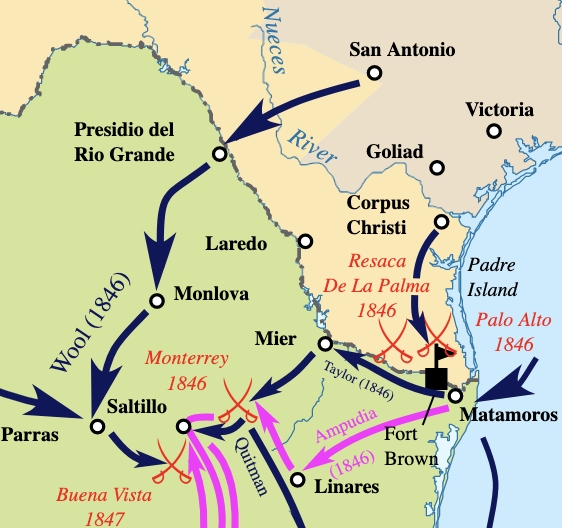
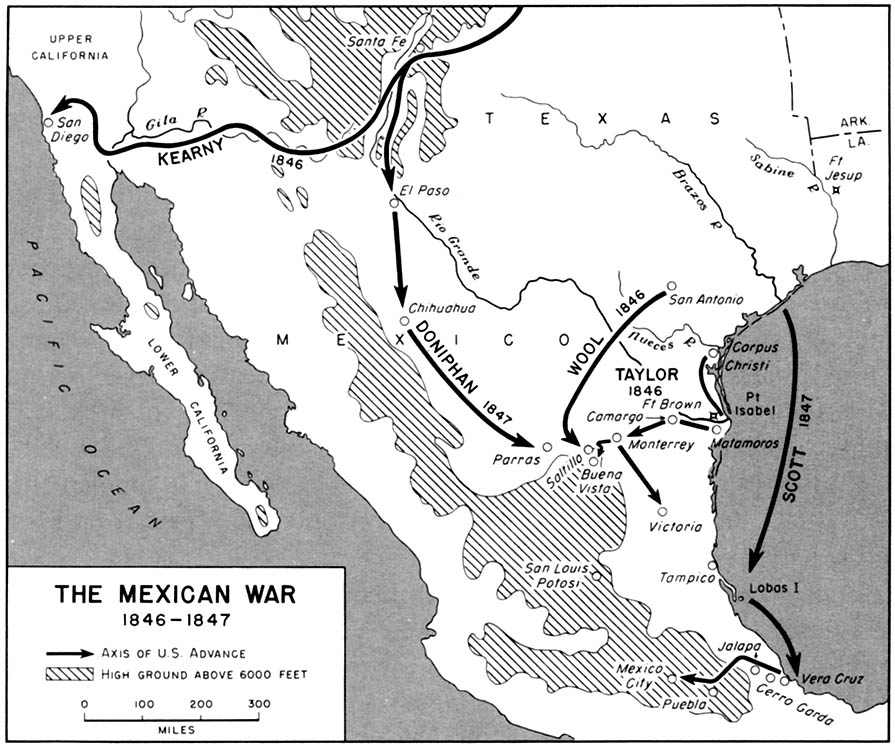
A Mexican War map serves as a visual chronicle of the conflict, highlighting the key battlegrounds, territorial claims, and strategic movements of both sides. It provides a tangible representation of the vast geographical scope of the war, encompassing territories that today encompass parts of California, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, and Colorado.
Key Features of a Mexican War Map:
- Battle Locations: The map clearly identifies major battles fought during the war, such as the Battle of Palo Alto, the Battle of Monterrey, and the Battle of Buena Vista. These locations are often marked with symbols or annotations, providing a visual overview of the key engagements.
- Territorial Claims: The map delineates the disputed territories, including Texas, California, and New Mexico, which were claimed by both Mexico and the United States. These areas are often highlighted with different colors or shading, showcasing the territorial ambitions of each nation.
- Strategic Movements: The map traces the movements of armies and military campaigns, illustrating the tactical maneuvers and strategic decisions made by both sides. Lines of march, troop deployments, and key supply routes are often depicted, providing insights into the logistical challenges faced during the war.
- Major Cities and Settlements: The map identifies important cities and settlements within the war zone, including San Antonio, Monterrey, and Mexico City. These locations served as strategic centers, logistical hubs, and centers of political power during the conflict.
Unraveling the Historical Narrative: A Visual Guide to Understanding the War
Beyond its geographical significance, a Mexican War map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the historical narrative of the conflict. It provides a visual context for the key events, strategic decisions, and political machinations that shaped the course of the war.
Key Insights from a Mexican War Map:
- Territorial Disputes and Expansion: The map clearly illustrates the territorial disputes that fueled the conflict, highlighting the expansionist ambitions of the United States and the resistance of Mexico. The map reveals the strategic importance of California and New Mexico, which were coveted by both nations.
- Strategic Advantage: The map underscores the strategic advantages held by the United States, particularly in terms of resources and manpower. The map reveals the logistical challenges faced by Mexico, particularly in defending its vast and geographically diverse territories.
- Impact of Key Battles: The map showcases the significance of key battles, such as the Battle of Monterrey and the Battle of Buena Vista, which significantly influenced the course of the war. These battles are often depicted with annotations that provide details about the tactics employed, the casualties incurred, and the strategic outcomes.
- Political and Diplomatic Negotiations: The map helps visualize the political and diplomatic negotiations that occurred during the war, including the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which officially ended the conflict. The map shows the territorial concessions made by Mexico and the resulting expansion of the United States.
Beyond the Battlefields: The Lasting Legacy of the Mexican War
The Mexican War map serves as a reminder of the profound impact of the conflict, not just on the geographical landscape of North America, but also on the social, cultural, and political fabric of both nations.
The Lasting Legacy:
- Territorial Expansion of the United States: The war resulted in the United States acquiring vast territories from Mexico, including California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and parts of Wyoming and Kansas. This expansion significantly increased the size and influence of the United States.
- Rise of Manifest Destiny: The war fueled the concept of Manifest Destiny, the belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent. This ideology shaped American expansionism and westward migration for decades to come.
- Enduring Tensions: The war left behind enduring tensions between the United States and Mexico, particularly regarding border disputes and the treatment of Mexican-Americans. These tensions continue to shape the relationship between the two nations today.
- Impact on Indigenous Communities: The war had a devastating impact on indigenous communities in the territories acquired by the United States. The expansion of American settlements and the introduction of new diseases led to displacement, cultural disruption, and loss of land.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Mexican War Map
Q: What are the key battlefields depicted on a Mexican War map?
A: Major battlefields depicted on a Mexican War map include:
- Battle of Palo Alto (May 8, 1846): Located near Brownsville, Texas, this battle marked the beginning of the war.
- Battle of Resaca de la Palma (May 9, 1846): Fought near the Rio Grande, this victory for the United States secured control of the disputed territory.
- Battle of Monterrey (September 21-23, 1846): A major battle in northern Mexico, this victory for the United States led to the capture of Monterrey.
- Battle of Buena Vista (February 22-23, 1847): A fierce battle near Saltillo, Mexico, this victory for the United States helped secure the northern part of Mexico.
- Siege of Veracruz (March 9-29, 1847): This crucial victory for the United States allowed them to land troops and advance towards Mexico City.
- Battle of Cerro Gordo (April 18, 1847): A decisive victory for the United States, this battle opened the way to Mexico City.
- Battle of Contreras (August 19-20, 1847): A pivotal battle that paved the way for the capture of Mexico City.
- Battle of Churubusco (August 20, 1847): This major victory for the United States weakened Mexican defenses and led to the capture of Churubusco.
- Battle of Chapultepec (September 13, 1847): This decisive battle allowed the United States to capture Chapultepec Castle and enter Mexico City.
Q: What are the key territorial claims highlighted on a Mexican War map?
A: Key territorial claims highlighted on a Mexican War map include:
- Texas: The annexation of Texas by the United States in 1845 was a major catalyst for the war. The map shows the disputed territory of Texas, which was claimed by both Mexico and the United States.
- California: California was a highly coveted territory due to its strategic location and potential for economic development. The map shows the disputed territory of California, which was claimed by both Mexico and the United States.
- New Mexico: New Mexico was another strategically important territory due to its resources and access to trade routes. The map shows the disputed territory of New Mexico, which was claimed by both Mexico and the United States.
Q: How does a Mexican War map illustrate the strategic movements of both sides?
A: A Mexican War map illustrates the strategic movements of both sides by depicting lines of march, troop deployments, and key supply routes. For example, the map would show the advance of General Zachary Taylor’s army from Texas into Mexico, the movements of General Winfield Scott’s forces from Veracruz to Mexico City, and the deployment of Mexican troops to defend key locations.
Q: What are the key treaties and agreements depicted on a Mexican War map?
A: Key treaties and agreements depicted on a Mexican War map include:
- Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (February 2, 1848): This treaty officially ended the war and ceded California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and parts of Wyoming and Kansas to the United States. The map shows the new boundaries between the United States and Mexico established by the treaty.
- Gadsden Purchase (December 30, 1853): This agreement, negotiated by James Gadsden, further expanded the United States by purchasing a strip of land from Mexico, completing the present-day southern border of the United States. The map shows the territory acquired through the Gadsden Purchase.
Tips: Using a Mexican War Map Effectively
- Analyze the Scale: Consider the scale of the map and its ability to show the geographical extent of the war.
- Identify Key Locations: Pay attention to the key cities, battlefields, and territorial claims highlighted on the map.
- Trace Strategic Movements: Analyze the lines of march, troop deployments, and supply routes to understand the strategic decisions made by both sides.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare different maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the geographical context of the war.
- Consider the Context: Remember that the map is just one piece of the puzzle. It is important to combine the visual information from the map with historical accounts, primary sources, and other scholarly materials to gain a deeper understanding of the Mexican War.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of the Mexican War Map
A Mexican War map serves as a powerful visual tool for understanding the complex historical events that shaped the modern United States and Mexico. It provides a tangible representation of the geographical scope of the conflict, the key battlegrounds, the strategic movements of both sides, and the lasting impact of the war on the political and social landscape of North America. By studying and analyzing a Mexican War map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the historical context of this pivotal period in North American history and its enduring relevance to the present day.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mexican War Map: A Visual Chronicle of Territorial Transformation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!