The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity
Related Articles: The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity
- 3.1 A River of Significance: Understanding the Rio Grande’s Geography
- 3.2 A Historical Journey: The Rio Grande’s Impact on Texas
- 3.3 Navigating the Present: Challenges and Opportunities of the Rio Grande
- 3.4 Navigating the Future: Preserving the Rio Grande’s Legacy
- 3.5 FAQs about the Rio Grande
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Rio Grande
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity
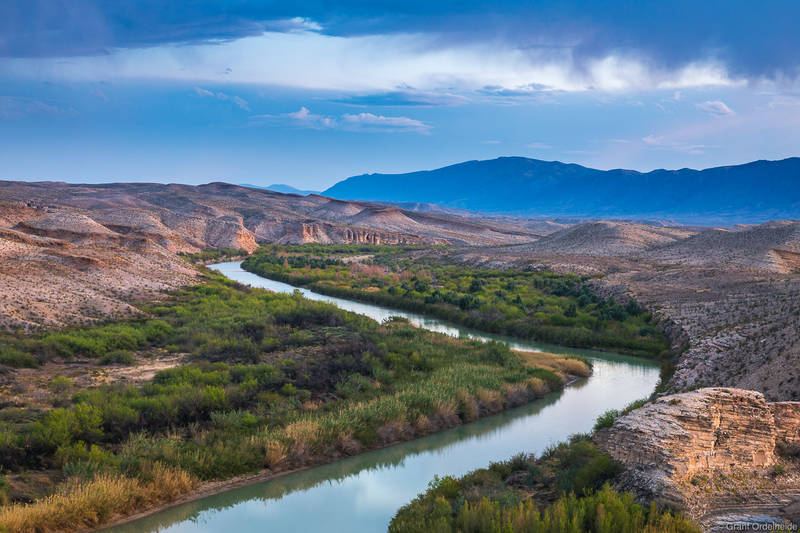

The Rio Grande, a river that flows for over 1,900 miles, holds a significant place in the history, geography, and culture of Texas. Its winding path, marking the border between Texas and Mexico, forms a natural boundary that has shaped the state’s development and its relationship with its southern neighbor. Understanding the Rio Grande’s geography, its role in the history of Texas, and its contemporary significance is crucial for appreciating the state’s complex tapestry.
A River of Significance: Understanding the Rio Grande’s Geography
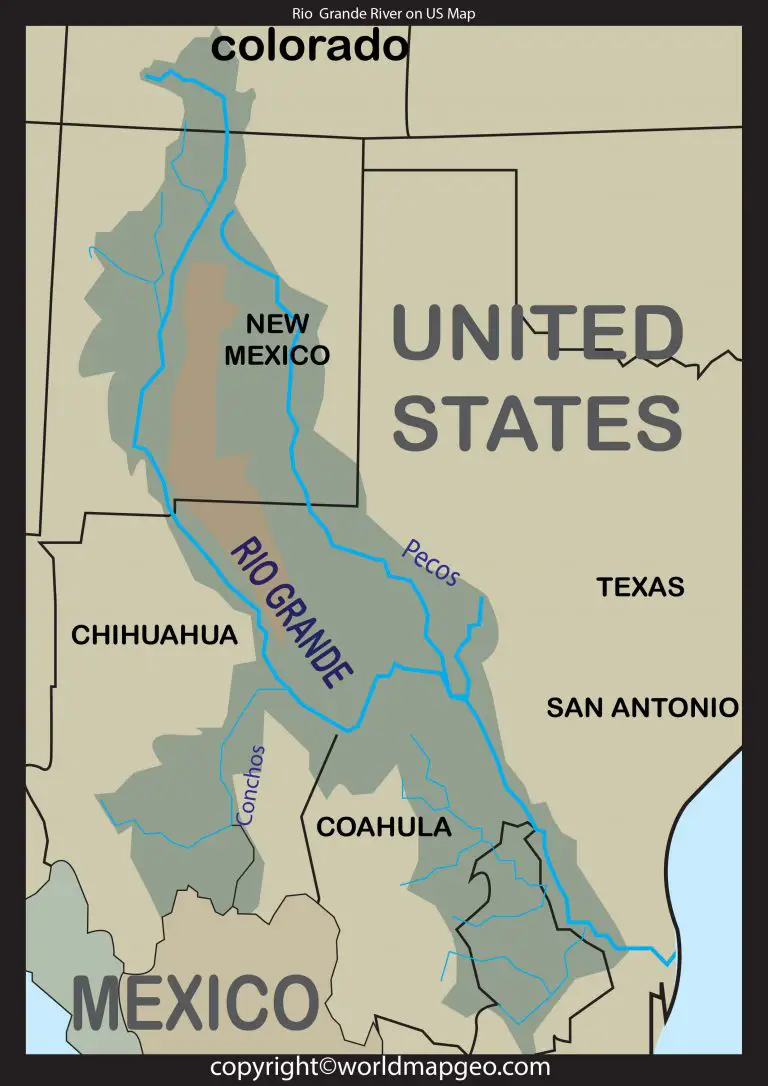
The Rio Grande originates in the San Juan Mountains of Colorado and flows southeastward, carving its path through the arid landscapes of New Mexico and Texas before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. Its course, meandering through diverse terrain, encompasses a variety of ecosystems, from high-altitude mountains to desert plains and fertile valleys.
Key Geographic Features:
- Headwaters: The Rio Grande’s journey begins in the San Juan Mountains, where snowmelt and rainfall contribute to its source.
- Upper Rio Grande: This section of the river, flowing through Colorado and New Mexico, is characterized by steep canyons and dramatic landscapes.
- Middle Rio Grande: As the river enters Texas, it traverses a more arid region, supporting agriculture through irrigation systems.
- Lower Rio Grande: This final stretch of the river, flowing through the Rio Grande Valley, is known for its fertile land and subtropical climate, supporting a diverse range of crops.
The Rio Grande’s Importance:
- Water Source: The river provides a vital source of water for numerous communities, supporting agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
- Ecosystem Support: The Rio Grande is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, including endangered species, making it a crucial habitat for biodiversity.
- Economic Engine: The river’s fertile land and access to water have fueled agricultural development and economic activity in the Rio Grande Valley.
- Cultural Heritage: The Rio Grande has played a pivotal role in the cultural development of Texas, influencing its music, food, and traditions.
A Historical Journey: The Rio Grande’s Impact on Texas
The Rio Grande’s history is intertwined with the history of Texas. From its role in the Spanish colonization of the region to its significance in the Texas Revolution and the Mexican-American War, the river has been a witness to pivotal events that shaped the state’s identity.
The Spanish Era:
- Exploration and Settlement: Spanish explorers first encountered the Rio Grande in the 16th century, recognizing its potential for navigation and resource extraction.
- Mission System: Spanish missionaries established a chain of missions along the Rio Grande, introducing agriculture, livestock, and European culture to the region.
- Borderland Expansion: The Rio Grande became a natural boundary between Spanish territories and Native American lands, shaping the dynamics of settlement and conflict.
The Texas Revolution:
- Anglo-American Settlement: Anglo-American settlers began migrating to Texas in the early 19th century, drawn by the fertile lands and opportunities offered by the Rio Grande Valley.
- Texas Independence: The Rio Grande became a focal point of conflict during the Texas Revolution, with battles fought along its banks.
- Border Disputes: The Rio Grande’s status as a border remained contested after Texas gained independence, leading to ongoing disputes with Mexico.
The Mexican-American War:
- Border Conflict: The Rio Grande was a key battleground in the Mexican-American War, with battles fought along its banks.
- Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo: The war’s conclusion, marked by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, formally established the Rio Grande as the border between the United States and Mexico.
- Legacy of Conflict: The war left a lasting legacy of tension and conflict, shaping the relationship between Texas and Mexico.
Navigating the Present: Challenges and Opportunities of the Rio Grande
Today, the Rio Grande faces numerous challenges, including water scarcity, pollution, and the impact of climate change. However, the river also presents opportunities for collaboration and sustainable development.
Challenges:
- Water Scarcity: The Rio Grande’s flow has been significantly reduced due to drought, overuse, and upstream diversions.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural runoff, as well as sewage discharges, have contaminated the river, posing risks to human health and aquatic life.
- Climate Change: Climate change is exacerbating water scarcity and increasing the frequency and intensity of droughts, impacting the river’s ecosystem.
- Border Security: The Rio Grande has become a focal point of border security measures, leading to environmental damage and human rights concerns.
Opportunities:
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-efficient irrigation technologies and promoting water conservation can help mitigate water scarcity.
- Pollution Control: Strengthening environmental regulations and investing in wastewater treatment infrastructure can reduce pollution levels.
- Collaborative Management: Working with Mexico and other stakeholders to develop a comprehensive management plan can ensure the river’s sustainable use.
- Economic Development: Investing in sustainable tourism, agriculture, and renewable energy projects can create economic opportunities while protecting the environment.
Navigating the Future: Preserving the Rio Grande’s Legacy
The Rio Grande’s future is inextricably linked to the well-being of Texas and its relationship with Mexico. Addressing the challenges facing the river requires collaborative efforts, a commitment to sustainable development, and a shared understanding of the river’s importance.
Key Priorities:
- Water Management: Ensuring the equitable and sustainable allocation of water resources is crucial for safeguarding the river’s ecosystem and meeting the needs of communities.
- Environmental Protection: Reducing pollution, protecting biodiversity, and mitigating the impacts of climate change are essential for preserving the river’s health.
- Border Cooperation: Collaborating with Mexico on issues such as water management, environmental protection, and border security is essential for ensuring the river’s long-term sustainability.
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of the Rio Grande and its challenges can foster support for conservation efforts.
FAQs about the Rio Grande
Q: What is the length of the Rio Grande?
A: The Rio Grande is approximately 1,900 miles long, making it one of the longest rivers in North America.
Q: Where does the Rio Grande begin and end?
A: The Rio Grande originates in the San Juan Mountains of Colorado and flows southeastward, emptying into the Gulf of Mexico.
Q: What is the Rio Grande’s significance to Texas?
A: The Rio Grande is a vital water source, supports a diverse ecosystem, fuels economic activity, and holds significant cultural importance for Texas.
Q: What are the challenges facing the Rio Grande?
A: The Rio Grande faces challenges such as water scarcity, pollution, climate change, and border security issues.
Q: What are the opportunities for preserving the Rio Grande?
A: Opportunities for preserving the Rio Grande include water conservation, pollution control, collaborative management, and sustainable economic development.
Tips for Understanding the Rio Grande
- Explore Maps and Resources: Utilize online maps and resources to visualize the Rio Grande’s course, its key geographic features, and its major tributaries.
- Visit the Rio Grande: Experiencing the river firsthand, whether through kayaking, hiking, or simply observing its flow, can deepen your understanding of its significance.
- Learn About its History: Explore the history of the Rio Grande, from its role in Spanish colonization to its influence on the Texas Revolution and the Mexican-American War.
- Engage with Local Communities: Connect with communities living along the Rio Grande to understand their experiences and perspectives on the river’s challenges and opportunities.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Advocate for policies and initiatives aimed at preserving the Rio Grande’s health and ensuring its sustainable future.
Conclusion
The Rio Grande is a remarkable river, its winding path a testament to the forces of nature and the history of human interaction. Understanding its geography, its role in shaping Texas’s identity, and the challenges it faces is crucial for appreciating the state’s complex tapestry and fostering responsible stewardship of this vital resource. By working together, Texans and their neighbors can ensure that the Rio Grande continues to flow for generations to come, a testament to the enduring power of nature and the human spirit.
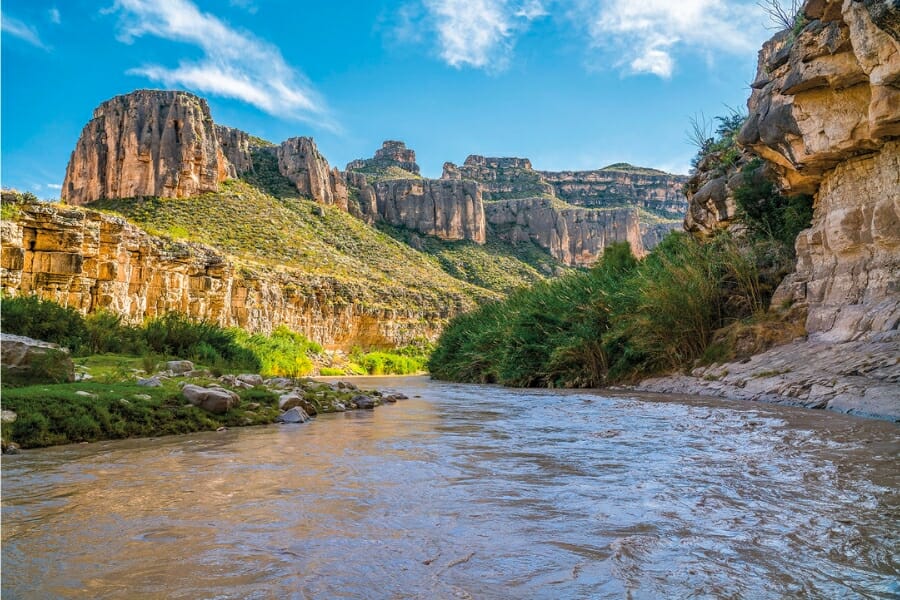
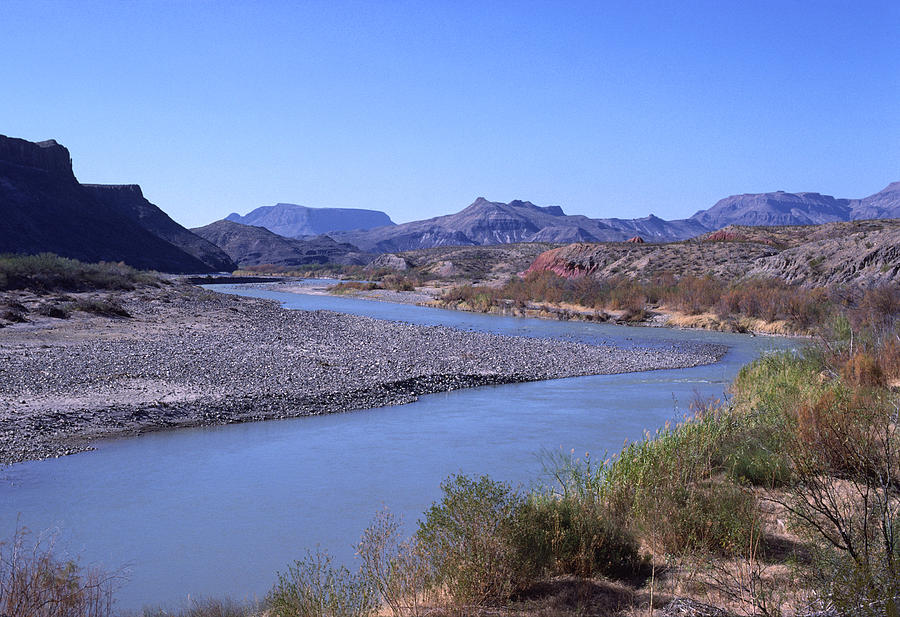
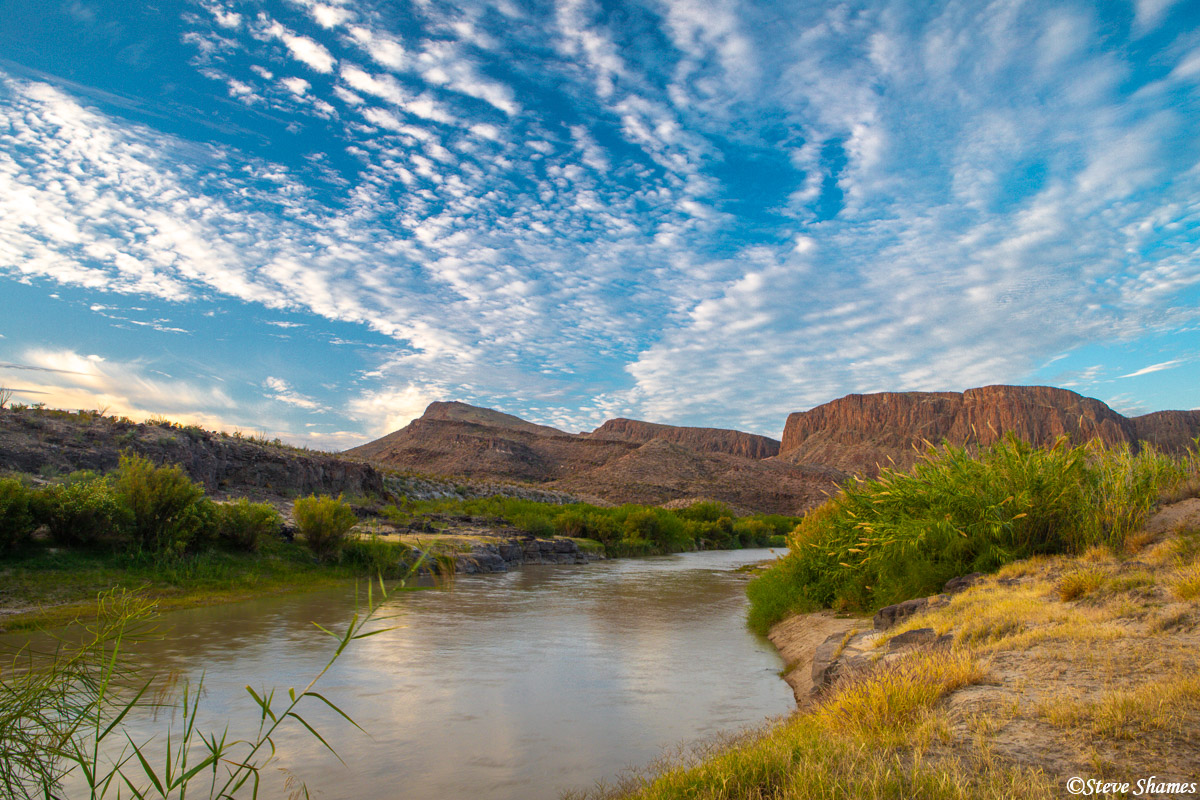







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rio Grande: A River Shaping Texas’s Identity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!