The Shifting Sands of History: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Turkestan
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of History: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Turkestan
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of History: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Turkestan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of History: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Turkestan

Turkestan, a vast and historically significant region spanning Central Asia, has long been a crossroads of cultures, empires, and trade routes. Its geographical boundaries have shifted throughout history, making it difficult to define with absolute precision. However, the concept of Turkestan remains potent, representing a region with a shared cultural heritage and enduring historical significance. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Turkestan, exploring its historical evolution, geographical features, cultural influences, and contemporary relevance.
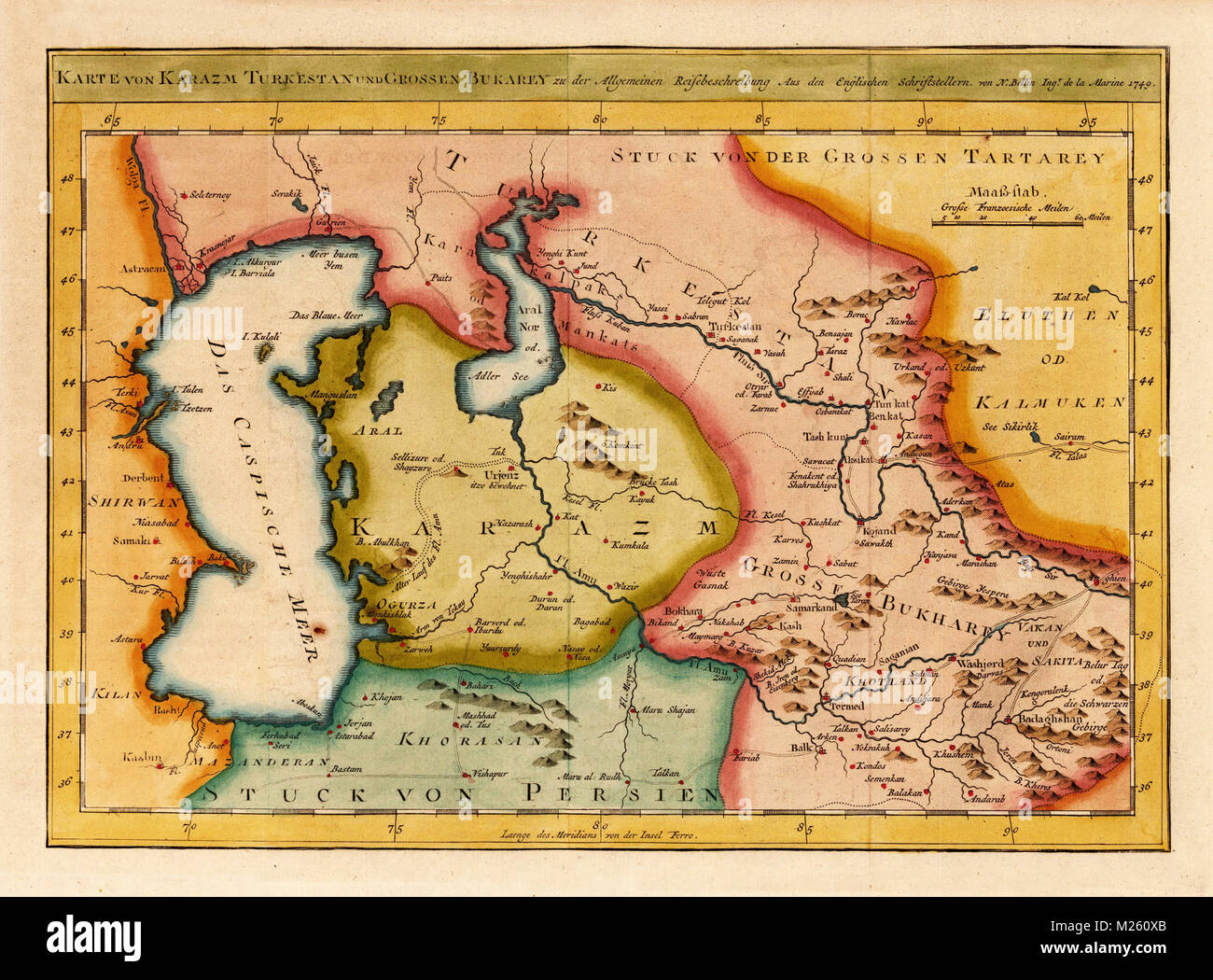
Defining the Boundaries: A Complex History
The term "Turkestan" derives from the Turkic language and translates to "land of the Turks." While the term evokes a sense of homogeneity, the region has historically been home to a diverse array of ethnicities, languages, and cultures. The geographical boundaries of Turkestan have been fluid and contested throughout history, shaped by the rise and fall of empires, the ebb and flow of migration, and the changing political landscape.
During the early centuries of the Common Era, Turkestan encompassed a vast territory extending from the Caspian Sea in the west to the Altai Mountains in the east, and from the Aral Sea in the north to the Pamir Mountains in the south. This region was dominated by nomadic Turkic tribes, who played a pivotal role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of Central Asia.
The rise of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century further transformed the map of Turkestan. Under the leadership of Genghis Khan, the Mongols conquered a vast swathe of territory, including much of Central Asia. The Mongol Empire’s legacy left a lasting impact on the region’s political and cultural landscape.
In the centuries following the Mongol conquest, Turkestan was divided into various khanates and principalities. The Timurid Empire, founded by Timur (Tamerlane) in the 14th century, further fragmented the region, leaving it vulnerable to external forces.
The 19th Century and the Rise of Russian Influence
The 19th century witnessed the rise of Russian influence in Central Asia. The Russian Empire gradually expanded its control over Turkestan, incorporating it into its vast territory. This period marked a significant shift in the political landscape of the region, with Russian rule replacing the traditional khanates and principalities.
The Russian annexation of Turkestan had a profound impact on the region’s demographics, economy, and culture. Russian settlers began to migrate to the region, bringing with them their language, culture, and administrative systems. The Russian government also implemented policies aimed at integrating Turkestan into the Russian Empire, including the establishment of schools, hospitals, and infrastructure.
Turkestan in the 20th Century: Revolution and Partition
The 20th century witnessed further upheaval in Turkestan. The Russian Revolution of 1917 led to the collapse of the Russian Empire and the emergence of independent republics in Central Asia. Turkestan was divided among these newly formed republics, including Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan.
The Soviet era saw significant changes in Turkestan. The Soviet government implemented policies aimed at promoting industrialization, collectivization, and cultural transformation. The Soviet Union’s emphasis on modernization and secularization had a profound impact on the region’s traditional ways of life.
Contemporary Turkestan: A Region in Transition
After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the five republics of Central Asia gained independence. The post-Soviet period has been marked by political and economic instability, as well as ongoing efforts to establish democratic institutions and market economies.
Despite these challenges, Turkestan remains a region of immense strategic importance. It is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. It also serves as a crucial transit route connecting East and West.
Geographical Features: A Land of Diverse Landscapes
Turkestan is characterized by a diverse array of landscapes, from the vast steppes of Kazakhstan to the towering mountains of the Pamir range. The region is largely arid and semi-arid, with limited rainfall and a continental climate.
The Steppes: The steppes of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan are vast, flat plains covered in grasslands. These steppes have traditionally been home to nomadic pastoralists, who have adapted to the region’s harsh conditions.
The Mountains: The Pamir Mountains, located in Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan, are among the highest mountains in the world. These mountains are a source of numerous rivers, including the Amu Darya and Syr Darya, which flow through Central Asia.
The Deserts: Turkestan is home to several deserts, including the Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan and the Kyzylkum Desert in Uzbekistan. These deserts are characterized by extreme temperatures, limited rainfall, and sparse vegetation.
The Rivers: The Amu Darya and Syr Darya are two of the most important rivers in Central Asia. These rivers originate in the mountains and flow through the region, providing water for irrigation and drinking.
Cultural Influences: A Crossroads of Civilizations
Turkestan has long been a crossroads of cultures, where diverse ethnicities, languages, and religions have interacted and blended. The region’s cultural heritage is a rich tapestry woven from threads of Turkic, Persian, Arabic, Russian, and other influences.
Turkic Influence: The Turkic language family has been a major influence on the culture of Turkestan. Turkic languages are spoken by a majority of the region’s population, and Turkic traditions, such as nomadism, horseback riding, and the use of felt and leather, are deeply ingrained in the region’s cultural identity.
Persian Influence: Persian culture has also played a significant role in shaping the culture of Turkestan. The Persian language, literature, and art have had a profound impact on the region’s intellectual and artistic life.
Islamic Influence: Islam is the dominant religion in Turkestan, and its influence is evident in the region’s architecture, art, music, and literature. Mosques, madrasas (religious schools), and other Islamic institutions are found throughout the region.
Russian Influence: Russian influence on the culture of Turkestan is evident in the region’s language, education system, and architecture. Russian is widely spoken in the region, and many of the region’s cities feature buildings built during the Russian era.
Contemporary Relevance: A Region of Strategic Importance
Turkestan remains a region of immense strategic importance in the 21st century. Its geographical location, natural resources, and cultural heritage make it a crucial player in the global geopolitical landscape.
Energy Resources: Turkestan is rich in energy resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. These resources have made the region a target of foreign investment and a source of geopolitical tension.
Transportation Hub: Turkestan is a crucial transportation hub, connecting East and West. Its network of roads, railways, and pipelines serves as a vital link for trade and commerce.
Cultural Heritage: Turkestan’s cultural heritage is a source of pride and a draw for tourists from around the world. The region’s ancient cities, historical monuments, and vibrant cultural traditions attract visitors seeking a glimpse into a rich and diverse past.
Challenges and Opportunities: Turkestan faces a number of challenges, including political instability, economic hardship, and environmental degradation. However, the region also presents significant opportunities for development, including the potential for economic growth, improved infrastructure, and cultural exchange.
FAQs about Turkestan
What is the current status of Turkestan?
Turkestan is not a single political entity but rather a geographical region encompassing five independent republics in Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan.
What are the main ethnic groups in Turkestan?
Turkestan is home to a diverse array of ethnic groups, including Kazakhs, Uzbeks, Kyrgyz, Turkmens, Tajiks, Russians, and others.
What is the significance of the Silk Road in Turkestan?
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting East and West, played a crucial role in the development of Turkestan. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, contributing to the region’s economic prosperity and cultural diversity.
What are the major cities in Turkestan?
Some of the major cities in Turkestan include Tashkent (Uzbekistan), Almaty (Kazakhstan), Bishkek (Kyrgyzstan), Ashgabat (Turkmenistan), and Dushanbe (Tajikistan).
What are the major industries in Turkestan?
The major industries in Turkestan include agriculture, mining, energy, and tourism.
Tips for Visiting Turkestan
Plan Your Itinerary: Turkestan is a vast region with diverse landscapes and cultural attractions. It’s essential to plan your itinerary carefully, considering your interests and the time available.
Learn a Few Basic Phrases: While Russian and English are widely spoken in Turkestan, learning a few basic phrases in the local language can enhance your travel experience and foster cultural exchange.
Respect Local Customs: Turkestan has a rich cultural heritage, and it’s important to respect local customs and traditions. Dress modestly, avoid public displays of affection, and be mindful of religious sensitivities.
Be Prepared for Harsh Conditions: Turkestan is a region with a continental climate, characterized by extreme temperatures and limited rainfall. Be prepared for hot summers, cold winters, and dry conditions.
Consider Hiring a Guide: A local guide can provide valuable insights into the history, culture, and attractions of Turkestan. They can also help you navigate the region and ensure a safe and enjoyable travel experience.
Conclusion
Turkestan, with its shifting sands of history, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the ebb and flow of migration, and the convergence of diverse cultures. Its geographical boundaries may have changed over time, but the region’s cultural heritage and strategic importance remain enduring. Today, Turkestan stands as a region in transition, facing challenges and opportunities alike. As it navigates the complexities of the 21st century, its rich history, diverse landscapes, and strategic location continue to shape its destiny.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of History: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Turkestan. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!