Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Geography of Shark Attacks: Mapping the Encounters
- 3.2 Understanding the Data: A Closer Look at Shark Attack Statistics
- 3.3 The Importance of Data: A Tool for Informed Decision Making
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Shark Attacks in California
- 3.5 Tips for Safe Interactions with the Ocean Environment
- 3.6 Conclusion: Coexisting with Sharks in California
- 4 Closure
Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide

The Pacific Ocean coast of California is renowned for its stunning beauty, diverse marine life, and popular surfing destinations. However, this alluring landscape also harbors a potential threat: shark attacks. While the likelihood of encountering a shark, let alone experiencing an attack, is statistically low, understanding the dynamics of these incidents is crucial for ensuring safety and fostering responsible interactions with the ocean environment.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of shark attacks in California, exploring their occurrence, risk factors, and prevention strategies. By examining the historical data, geographical distribution, and contributing factors, we aim to shed light on this often misunderstood phenomenon and empower individuals to make informed decisions when enjoying the California coastline.
The Geography of Shark Attacks: Mapping the Encounters
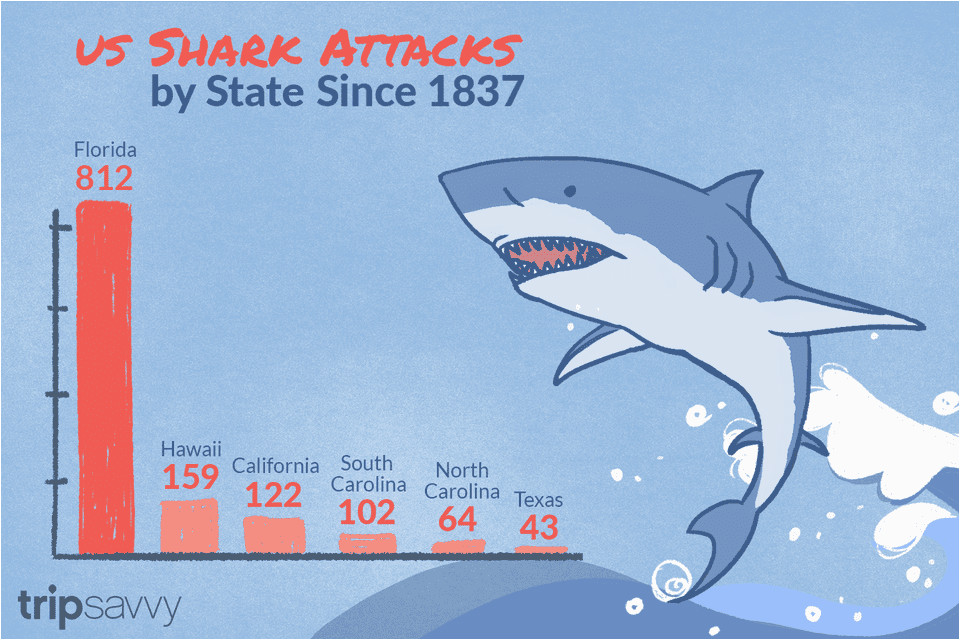
A visual representation of shark attacks, often depicted on a map, provides valuable insights into their spatial distribution. This geographical analysis reveals patterns and hotspots, helping researchers, authorities, and the public understand the areas where encounters are more likely to occur.
Key Observations from Shark Attack Maps:
- Coastal Concentration: Shark attacks in California overwhelmingly occur in coastal waters, particularly in areas with high human activity. This proximity to popular beaches, surfing spots, and boating routes increases the chance of interactions.
- Regional Variations: Certain regions within California exhibit higher attack rates than others. For instance, the central coast, encompassing areas like Monterey Bay and Big Sur, has historically witnessed a significant number of incidents.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: Shark activity, and consequently the risk of attacks, can vary depending on the season. Warmer months, when water temperatures rise and marine life congregates, often coincide with increased shark sightings and encounters.
- Specific Locations: Specific locations within the California coastline, such as popular beaches, harbors, and known surf breaks, may stand out as hotspots for shark attacks. These areas often attract a large number of marine animals, including sharks, increasing the likelihood of interactions.
Understanding the Data: A Closer Look at Shark Attack Statistics
Analyzing shark attack data is essential for gaining a deeper understanding of the phenomenon. While the number of attacks may seem alarming at first glance, it is crucial to contextualize them within the broader picture.
Key Considerations for Interpreting Shark Attack Data:
- Underreporting: It is important to acknowledge that not all shark attacks are reported. Many minor incidents, involving bites or superficial injuries, may go unrecorded, leading to an underestimation of the actual occurrence.
- Species Identification: Identifying the specific shark species involved in an attack is not always possible. However, when available, this information provides insights into the behavior and habitat preferences of different species, aiding in risk assessment.
- Factors Influencing Attacks: Shark attacks are not random events. They are often influenced by a combination of factors, including water conditions, prey availability, human activities, and the presence of other marine life.
- Statistical Fluctuations: The number of shark attacks in a given year can fluctuate significantly. This variability can be attributed to natural cycles, environmental changes, and even media attention, which can influence reporting and public perception.
The Importance of Data: A Tool for Informed Decision Making
Understanding the geographical distribution and statistical trends of shark attacks is crucial for informing responsible decision-making and promoting ocean safety. This data empowers individuals, authorities, and researchers to:
- Identify High-Risk Areas: By mapping and analyzing attack data, authorities can identify areas with a higher prevalence of encounters. This information can guide the implementation of safety measures, such as warning signs, increased patrols, and educational campaigns.
- Implement Targeted Prevention Strategies: Understanding the factors contributing to shark attacks allows for the development of targeted prevention strategies. These may include reducing fishing activities in sensitive areas, promoting responsible beach etiquette, and implementing technologies like shark detection systems.
- Educate the Public: Data-driven insights can inform public education campaigns, promoting awareness about shark behavior, risk factors, and responsible practices when interacting with the ocean environment.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Shark Attacks in California
1. Are shark attacks common in California?
Shark attacks in California are relatively rare. While the Pacific Ocean is home to a diverse population of sharks, the vast majority of encounters are non-aggressive and involve no injuries. The risk of experiencing a shark attack is statistically low.
2. Which sharks are most likely to attack humans?
The most common species involved in shark attacks in California are Great White Sharks, followed by Blue Sharks and Sevengill Sharks. These species are known to inhabit coastal waters and may occasionally interact with humans.
3. What are the risk factors for shark attacks?
Several factors can increase the risk of a shark attack, including:
- Water Conditions: Murky water, strong currents, and limited visibility can make it harder for sharks to identify potential prey, increasing the likelihood of mistaken encounters.
- Prey Availability: Areas with abundant prey, such as seals, sea lions, and fish, can attract sharks, increasing the chance of human-shark interactions.
- Human Activities: Activities like surfing, diving, and fishing can increase the likelihood of encounters, especially in areas known to have a higher concentration of sharks.
- Time of Day: Dawn and dusk are often considered peak times for shark activity, as these periods coincide with feeding patterns.
4. What can I do to reduce my risk of a shark attack?
While eliminating all risk is impossible, individuals can take steps to minimize their chances of encountering a shark:
- Avoid Swimming at Dawn and Dusk: These periods are known for increased shark activity.
- Stay Close to Shore: Sharks are less likely to venture into shallow, well-lit areas.
- Avoid Swimming in Murky Water: Visibility is crucial for both sharks and humans to avoid accidental encounters.
- Don’t Swim Alone: Having a companion can provide assistance in case of an emergency.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Pay attention to any signs of shark activity, such as unusual fish behavior or changes in water conditions.
- Respect Marine Life: Avoid disturbing or harassing marine animals, including sharks.
5. What should I do if I encounter a shark?
If you encounter a shark, it is important to remain calm and avoid panicking. Follow these steps:
- Stay Calm: Panicking can attract a shark’s attention.
- Exit the Water Slowly: Don’t make sudden movements that could be perceived as threatening.
- Maintain Eye Contact: Keeping an eye on the shark can help assess its behavior.
- Don’t Splash or Scream: These actions can attract the shark’s attention.
- If Attacked, Fight Back: If a shark attacks, try to strike it in the eyes or gills.
Tips for Safe Interactions with the Ocean Environment
- Be Informed: Stay informed about local shark activity and potential risks.
- Respect Ocean Boundaries: Avoid swimming in areas known to have a high concentration of sharks.
- Use Caution at Dusk and Dawn: These periods are associated with increased shark activity.
- Avoid Swimming Alone: Having a companion can increase safety and provide assistance in case of an emergency.
- Choose Beaches with Lifeguards: Lifeguards can provide safety measures and respond to emergencies.
- Report Sightings: If you observe a shark, report it to local authorities or lifeguards.
Conclusion: Coexisting with Sharks in California
The presence of sharks in California’s waters is a natural phenomenon that underscores the interconnectedness of the marine ecosystem. While the potential for encounters exists, the likelihood of a shark attack remains statistically low. By understanding the geographical distribution, risk factors, and prevention strategies associated with shark attacks, individuals can make informed decisions, promote responsible ocean practices, and foster a harmonious coexistence with these magnificent creatures. Remember, the ocean is a shared environment, and respecting its inhabitants is crucial for ensuring both human safety and the long-term health of the marine ecosystem.



![Shark Attacks in California [Updated July 2024]](https://www.sharksider.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Shark-Attacks-in-California.webp)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Shark Attacks in California: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!