Understanding the Administrative Divisions of France: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions and Departments
Related Articles: Understanding the Administrative Divisions of France: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions and Departments
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Administrative Divisions of France: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions and Departments. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Administrative Divisions of France: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions and Departments

France, a nation renowned for its rich history, diverse culture, and captivating landscapes, is also a country with a complex and fascinating administrative structure. Unlike many other nations, France does not operate with a system of states. Instead, its territory is divided into a hierarchical system of regions and departments, each with its own unique characteristics and responsibilities. This article will delve into the intricacies of this administrative framework, providing a comprehensive understanding of the map of France’s regions and departments.
Historical Context: From Provinces to Regions
The current administrative system of France has evolved over centuries, reflecting the nation’s political and social transformations. Before the French Revolution, France was divided into a system of provinces, each with its own distinct history, culture, and traditions. However, the revolution brought about a radical shift, leading to the establishment of a centralized government and the abolition of the old provincial system.
In 1790, the National Assembly implemented a new administrative structure, dividing France into 83 departments, each named after a geographical feature or historical event. This system, known as the departmental system, aimed to create a more uniform and equitable administrative framework across the country.
The 19th and 20th centuries saw further adjustments to the departmental system, with the creation of new departments and the modification of existing ones. However, the fundamental structure remained largely unchanged.
The Emergence of Regions: Decentralization and Regional Identity
The concept of regions as administrative units emerged in the 20th century, driven by a desire to decentralize power and promote regional identities. The first regionalization efforts began in the 1960s, with the creation of 22 regions, primarily for economic and planning purposes.
In 1982, a major reform led to the establishment of 22 metropolitan regions, each with a regional council responsible for managing regional affairs. This system aimed to foster regional autonomy and give citizens a greater voice in decision-making.
The 2014 territorial reform further reshaped the regional landscape, merging some regions and reducing their number to 13 metropolitan regions and 5 overseas regions. This reorganization aimed to streamline administrative processes, enhance regional cooperation, and foster a stronger sense of regional identity.
Understanding the Map of France: Regions and Departments
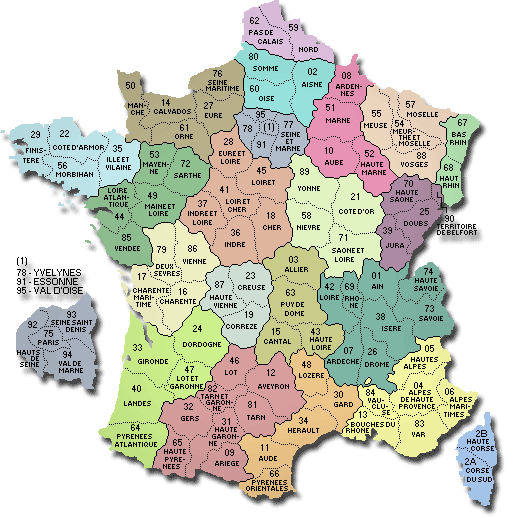
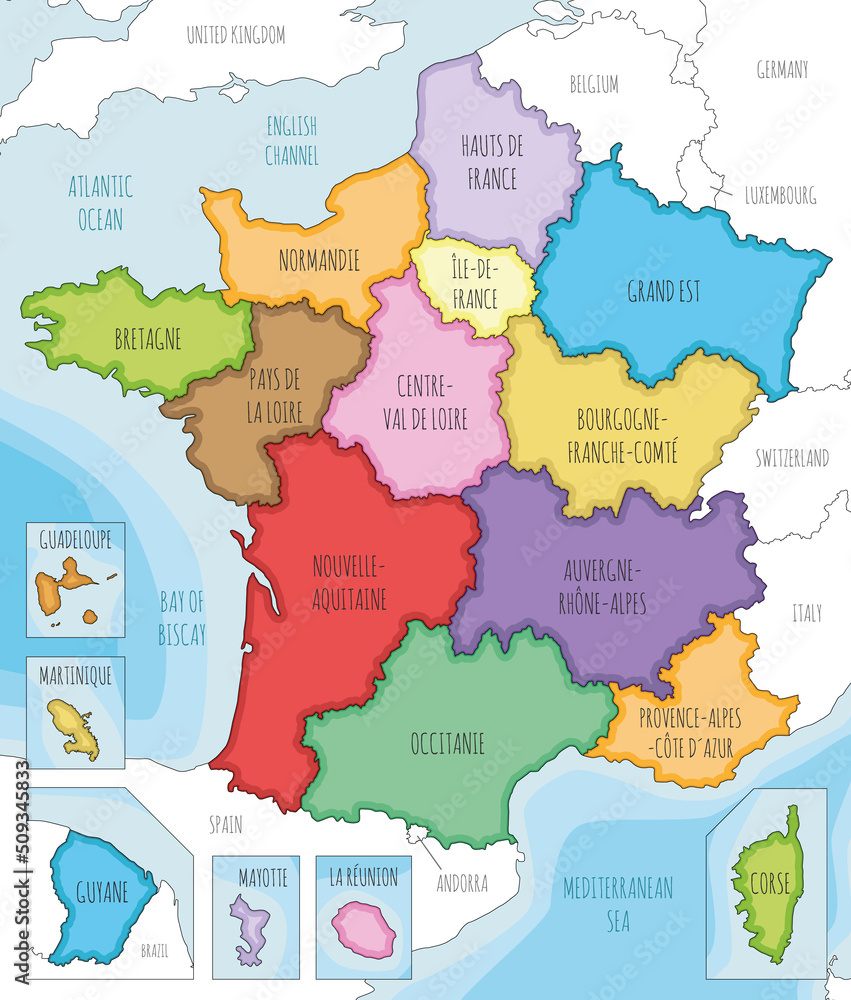
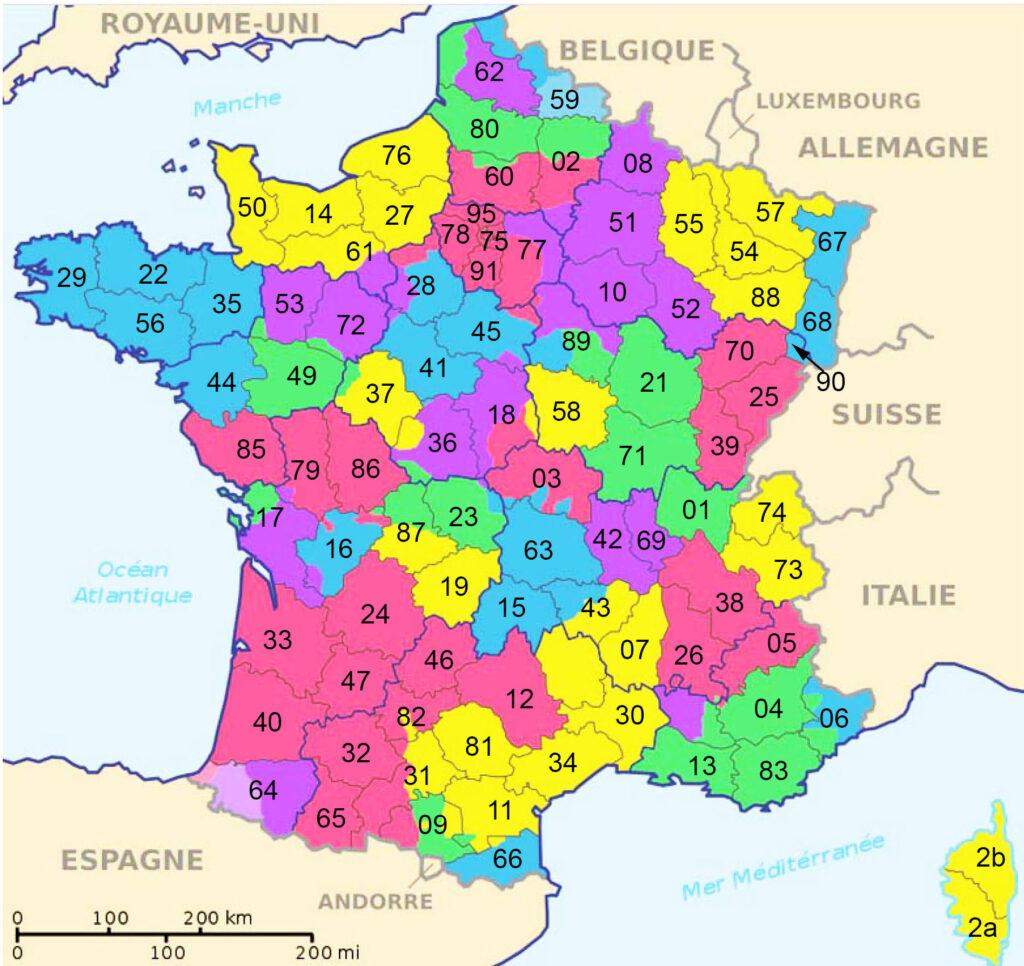
The current map of France features 18 regions, including 13 metropolitan regions and 5 overseas regions. Each region is further subdivided into departments, with a total of 101 departments in mainland France and 5 overseas departments.
Metropolitan Regions:
The 13 metropolitan regions encompass the mainland territory of France, each with its unique geographical, cultural, and economic characteristics. They are:
- Île-de-France: Home to Paris, the capital city, and its surrounding areas.
- Centre-Val de Loire: Characterized by its rolling hills, castles, and vineyards.
- Grand Est: A region in the northeast of France, known for its diverse landscapes and rich history.
- Hauts-de-France: A region in the north of France, known for its industrial heritage and coastal areas.
- Normandie: A region in the northwest of France, known for its picturesque coastline, historic cities, and apple orchards.
- Pays de la Loire: A region in the west of France, known for its Atlantic coastline, vineyards, and historical cities.
- Bretagne: A region in the northwest of France, known for its Celtic culture, rugged coastline, and picturesque villages.
- Nouvelle-Aquitaine: A region in the southwest of France, known for its vineyards, beaches, and historical sites.
- Occitanie: A region in the south of France, known for its Mediterranean climate, beautiful landscapes, and rich cultural heritage.
- Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes: A region in the southeast of France, known for its mountains, lakes, and vibrant cities.
- Bourgogne-Franche-Comté: A region in the east of France, known for its vineyards, historic cities, and picturesque countryside.
- Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur: A region in the southeast of France, known for its Mediterranean climate, beaches, and historic cities.
- Corse: An island region in the Mediterranean Sea, known for its mountainous landscapes, beautiful beaches, and unique culture.
Overseas Regions:
The 5 overseas regions are located outside mainland France, each with its own distinct history, culture, and administrative structure. They are:
- Guadeloupe: An archipelago in the Caribbean Sea, known for its lush vegetation, beautiful beaches, and rich culture.
- Martinique: An island in the Caribbean Sea, known for its volcanic landscapes, beautiful beaches, and vibrant culture.
- Guyane: A territory on the northern coast of South America, known for its rainforests, gold mines, and diverse wildlife.
- La Réunion: An island in the Indian Ocean, known for its volcanic landscapes, beautiful beaches, and unique culture.
- Mayotte: An island in the Indian Ocean, known for its coral reefs, beautiful beaches, and diverse wildlife.
Departments: Local Administration and Representation
Within each region, there are departments, serving as the primary level of local administration. Each department is headed by a prefect, appointed by the central government, and has a departmental council, elected by the local population.
Departments are responsible for a wide range of local services, including:
- Education: Managing primary and secondary schools.
- Social Services: Providing social assistance and healthcare services.
- Infrastructure: Maintaining roads, bridges, and other public infrastructure.
- Culture and Heritage: Promoting local culture and preserving historical sites.
- Economic Development: Supporting local businesses and promoting economic growth.
The Importance of Understanding the Map of France
Understanding the administrative divisions of France is crucial for various reasons:
- Navigating the Country: Knowing the regions and departments helps travelers plan their itineraries, understand local customs, and navigate the country effectively.
- Understanding French Politics: The regional and departmental elections play a significant role in French politics, shaping national policies and influencing the balance of power.
- Appreciating French Culture: Each region and department has its own unique cultural identity, traditions, and cuisine, contributing to the rich tapestry of French culture.
- Conducting Business in France: Businesses need to be aware of the administrative divisions of France to understand local regulations, taxes, and business practices.
FAQs about the Administrative Divisions of France:
Q: How many regions are there in France?
A: There are 18 regions in France, including 13 metropolitan regions and 5 overseas regions.
Q: What are the major differences between regions and departments?
A: Regions are larger administrative units with broader responsibilities, including regional planning, economic development, and cultural promotion. Departments are smaller units with a focus on local services, such as education, social services, and infrastructure.
Q: What is the role of the prefect in a department?
A: The prefect is the representative of the central government in a department. They are responsible for implementing national policies, ensuring public order, and coordinating local services.
Q: How are the regional councils elected?
A: The regional councils are elected by the local population through direct elections.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the French regional system?
A: Some challenges facing the French regional system include maintaining a balance between regional autonomy and central government control, addressing economic disparities between regions, and promoting regional cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Map of France:
- Use Online Resources: Websites like the French government’s official website and Wikipedia provide comprehensive information about the regions and departments of France.
- Consult Travel Guides: Travel guides often include maps and descriptions of the regions and departments, highlighting their unique features and attractions.
- Visit Local Tourist Offices: Local tourist offices can provide detailed information about the region and department you are visiting, including maps, brochures, and local events.
- Engage with Locals: Speaking with local residents can provide valuable insights into the region and department you are visiting, their history, culture, and way of life.
Conclusion:
The administrative divisions of France, with its regions and departments, are a testament to the country’s long and complex history. Understanding this system is essential for navigating the country, appreciating its diverse culture, and engaging with its political and social landscape. By exploring the map of France and delving into the unique characteristics of each region and department, one can gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating and multifaceted nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Administrative Divisions of France: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regions and Departments. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!