Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Oregon: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines
Related Articles: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Oregon: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Oregon: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Oregon: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines

Oregon, a state renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty, also resides within a dynamic and complex geological setting. The state is crisscrossed by numerous fault lines, remnants of past tectonic activity and potential sources of future seismic events. Understanding the location and characteristics of these fault lines is crucial for mitigating seismic risk, informing infrastructure development, and promoting community preparedness. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Oregon’s fault lines, exploring their geological significance, potential hazards, and the role they play in shaping the state’s landscape.
The Tectonic Foundation of Oregon’s Fault Lines:
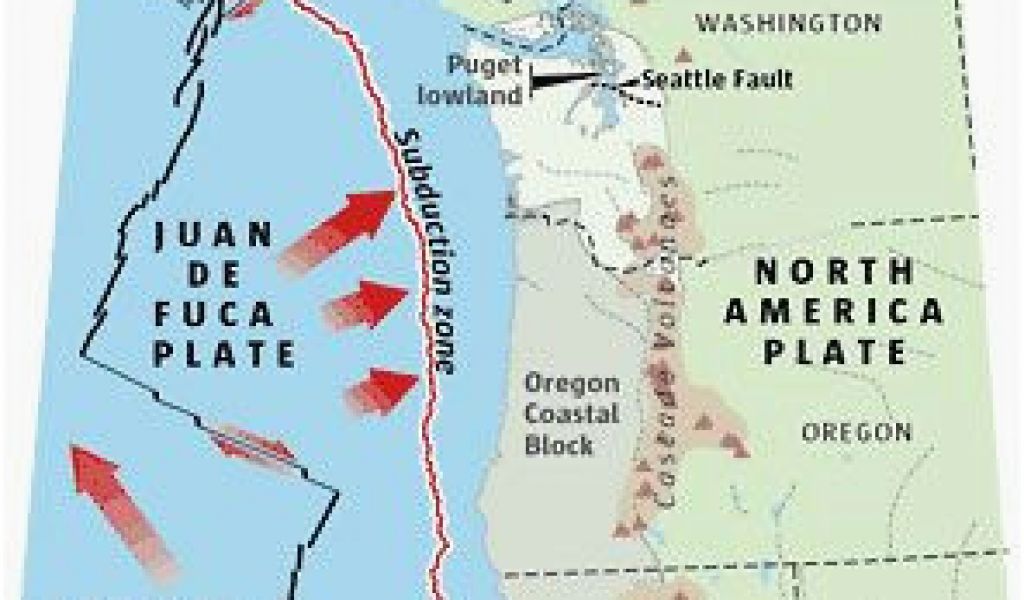
Oregon’s fault lines are a direct consequence of the ongoing interaction between the North American and Pacific tectonic plates. The Pacific Plate, carrying the Juan de Fuca Plate, is subducting beneath the North American Plate along the Cascadia Subduction Zone, a major geological feature stretching from northern California to Vancouver Island. This process, where one tectonic plate slides beneath another, generates immense pressure and stress, leading to the formation of fault lines.
Types of Faults in Oregon:
Oregon’s fault lines are categorized into various types, each with unique characteristics and potential for seismic activity:
- Subduction Zone Faults: The Cascadia Subduction Zone is the most prominent fault line in Oregon. It marks the boundary where the Juan de Fuca Plate descends beneath the North American Plate. This zone is responsible for the largest earthquakes in the region, including the magnitude 9.0 earthquake that struck in 1700.
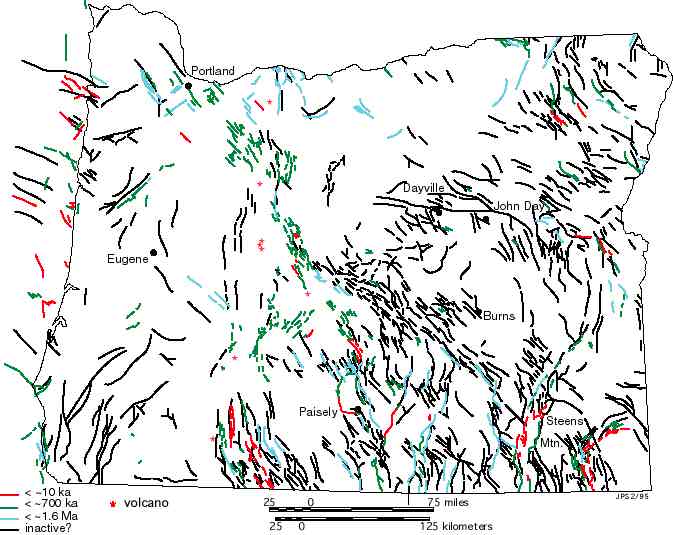
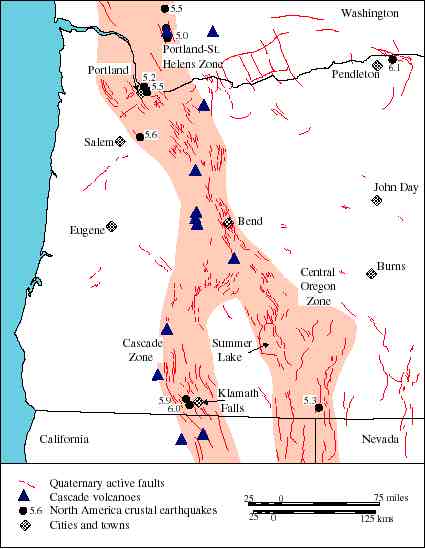
- Strike-Slip Faults: These faults involve horizontal movement of tectonic plates, either in the same or opposite directions. The Eastern Oregon Fault Zone, a series of interconnected faults running through eastern Oregon, is an example of a strike-slip fault system.
- Normal Faults: Characterized by extensional forces, normal faults result in the hanging wall block sliding down relative to the footwall block. These faults are common in areas where the Earth’s crust is being stretched, such as the Basin and Range Province in eastern Oregon.
Mapping Oregon’s Fault Lines: A Tool for Understanding and Mitigation:
The Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries (DOGAMI) plays a vital role in mapping and understanding the state’s fault lines. Their extensive research and data collection provide valuable insights into the location, extent, and potential hazards associated with these geological features. This information is crucial for:
- Seismic Hazard Assessment: By mapping fault lines, scientists can assess the likelihood and potential magnitude of earthquakes in specific areas. This knowledge is vital for developing building codes, infrastructure design, and emergency preparedness plans.
- Land-Use Planning: Understanding the location of fault lines helps inform land-use planning decisions. Development in areas with high seismic risk can be restricted or require specific mitigation measures to ensure safety.
- Earthquake Early Warning Systems: Real-time monitoring of fault lines can provide valuable data for earthquake early warning systems, allowing for timely alerts and potentially saving lives.
Living with Fault Lines: Understanding the Risks and Taking Action:
While the presence of fault lines presents a potential seismic risk, understanding these risks and taking proactive measures can significantly enhance safety and resilience. Here are some key steps individuals and communities can take:
- Educate Yourself: Familiarize yourself with the potential hazards posed by fault lines in your area. Learn about earthquake preparedness measures, including securing heavy objects, having an emergency plan, and maintaining a disaster kit.
- Strengthen Infrastructure: Buildings and infrastructure should be designed and constructed to withstand seismic forces. This includes incorporating earthquake-resistant features such as flexible connections and reinforced concrete.
- Promote Community Preparedness: Encourage community participation in earthquake drills and emergency response exercises. Develop communication plans and ensure access to emergency services during and after an earthquake.
- Monitor and Research: Support ongoing research and monitoring efforts by organizations like DOGAMI to enhance our understanding of fault lines and improve seismic hazard assessments.
FAQs about Oregon’s Fault Lines:
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Oregon?
A: Oregon experiences numerous earthquakes each year, ranging from small tremors barely noticeable to significant events. While large earthquakes are less frequent, the Cascadia Subduction Zone poses a significant risk of a major earthquake in the future.
Q: Can I find out if my home is located near a fault line?
A: DOGAMI provides online resources and maps that allow you to check the proximity of your home to known fault lines. This information can be valuable for understanding potential seismic risks and making informed decisions about home safety.
Q: What should I do if an earthquake occurs?
A: During an earthquake, seek cover under sturdy furniture or in a doorway. Stay away from windows and heavy objects that could fall. Once the shaking stops, assess your surroundings and evacuate if necessary. Follow instructions from local authorities.
Q: Are there any specific areas in Oregon at higher risk from earthquakes?
A: Areas along the Oregon coast, particularly those near the Cascadia Subduction Zone, are at higher risk from earthquakes. However, fault lines extend inland, impacting areas throughout the state.
Q: What are the long-term implications of fault lines on Oregon’s landscape?
A: Fault lines play a crucial role in shaping Oregon’s diverse landscape. They contribute to the formation of mountains, valleys, and other geological features. The ongoing movement of these faults continues to influence the state’s topography.
Tips for Living with Fault Lines in Oregon:
- Secure heavy objects: Secure bookcases, mirrors, and other heavy objects to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Prepare a disaster kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, first aid, and a flashlight.
- Learn CPR and first aid: Familiarize yourself with basic first aid and CPR techniques, which can be crucial in emergency situations.
- Participate in community preparedness programs: Engage in local earthquake drills and emergency response exercises to enhance community resilience.
- Stay informed: Follow updates and advisories from local authorities and organizations like DOGAMI to stay informed about potential seismic risks.
Conclusion:
Oregon’s fault lines are a testament to the dynamic geological forces shaping our planet. While they pose potential risks, understanding their location, characteristics, and associated hazards is crucial for mitigating seismic risk, promoting community preparedness, and ensuring the safety and well-being of Oregon’s residents. By embracing a proactive approach to seismic safety, we can minimize the impact of future earthquakes and foster a more resilient and sustainable future for the state.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Oregon: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!