Unlocking the Secrets of Your Garden: A Comprehensive Guide to Plant Growth Zone Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Your Garden: A Comprehensive Guide to Plant Growth Zone Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Your Garden: A Comprehensive Guide to Plant Growth Zone Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Your Garden: A Comprehensive Guide to Plant Growth Zone Maps

The world of gardening is a fascinating one, filled with endless possibilities and challenges. One of the most crucial aspects of successful gardening is understanding the specific climate conditions that influence plant growth. This is where plant growth zone maps come into play, offering invaluable insights into the suitability of various plants for different regions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of plant growth zone maps, explaining their significance, how they are created, and how they can empower gardeners to make informed decisions for thriving gardens.
Understanding Plant Growth Zones
Plant growth zone maps are visual representations of geographic areas with similar climate conditions, specifically focusing on the average annual minimum temperature. These maps are essential tools for gardeners because they provide a framework for selecting plants that are likely to thrive in a particular region.
The Importance of Minimum Temperatures
The primary factor determining plant growth zones is the average annual minimum temperature. This refers to the lowest average temperature a region experiences during the coldest month of the year. Plants have varying tolerances to cold temperatures, and a plant’s ability to survive the winter is crucial for its overall growth and survival.
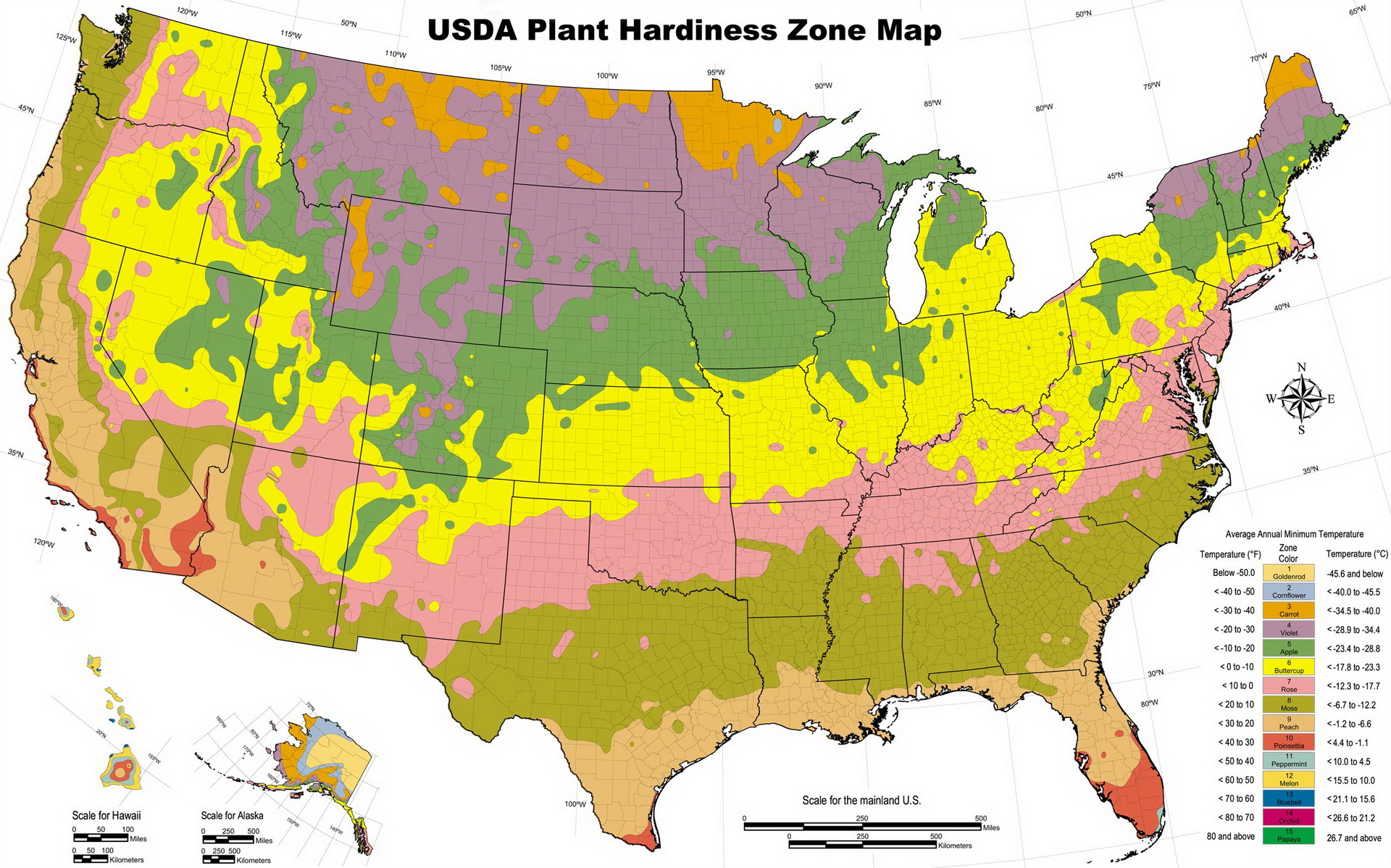
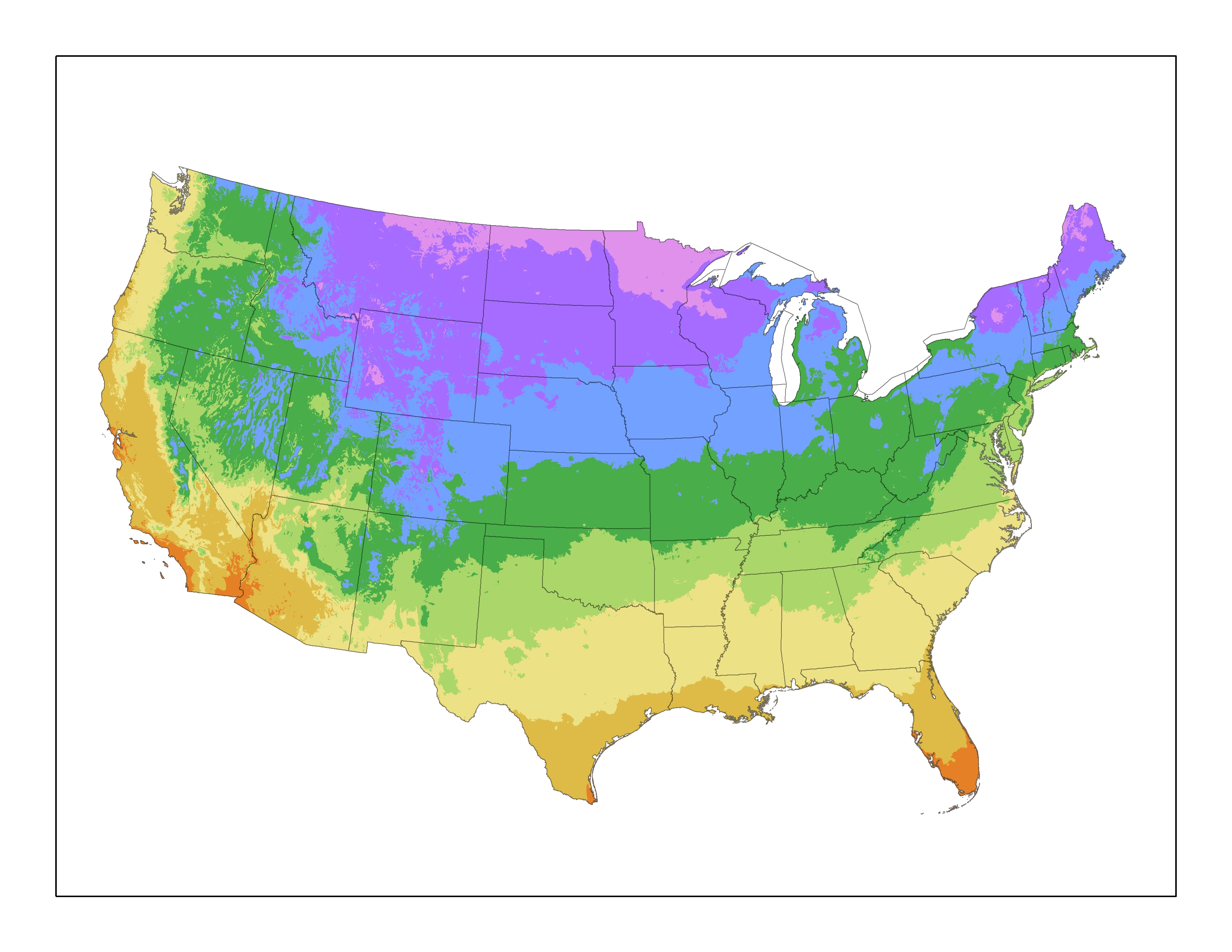
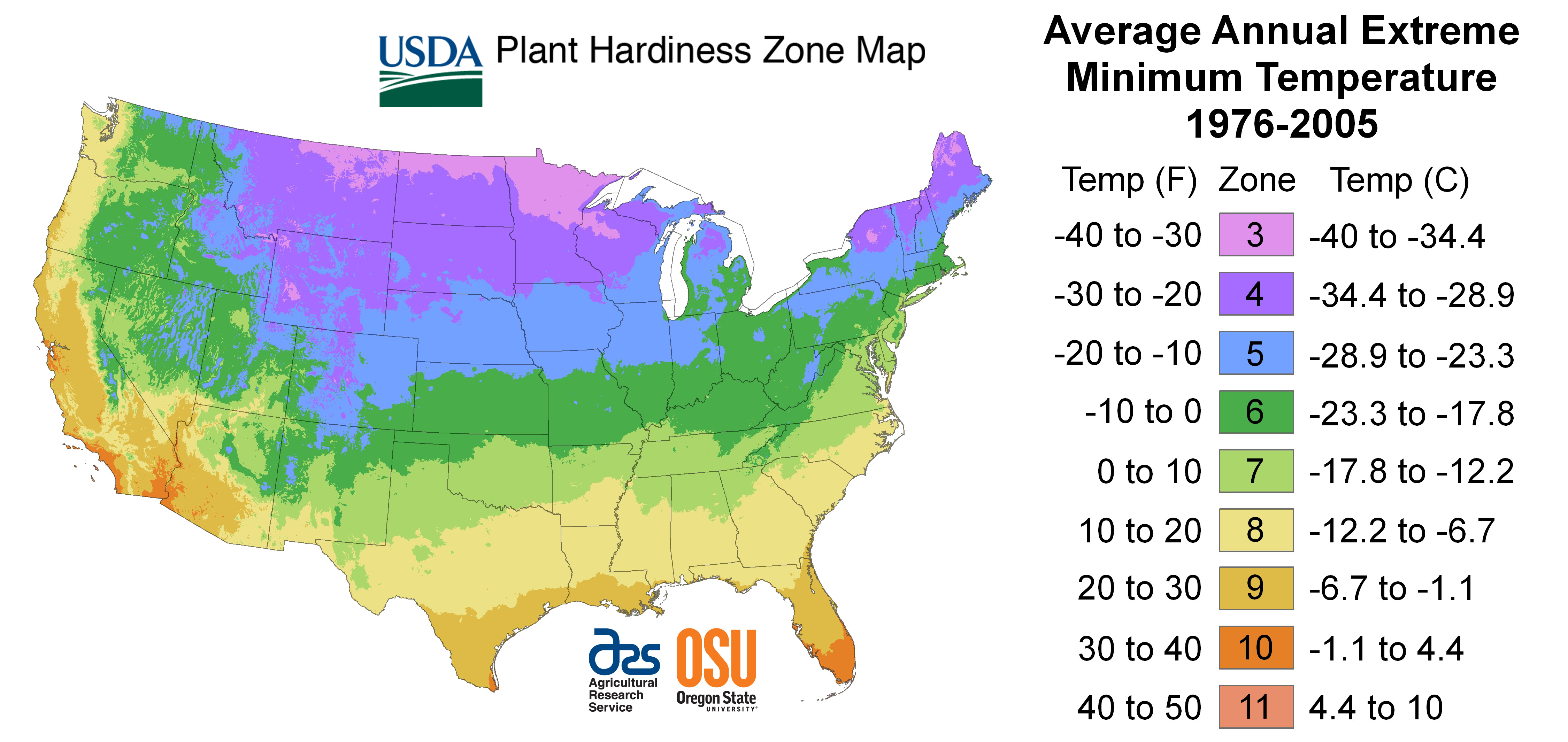
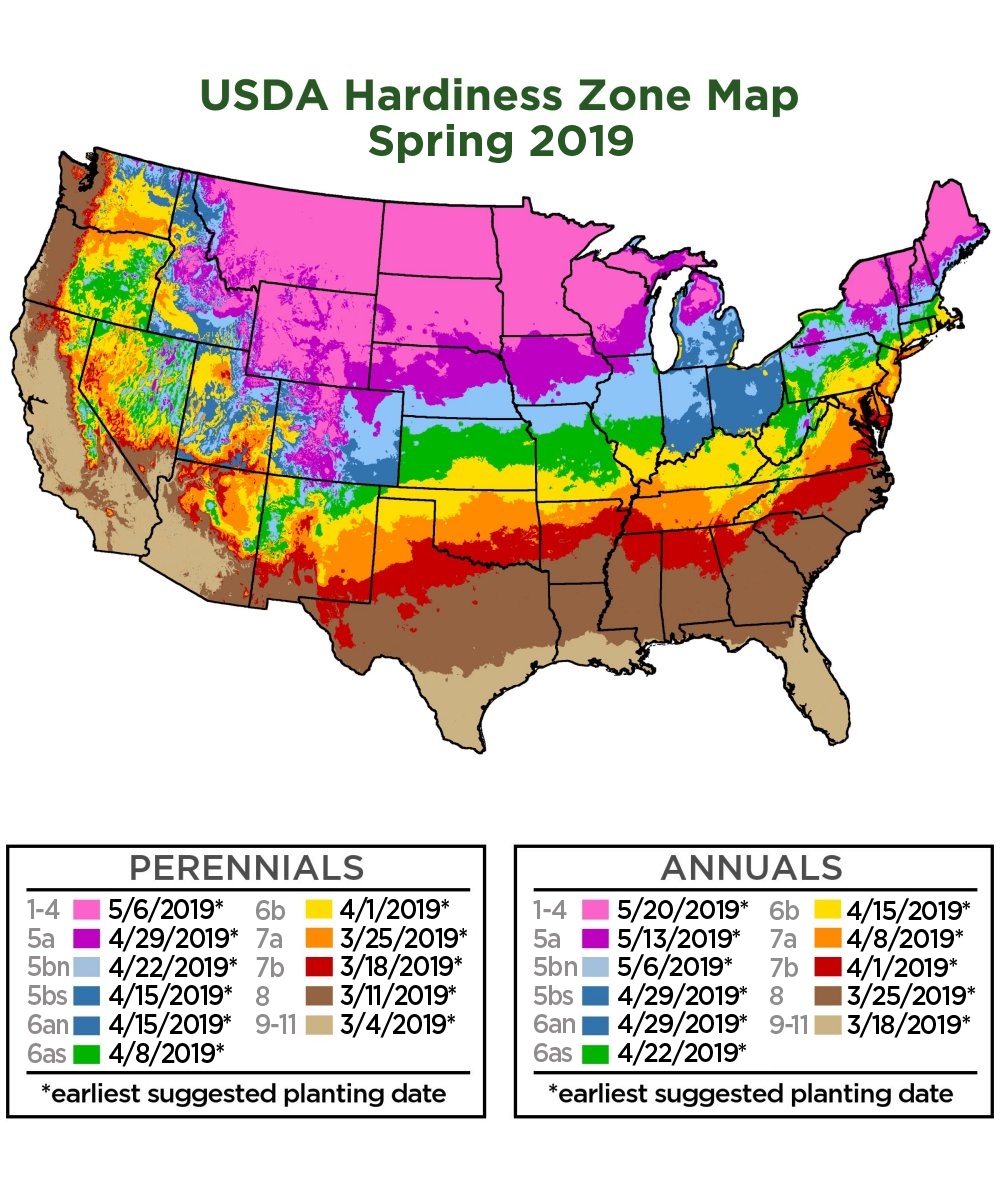
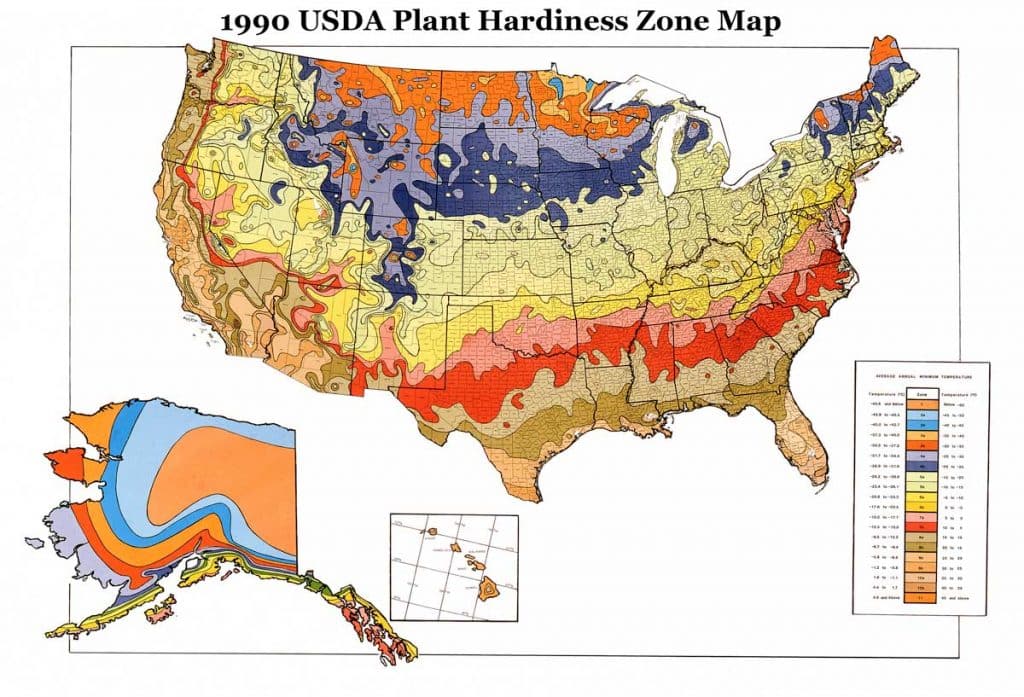
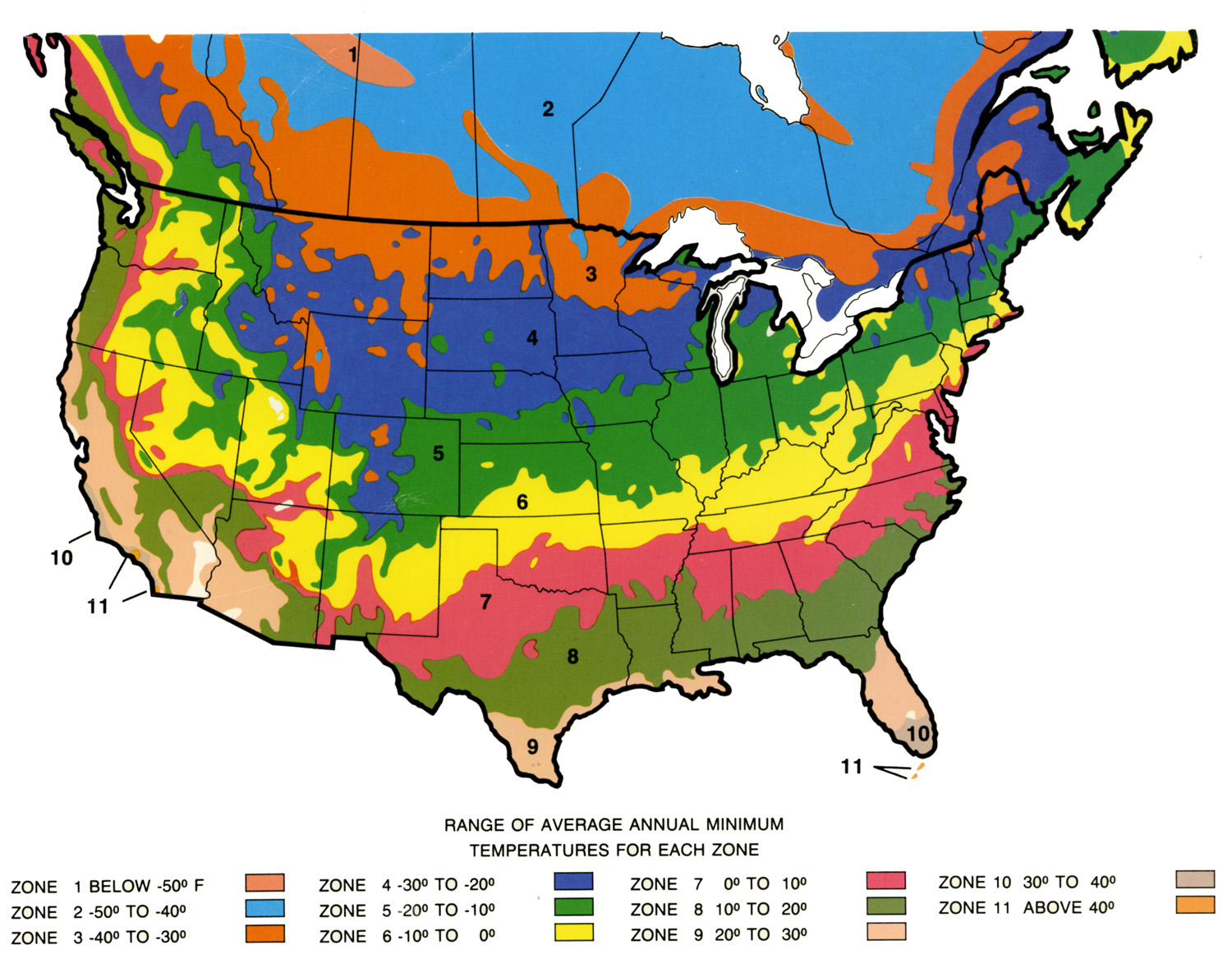
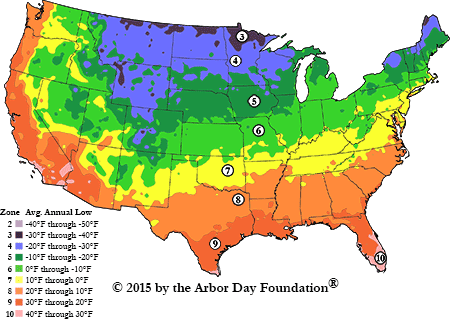
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The most widely recognized plant growth zone map is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. This map, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture, divides the United States into 13 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit temperature range. Zone 1, the coldest, encompasses areas with average minimum temperatures below -60 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 13, the warmest, includes areas with average minimum temperatures above 60 degrees Fahrenheit.
Beyond the Basics: Factors Influencing Plant Growth
While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map offers a valuable starting point, it’s important to understand that other factors can influence plant growth beyond the average minimum temperature. These include:
- Microclimates: Even within a single zone, variations in elevation, proximity to water bodies, and urban heat island effects can create distinct microclimates. These microclimates can significantly alter the local temperature conditions, impacting plant growth.
- Sunlight Exposure: The amount of sunlight a plant receives is crucial for photosynthesis and overall growth. Plant growth zone maps don’t explicitly address sunlight exposure, so gardeners need to consider the specific needs of their chosen plants.
- Soil Type: Soil composition, drainage, and pH levels play a significant role in plant growth. Different plants have varying soil preferences, and understanding these needs is essential for successful gardening.
- Precipitation: Rainfall and irrigation patterns influence plant growth, particularly in regions with limited water availability. Gardens in drier areas may require additional watering to compensate for low precipitation levels.
How Plant Growth Zone Maps Are Created
Creating plant growth zone maps involves a meticulous process of data collection and analysis.
- Temperature Data Collection: Historical temperature records from various weather stations across a region are meticulously collected and analyzed.
- Average Minimum Temperature Calculation: The average minimum temperature for the coldest month of the year is calculated for each location based on the collected data.
- Zone Boundaries: The data is used to draw boundaries between zones, separating areas with similar average minimum temperatures.
- Map Creation: The zones are then displayed on a map, providing a visual representation of plant hardiness across the region.
Benefits of Utilizing Plant Growth Zone Maps
Understanding plant growth zones offers numerous benefits to gardeners, enabling them to make informed decisions for successful gardening:
- Plant Selection: The maps help gardeners choose plants that are well-suited to their local climate, minimizing the risk of plant failure due to cold temperatures.
- Reduced Maintenance: By selecting plants that are naturally adapted to the region, gardeners can reduce the need for extensive winter protection, saving time and effort.
- Increased Success Rate: Matching plants to their appropriate growth zones significantly increases the likelihood of successful growth, leading to a more rewarding gardening experience.
- Sustainable Practices: Selecting plants that thrive in the local climate promotes sustainable gardening practices by reducing the need for invasive interventions and maximizing plant health.
FAQs About Plant Growth Zone Maps
Q: What is the difference between a hardiness zone and a growing zone?
A: Hardiness zones primarily focus on the average minimum winter temperature, determining a plant’s ability to survive the cold. Growing zones, on the other hand, consider a broader range of factors, including average temperatures throughout the year, precipitation, and growing season length.
Q: How do I find my plant hardiness zone?
A: You can easily find your plant hardiness zone by using the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map online. Simply enter your zip code or address, and the map will display your zone.
Q: Can I grow plants from a different zone in my garden?
A: While it’s possible to grow plants from different zones, it’s generally recommended to stick to plants within your zone or one zone warmer. Growing plants from significantly colder zones may require extra care and protection.
Q: Are plant growth zone maps accurate for all regions?
A: Plant growth zone maps provide a general guideline, but local microclimates can significantly affect plant growth. It’s always a good idea to consider the specific conditions in your garden and consult with local gardening experts for personalized advice.
Tips for Using Plant Growth Zone Maps
- Consider Microclimates: Pay attention to local microclimates within your zone, such as sun exposure, elevation, and proximity to water.
- Research Plant Needs: Always research the specific needs of the plants you choose, including sunlight exposure, soil type, and water requirements.
- Consult Local Experts: Seek advice from local gardening experts, nurseries, or garden clubs for personalized recommendations and insights.
- Experiment with Plants: Don’t be afraid to experiment with plants from slightly warmer or colder zones, but be prepared to provide additional care or protection.
Conclusion
Plant growth zone maps are invaluable tools for gardeners of all levels, offering crucial information for selecting plants that are likely to thrive in their specific region. By understanding the principles behind these maps and considering local factors, gardeners can make informed decisions, optimize their garden’s success, and experience the joy of growing healthy, vibrant plants. With the right knowledge and a little planning, any gardener can create a flourishing oasis, no matter their location.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Your Garden: A Comprehensive Guide to Plant Growth Zone Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!