Unraveling the Past: The Oldest Maps of the Middle East
Related Articles: Unraveling the Past: The Oldest Maps of the Middle East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Past: The Oldest Maps of the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Past: The Oldest Maps of the Middle East

The Middle East, a region steeped in history and civilization, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the birth of religions, and the development of trade routes that connected the world. The oldest maps of this region, though often fragmented and incomplete, offer a captivating glimpse into the understanding of geography and the world held by ancient civilizations. These cartographic artifacts are more than mere lines on paper; they are windows into the past, revealing cultural beliefs, political landscapes, and the evolving relationship between humans and their environment.
A Journey Through Time: Tracing the Origins of Middle Eastern Cartography
The earliest known maps of the Middle East emerged from the ancient civilizations that flourished in Mesopotamia and Egypt. The Sumerians, known for their advanced writing system and sophisticated city-states, left behind clay tablets depicting their understanding of the world. These tablets, dating back to the 3rd millennium BC, show rudimentary representations of cities, rivers, and surrounding regions.
The Egyptians, renowned for their architectural achievements and astronomical knowledge, developed maps for practical purposes. The Turin Papyrus, a map dating back to the 12th century BC, depicts the Nile River and surrounding areas with remarkable accuracy. It is believed to have been used for surveying land and navigating the waterways.
Beyond the Nile: Exploring the Expansion of Cartographic Knowledge
The influence of ancient Greek cartography, particularly the work of Ptolemy, significantly shaped the understanding of the Middle East in later centuries. Ptolemy’s maps, compiled around the 2nd century AD, provided a comprehensive and detailed depiction of the region. His work, based on a combination of observation, travel accounts, and previous maps, established a framework for geographical understanding that would be influential for centuries.
The Islamic Golden Age, from the 8th to the 13th century, saw a resurgence of cartographic activity. Muslim scholars, driven by a thirst for knowledge and a desire to understand the world around them, produced maps that incorporated new discoveries and geographical insights. These maps, often incorporating information from travelers and explorers, were instrumental in the development of trade routes and the spread of knowledge across the Islamic world.
Decoding the Maps: Unveiling the Secrets of Ancient Cartography
The oldest maps of the Middle East are not simply representations of physical landscapes; they are intricate expressions of cultural values and societal understanding.
- Political Boundaries: Maps often depicted the territories of different empires and kingdoms, highlighting the shifting political landscapes of the region. The boundaries between these entities, often fluid and contested, reflected the complexities of power dynamics and territorial disputes.
- Religious Significance: Maps frequently incorporated religious sites and pilgrimage routes, reflecting the deep religious beliefs of the time. The location of holy cities, temples, and shrines provided a framework for understanding the spiritual landscape of the region.
- Economic Importance: Maps often highlighted trade routes and important commercial centers, showcasing the economic vitality of the region. The flow of goods and people, facilitated by these routes, had a significant impact on the cultural and social fabric of the Middle East.
- Cultural Symbolism: Many maps incorporated symbolic elements, such as mythical creatures or celestial bodies, reflecting the cultural beliefs and worldview of the time. These elements provide insights into the artistic and symbolic traditions of the societies that created them.
Preserving the Past: The Significance of Ancient Maps
The oldest maps of the Middle East hold immense historical and cultural significance. They offer valuable insights into:
- Historical Reconstructions: Maps provide crucial information about the geography, political structures, and cultural practices of past civilizations. They help historians reconstruct the past and understand the evolution of societies over time.
- Understanding Cultural Values: The symbolic elements and representations found in ancient maps reveal the beliefs, values, and worldview of the people who created them. They provide a window into the cultural tapestry of the Middle East.
- Tracing Geographic Change: By comparing ancient maps with modern ones, scholars can track changes in the landscape, such as the shifting course of rivers, the emergence of new settlements, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Inspiring Future Exploration: The ingenuity and artistry of ancient cartographers continue to inspire modern mapmakers and geographers. Their work serves as a testament to the human desire to explore, understand, and map the world around us.
FAQs: Exploring the Mysteries of Ancient Middle Eastern Maps
Q: What are the oldest known maps of the Middle East?
A: The oldest known maps of the Middle East date back to the 3rd millennium BC, created by the Sumerians. These maps, often depicted on clay tablets, show rudimentary representations of cities, rivers, and surrounding regions.
Q: What were the purposes of ancient maps?
A: Ancient maps served a variety of purposes, including:
- Navigation: Maps helped travelers and sailors navigate unfamiliar territories and waterways.
- Land Surveying: Maps were used to measure land, establish boundaries, and manage resources.
- Military Strategy: Maps provided information about terrain, fortifications, and enemy locations, aiding in military planning and execution.
- Cultural Expression: Maps often incorporated symbolic elements and artistic representations, reflecting the beliefs and values of the societies that created them.
Q: How did ancient maps influence later cartographic developments?
A: Ancient maps provided a foundation for later cartographic developments. The techniques and knowledge developed by ancient civilizations, such as the use of coordinates and the understanding of celestial navigation, were passed down and refined over time. The work of ancient cartographers, particularly the Greeks and Muslims, laid the groundwork for the sophisticated maps that we use today.
Tips for Understanding Ancient Maps
- Context is Key: It is essential to understand the historical, cultural, and geographical context of the map to interpret its meaning accurately.
- Look for Patterns: Pay attention to the way features are represented, the use of symbols, and the overall layout of the map. These elements can reveal important insights into the mapmaker’s intentions.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare different maps from the same period or different regions to identify similarities and differences in cartographic styles and representations.
- Embrace the Ambiguity: Ancient maps are often incomplete, inaccurate, or based on limited knowledge. Instead of seeking absolute truth, embrace the ambiguity and appreciate the insights they offer into the understanding of the world held by ancient civilizations.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Cartographic Exploration
The oldest maps of the Middle East stand as a testament to the enduring human desire to understand and explore the world around us. These cartographic artifacts, though often fragmented and incomplete, offer a captivating glimpse into the past, revealing the cultural beliefs, political landscapes, and the evolving relationship between humans and their environment. By studying these ancient maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ingenuity and creativity of past civilizations and the enduring legacy of cartographic exploration.
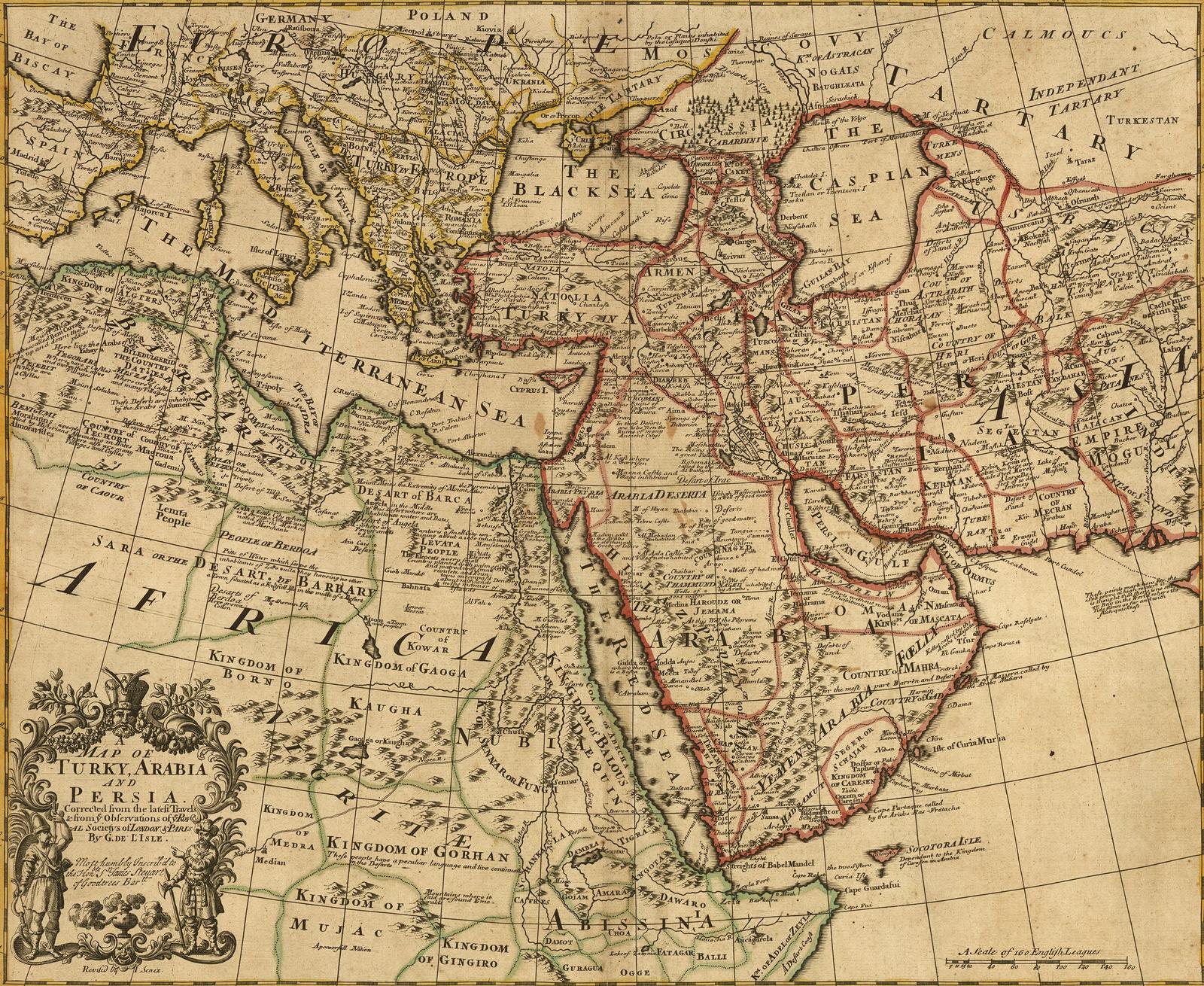


![Ancient Middle East - 1325 BC [5906x4429] [OC] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/9oqz90zsjun21.jpg)

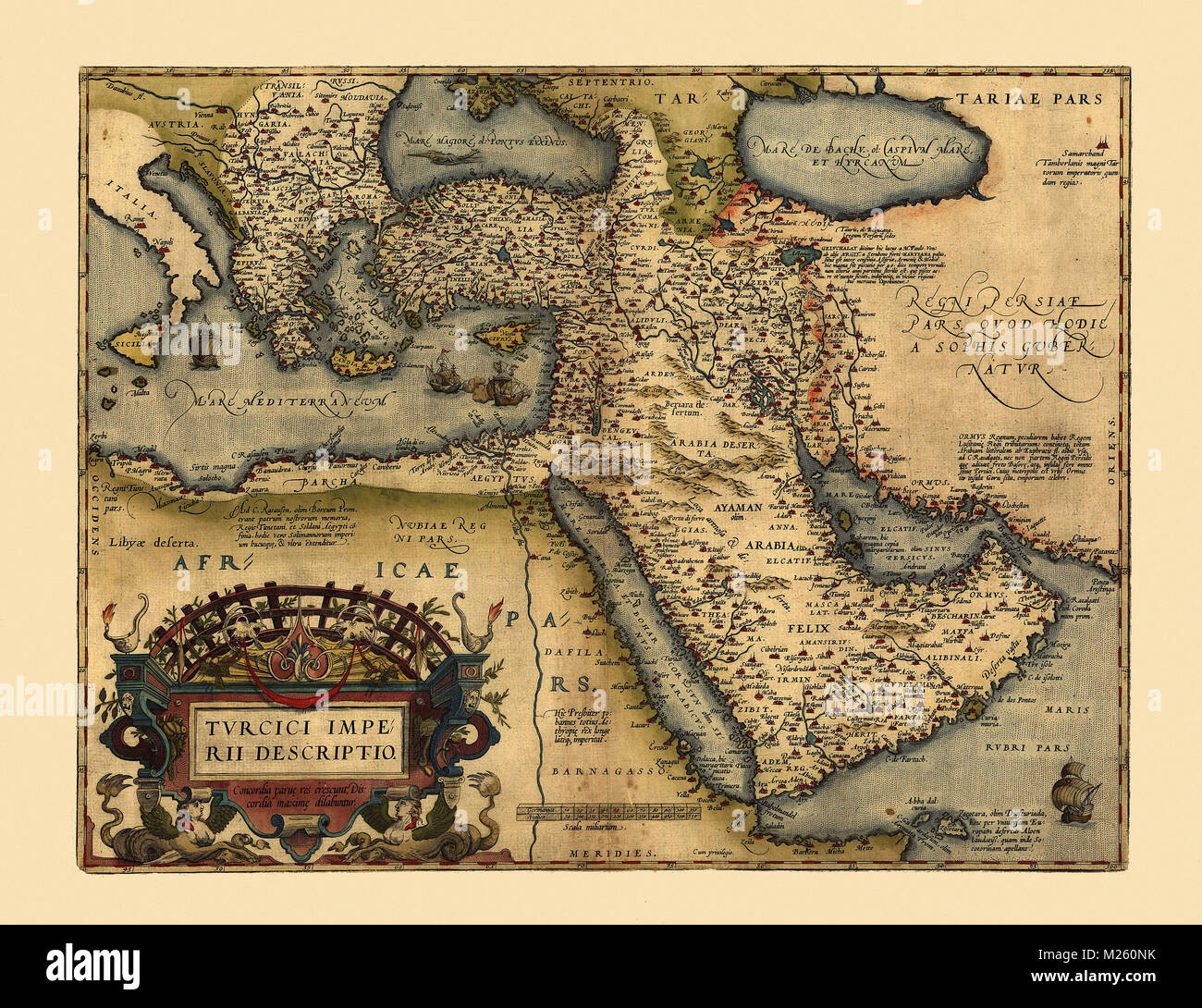

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Past: The Oldest Maps of the Middle East. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!