Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps
- 3.1 The Power of Visual Representation: Maps as Windows to the Past
- 3.2 Navigating the Complexity: Types of Maps and Their Significance
- 3.3 The Importance of Map Interpretation: Beyond the Lines
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Maps of Ancient Americas
- 3.5 Tips for Exploring Maps of Ancient Americas:
- 3.6 Conclusion: Maps as Tools for Understanding the Past
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps

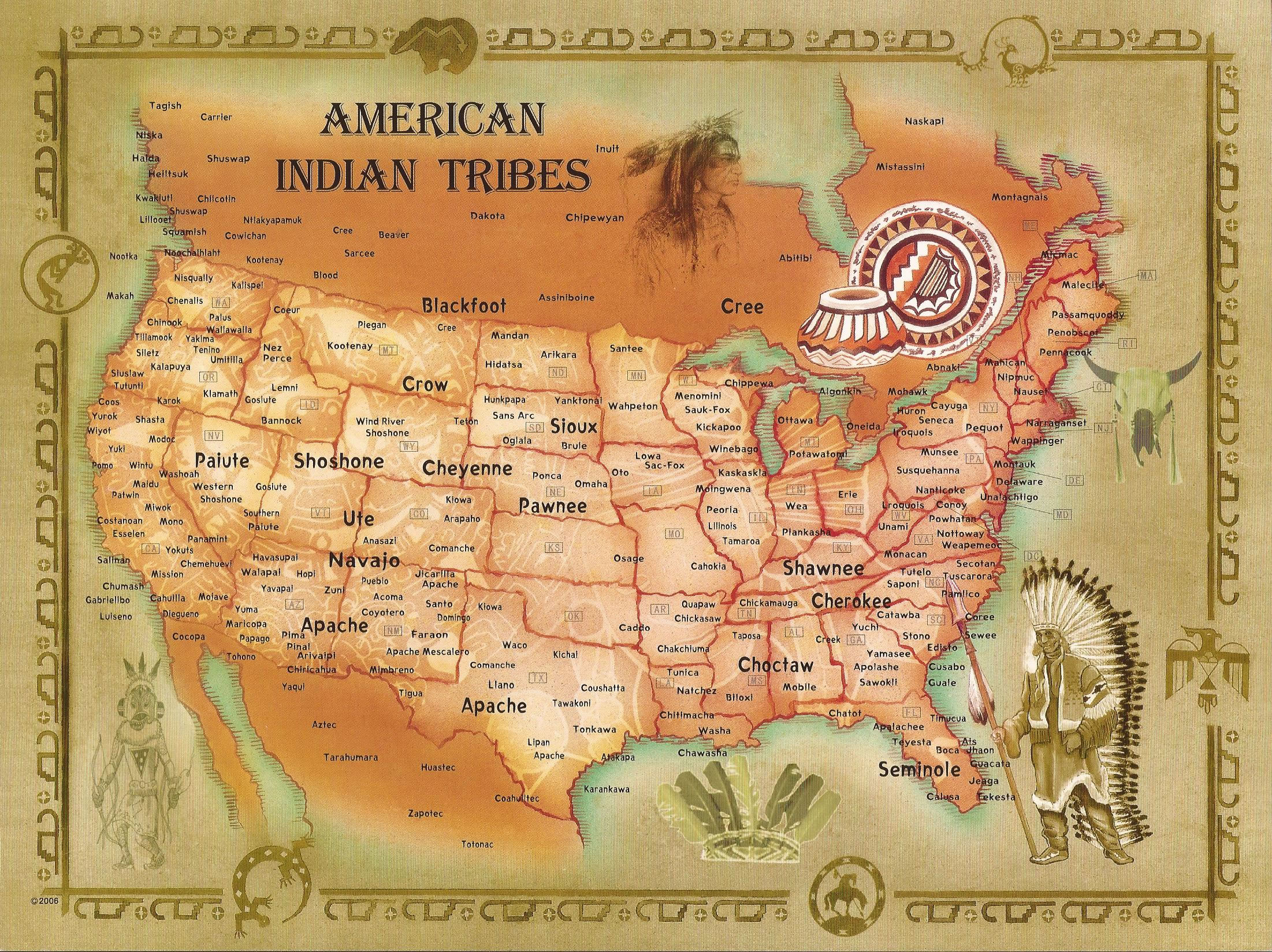
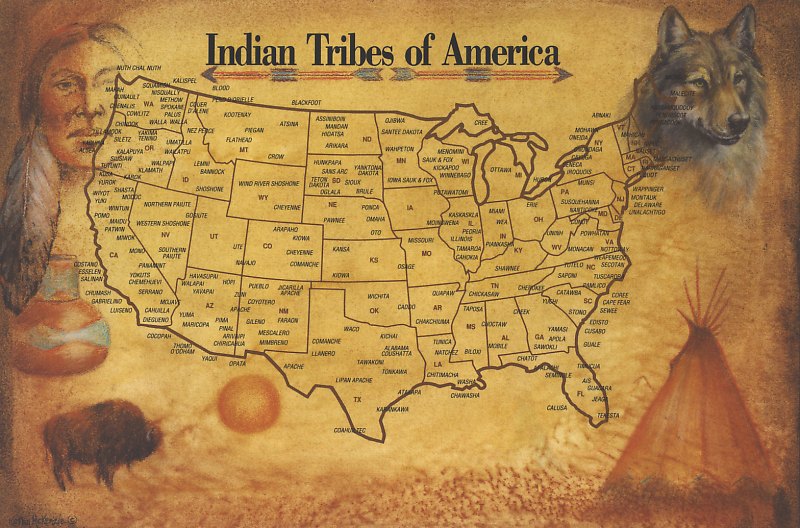
The Americas, a vast and diverse continent, holds a rich tapestry of ancient civilizations, each with its own unique story to tell. To understand the complexities of these societies, their interactions, and their enduring legacies, it is essential to explore the geographical landscape through the lens of maps. Maps of ancient Americas serve as invaluable tools, providing a visual representation of the physical and cultural geography that shaped the lives of these early inhabitants.
The Power of Visual Representation: Maps as Windows to the Past
Maps are more than just static representations of landmasses. They are dynamic narratives, capturing the essence of a region’s history, environment, and cultural practices. In the context of ancient Americas, maps offer several crucial insights:
1. Tracing the Paths of Ancient Civilizations: Maps illuminate the geographic distribution of ancient societies, revealing their settlements, trade routes, and cultural influence. They showcase the intricate networks that connected different communities, fostering exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge. For instance, maps highlight the extensive network of roads and waterways that connected the Maya cities, facilitating trade and communication across their vast empire.
2. Understanding Environmental Influences: Maps reveal the intricate relationship between ancient societies and their environment. They showcase the natural resources that sustained these communities, the challenges posed by geographical features, and the strategies employed to adapt to diverse landscapes. Maps of the Andes Mountains, for example, illustrate the ingenious agricultural techniques developed by the Inca, allowing them to cultivate crops in the challenging terrain.
3. Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Cultures: Maps can shed light on the cultural practices, beliefs, and artistic expressions of ancient civilizations. They reveal the location of sacred sites, ceremonial centers, and monumental architecture, providing valuable clues about the spiritual and social fabric of these societies. Maps of the Nazca Lines, for instance, depict the intricate geoglyphs etched into the desert, hinting at the complex astronomical knowledge and artistic prowess of this ancient culture.
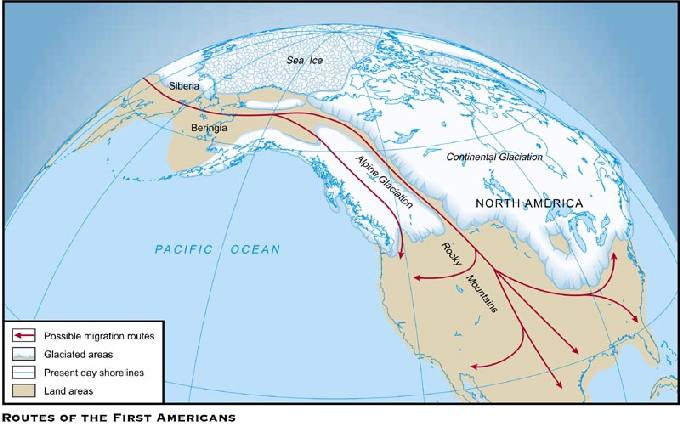
4. Reconstructing Ancient Landscapes: Maps are powerful tools for reconstructing the ancient landscapes of the Americas. They help us understand the impact of climate change, deforestation, and other environmental shifts on these societies. By comparing ancient maps with modern ones, researchers can identify changes in river courses, vegetation patterns, and settlement patterns, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of ancient ecosystems.
Navigating the Complexity: Types of Maps and Their Significance
The study of ancient Americas relies on various types of maps, each offering unique perspectives on the past:
1. Archaeological Maps: These maps depict the locations of archaeological sites, including settlements, burial grounds, temples, and other structures. They provide crucial information about the spatial distribution of ancient cultures and their material remains.
2. Ethnohistorical Maps: These maps combine archaeological data with historical records, oral traditions, and ethnographic accounts to reconstruct the cultural landscape of ancient societies. They offer insights into the social organization, political structures, and religious practices of these communities.
3. Linguistic Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of ancient languages and their dialects, providing valuable clues about the migration patterns, cultural interactions, and linguistic evolution of ancient populations.
4. Environmental Maps: These maps depict the natural environment of ancient Americas, including vegetation zones, climate patterns, and geological formations. They help us understand the ecological context in which ancient societies thrived and the challenges they faced.
5. Geographic Information System (GIS) Maps: These digital maps integrate various datasets, allowing for advanced spatial analysis and visualization. GIS maps are particularly useful for studying the spatial relationships between archaeological sites, environmental factors, and cultural patterns.
The Importance of Map Interpretation: Beyond the Lines
While maps offer valuable insights, it is crucial to interpret them critically, recognizing their limitations and potential biases. Maps are products of their time, reflecting the knowledge, perspectives, and assumptions of their creators. It is essential to consider the following factors when interpreting maps of ancient Americas:
-
Scale and Resolution: Maps vary in their scale and resolution, affecting the level of detail they can provide. Large-scale maps may offer a broad overview, while small-scale maps can reveal intricate details.
-
Data Sources: The accuracy and completeness of maps depend on the sources of data used. Archaeological evidence, historical records, and oral traditions all have their strengths and limitations.
-
Interpretations: Mapmakers often make assumptions and interpretations based on their own understanding of the past. These interpretations may be influenced by cultural biases, political agendas, or limited knowledge.
-
Technological Constraints: Early maps were limited by the available technology and tools. They often reflected incomplete knowledge of the world and may contain inaccuracies.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Maps of Ancient Americas
1. What are some of the earliest maps of the Americas?
Some of the earliest maps of the Americas were created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries. These maps were often based on limited knowledge and were prone to inaccuracies. One notable example is the "Waldseemüller map," created in 1507, which depicted the newly discovered continent as a single landmass.
2. How accurate are maps of ancient Americas?
The accuracy of maps of ancient Americas varies depending on the time period, the data sources used, and the methods employed. Archaeological maps based on meticulous excavation and analysis are generally more accurate than those relying on historical records or oral traditions.
3. How do maps help us understand the decline of ancient civilizations?
Maps can help us understand the environmental and social factors that contributed to the decline of ancient civilizations. By studying the locations of settlements, agricultural practices, and resource availability, researchers can identify potential factors such as climate change, resource depletion, or disease outbreaks.
4. What are some of the most important maps of ancient Americas?
Some of the most important maps of ancient Americas include:
-
The Maya Road Map: This map depicts the extensive network of roads that connected the Maya cities, highlighting the importance of trade and communication in their society.
-
The Inca Road System Map: This map showcases the impressive network of roads built by the Inca, facilitating transportation and communication across their vast empire.
-
The Nazca Lines Map: This map depicts the intricate geoglyphs etched into the desert by the Nazca people, offering insights into their astronomical knowledge and artistic prowess.
Tips for Exploring Maps of Ancient Americas:
-
Consult multiple maps: Compare different maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region and its ancient inhabitants.
-
Consider the context: Analyze the map’s creators, their motivations, and the time period in which it was created.
-
Look for patterns: Identify patterns in settlement distribution, trade routes, and cultural practices.
-
Use digital tools: Explore online maps and GIS databases to visualize and analyze data in new ways.
-
Engage in critical thinking: Question the information presented on the map and consider alternative interpretations.
Conclusion: Maps as Tools for Understanding the Past
Maps of ancient Americas provide a powerful lens through which to explore the rich history and cultural diversity of this vast continent. They offer valuable insights into the lives, beliefs, and achievements of ancient civilizations, revealing the intricate connections between geography, culture, and human society. By critically examining and interpreting these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the enduring legacies of ancient Americas and their relevance to our understanding of the world today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Americas: A Journey Through Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!