Unveiling Montana’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Montana Geologic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Montana’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Montana Geologic Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Montana’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Montana Geologic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Montana’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Montana Geologic Map
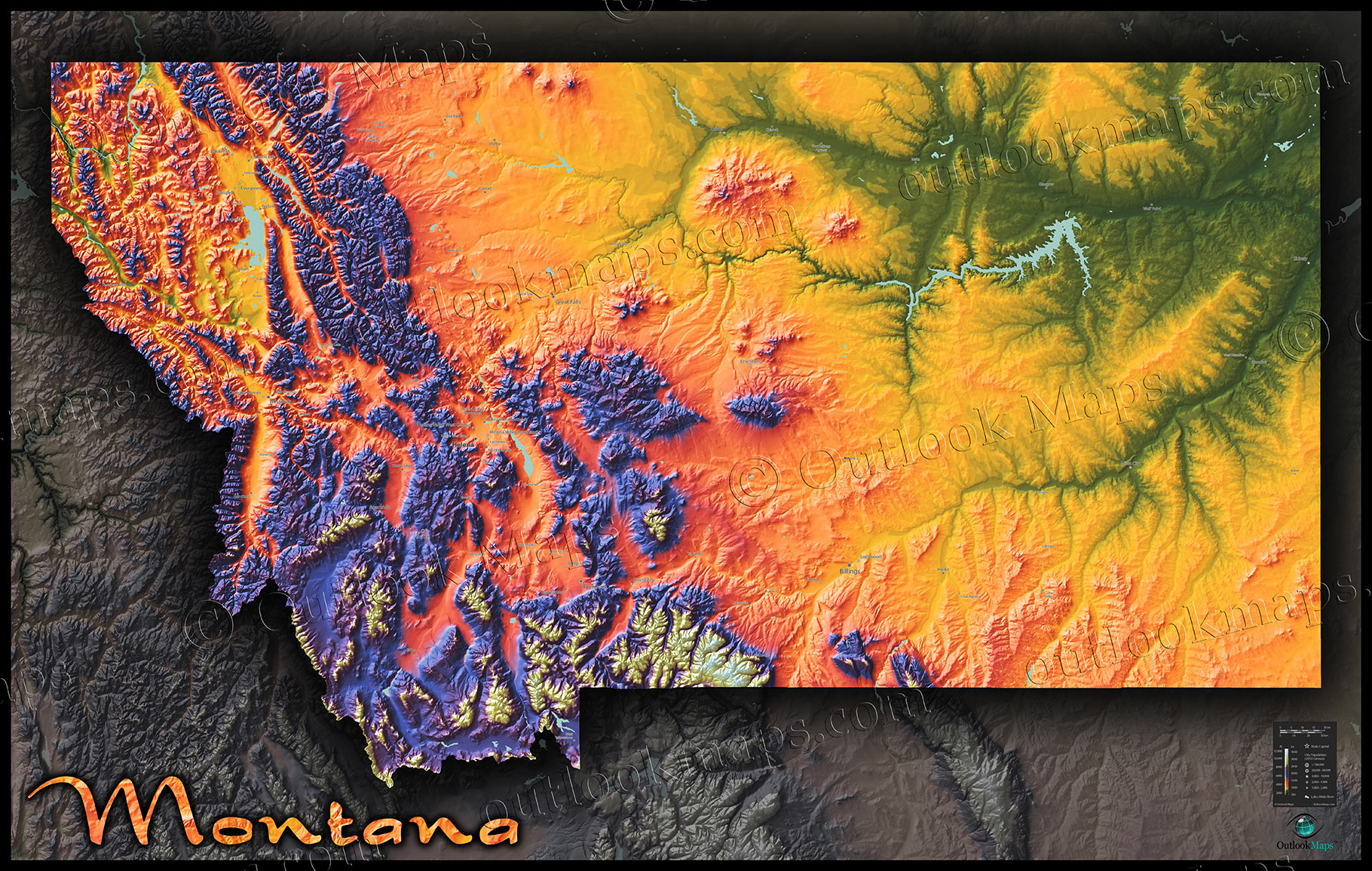
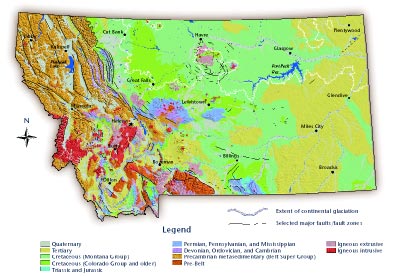
Montana, the "Treasure State," boasts a landscape sculpted by millennia of geological forces. From the towering peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the vast plains of the eastern portion, its diverse topography reflects a complex and fascinating geological history. The Montana Geologic Map, a valuable resource for understanding the state’s geological makeup, provides a detailed visual representation of this history.
Understanding the Montana Geologic Map: A Window into the Past
The Montana Geologic Map is a comprehensive document that illustrates the distribution of various rock formations across the state. It serves as a key tool for geologists, researchers, and anyone interested in understanding the state’s geological history and its implications for various aspects of human activity.
Key Elements of the Montana Geologic Map:
- Rock Formations: The map depicts the distribution of different rock formations, each representing a specific geological period and environment of formation. This includes sedimentary rocks, igneous rocks, and metamorphic rocks, each offering insights into the geological processes that shaped Montana.
- Geological Structures: The map highlights major geological structures like faults, folds, and intrusions, which play a significant role in shaping the landscape and influencing natural resources.
- Mineral Resources: The map indicates the location of various mineral deposits, including coal, oil, gas, and precious metals. This information is crucial for resource exploration and development.
- Hydrogeology: The map provides information on groundwater resources, including aquifers and their potential for water supply. Understanding these features is essential for water management and conservation.
- Geologic Hazards: The map identifies areas prone to geological hazards such as earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic activity. This information is crucial for planning and mitigating potential risks.
Benefits of Using the Montana Geologic Map:
- Resource Exploration and Development: The map is a valuable tool for locating and evaluating potential mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and other natural resources.
- Environmental Management: The map helps in understanding the distribution of aquifers, identifying areas prone to pollution, and developing strategies for environmental protection.
- Infrastructure Planning: The map informs planning for transportation infrastructure, construction projects, and other developments, ensuring they are located in geologically stable areas.
- Geological Research: The map serves as a foundational resource for geological research, providing a framework for understanding the state’s geological history and processes.
- Education and Public Awareness: The map promotes public understanding of Montana’s geological heritage and the importance of responsible land management.
A Journey Through Time: Understanding Montana’s Geological History
The Montana Geologic Map reveals a narrative spanning billions of years, showcasing the state’s geological evolution from its Precambrian origins to the present day.
- Precambrian Era (4.5 Billion to 541 Million Years Ago): This era witnessed the formation of the Earth’s first continents, including the ancient core of Montana. The map reveals the presence of Precambrian metamorphic rocks, indicating intense heat and pressure that transformed earlier rocks.
- Paleozoic Era (541 to 252 Million Years Ago): During this era, Montana was submerged beneath a shallow sea, leading to the deposition of vast amounts of sediment that later formed sedimentary rocks. The map depicts the presence of Paleozoic sedimentary rocks, containing fossils of ancient marine life.
- Mesozoic Era (252 to 66 Million Years Ago): The Mesozoic Era saw the rise of dinosaurs and the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea. Montana experienced volcanic activity and the formation of sedimentary basins, as evidenced by the presence of Mesozoic igneous and sedimentary rocks on the map.
- Cenozoic Era (66 Million Years Ago to Present): This era witnessed the uplift of the Rocky Mountains, shaping Montana’s dramatic landscape. The map reveals the presence of Cenozoic sedimentary rocks and volcanic deposits, showcasing the ongoing geological processes that continue to shape the state.
Exploring the Depths: Understanding Montana’s Geological Structures
The Montana Geologic Map also highlights major geological structures that have played a crucial role in shaping the state’s landscape and influencing its natural resources.
- Faults: These are fractures in the Earth’s crust where rocks have moved past each other. Faults can create earthquakes, influence the distribution of mineral deposits, and shape the topography.
- Folds: These are bends or wrinkles in rock layers, often formed by compressional forces. Folds can trap oil and gas, influence groundwater flow, and create dramatic landscapes.
- Intrusions: These are masses of igneous rock that have been injected into existing rock layers. Intrusions can create mineral deposits, influence the surrounding geology, and create distinctive landforms.
The Montana Geologic Map: A Resource for All
The Montana Geologic Map is a vital resource for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Geologists and Researchers: The map provides a foundational framework for understanding the state’s geological history and conducting research on various geological processes.
- Mining and Energy Companies: The map helps in identifying potential mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and other natural resources, guiding exploration and development efforts.
- Environmental Agencies: The map assists in understanding the distribution of groundwater resources, identifying areas prone to pollution, and developing strategies for environmental protection.
- Civil Engineers and Planners: The map informs planning for transportation infrastructure, construction projects, and other developments, ensuring they are located in geologically stable areas.
- Educators and Students: The map provides a valuable tool for teaching about Montana’s geological history and the importance of responsible land management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Montana Geologic Map:
Q: Where can I find the Montana Geologic Map?
A: The Montana Geologic Map is available from the Montana Bureau of Mines and Geology (MBMG). It can be accessed online or purchased as a printed copy.
Q: What are the different types of rocks depicted on the map?
A: The map depicts sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks, representing various geological periods and environments of formation.
Q: How does the map help in understanding Montana’s natural resources?
A: The map indicates the location of various mineral deposits, including coal, oil, gas, and precious metals, guiding resource exploration and development.
Q: What are the geological hazards identified on the map?
A: The map identifies areas prone to earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic activity, providing information for hazard mitigation and planning.
Q: How can I use the map for educational purposes?
A: The map can be used to teach about Montana’s geological history, the different types of rocks, and the importance of responsible land management.
Tips for Using the Montana Geologic Map:
- Start with the legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend, which explains the symbols and colors used to represent different rock formations, geological structures, and other features.
- Focus on specific areas: Use the map to investigate specific areas of interest, such as a particular mountain range, a potential mining site, or an area prone to geological hazards.
- Combine with other resources: Integrate the Montana Geologic Map with other geological and geographical data, such as satellite imagery, topographic maps, and aerial photographs, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the area.
- Use online tools: Take advantage of online tools and interactive maps that provide additional information and analysis capabilities.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Geological Wonder
The Montana Geologic Map is a testament to the state’s rich geological history and its diverse landscape. It serves as a valuable resource for understanding the complex geological processes that have shaped Montana over millions of years. By using this map, we can gain insights into the state’s natural resources, geological hazards, and environmental challenges, promoting responsible land management and fostering a deeper appreciation for the geological wonders of Montana.


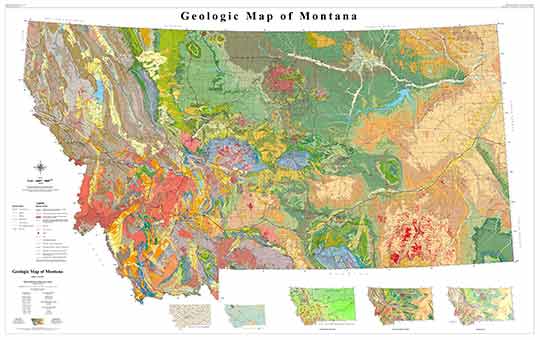
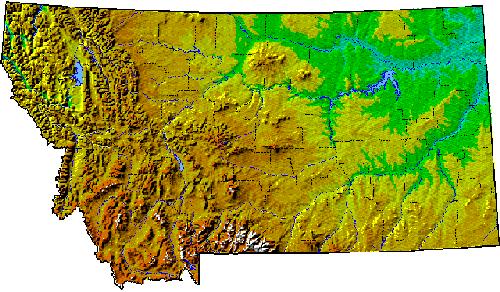

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Montana’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Montana Geologic Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!