Unveiling the Altitudes of South America: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Altitudes of South America: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Altitudes of South America: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Altitudes of South America: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map
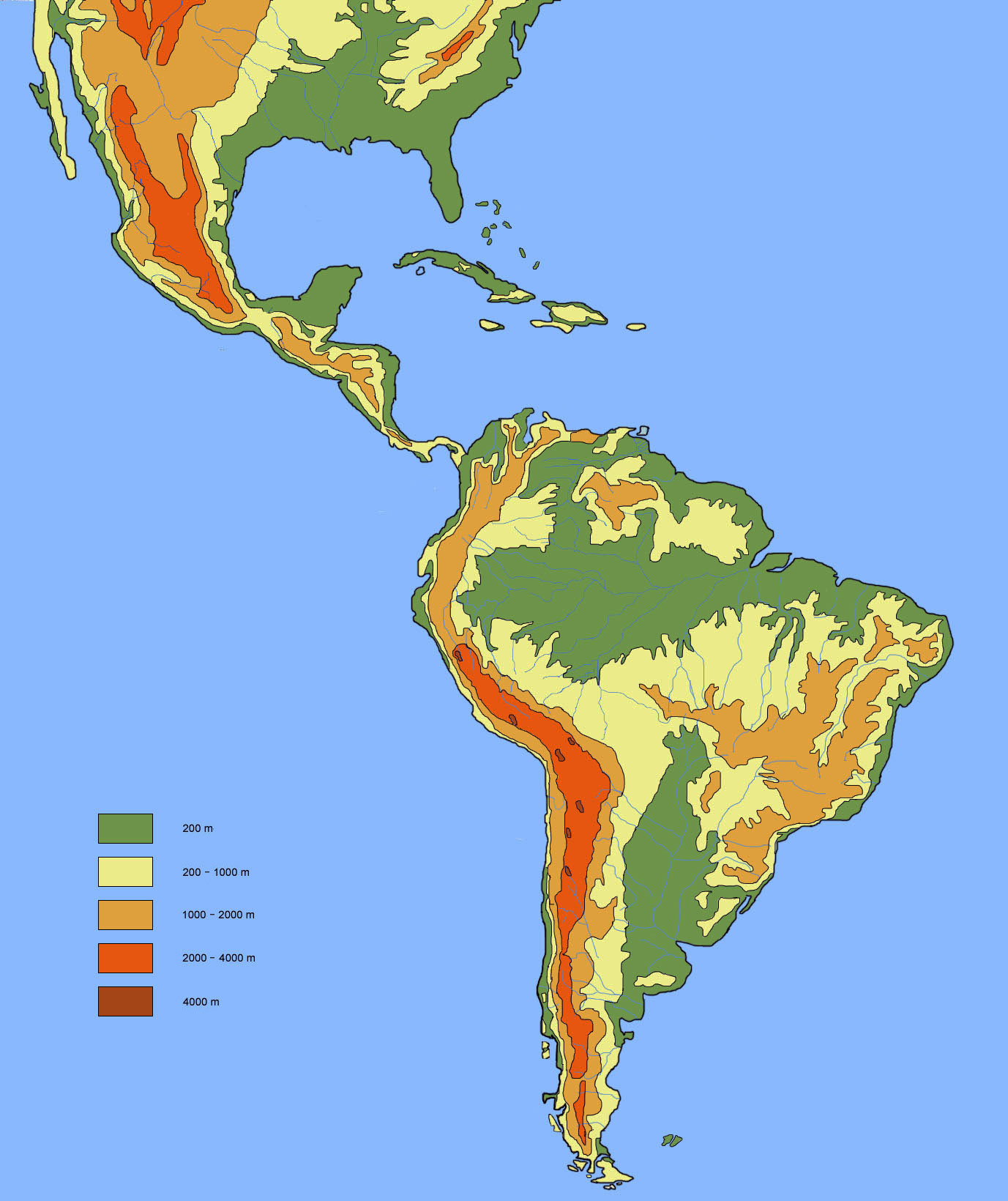
South America, a continent of vast landscapes and diverse ecosystems, boasts a remarkable array of topographic features. From the towering peaks of the Andes to the sprawling plains of the Amazon Basin, the continent’s elevation map tells a captivating story of geological forces, climatic influences, and the evolution of life. This article delves into the intricacies of this map, exploring its key features, revealing its significance, and offering insights into its applications.
Understanding the Elevation Map: A Visual Depiction of Altitude
An elevation map, also known as a topographic map, visually represents the height of the land above sea level. It utilizes a system of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, to create a three-dimensional representation of the terrain. Areas with closely spaced contour lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines signify gentle gradients.
Key Features of South America’s Elevation Map:
- The Andes Mountains: This majestic mountain range, the longest in the world, dominates the western spine of South America. Its towering peaks, including Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside Asia, are depicted by densely packed contour lines, highlighting the steep and rugged terrain.
- The Amazon Basin: This vast lowland region, encompassing the Amazon River and its tributaries, is characterized by low elevations, indicated by widely spaced contour lines. The flat, gently sloping terrain is conducive to the formation of extensive wetlands and rainforests.
- The Guiana Shield: Located in northeastern South America, this ancient geological formation features a plateau with a relatively high elevation, depicted by intermediate contour lines. It harbors a unique biodiversity and is characterized by rugged landscapes.
- The Brazilian Highlands: This vast plateau region, encompassing much of eastern and central Brazil, exhibits a moderately high elevation, with a diverse landscape of hills, plateaus, and valleys. The contour lines reflect the undulating nature of the terrain.
- The Patagonian Plateau: Located in southern Argentina and Chile, this plateau is characterized by a high elevation and a rugged landscape with numerous glaciers and mountains. The elevation map depicts the dramatic drop in elevation towards the Atlantic Ocean.
The Significance of South America’s Elevation Map:
- Understanding the Distribution of Biodiversity: The elevation map reveals the diverse habitats across South America, influencing the distribution of plant and animal species. For example, the high elevations of the Andes support unique alpine ecosystems, while the lowlands of the Amazon Basin host a vast array of rainforest species.
- Identifying Areas Vulnerable to Climate Change: The elevation map helps identify areas susceptible to climate change impacts. For instance, the Andean glaciers, depicted by high elevations, are particularly vulnerable to melting due to rising temperatures.
- Planning Infrastructure Development: The elevation map is crucial for planning infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and dams. It helps determine the feasibility of construction in mountainous or low-lying areas, considering potential challenges like steep slopes or flooding.
- Supporting Environmental Conservation: The elevation map is essential for understanding the distribution of natural resources and identifying areas requiring protection. For example, the high elevation rainforests of the Andes are crucial for maintaining biodiversity and regulating water flow.
- Facilitating Scientific Research: The elevation map is a valuable tool for researchers studying various aspects of South America, including geology, climate, biodiversity, and human geography. It provides a spatial framework for analyzing data and understanding the relationship between elevation and other variables.
FAQs on South America’s Elevation Map:
1. What is the highest point in South America?
The highest point in South America is Mount Aconcagua, located in the Andes Mountains of Argentina, with an elevation of 6,961 meters (22,838 feet) above sea level.
2. What is the lowest point in South America?
The lowest point in South America is the Valdes Peninsula in Argentina, which lies below sea level at -40 meters (-131 feet).
3. How does the elevation map impact the climate of South America?
Elevation plays a significant role in shaping South America’s climate. Higher elevations experience cooler temperatures and increased precipitation, while lower elevations are typically warmer and drier. The Andes Mountains create a rain shadow effect, blocking moisture from reaching the eastern side of the continent.
4. How is the elevation map used in disaster management?
The elevation map is crucial for disaster management, particularly in areas prone to natural hazards like earthquakes, landslides, and floods. It helps identify areas at risk, plan evacuation routes, and allocate resources effectively.
5. How can I access South America’s elevation map online?
Various online platforms provide access to South America’s elevation map, including Google Earth, ArcGIS Online, and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) website.
Tips for Utilizing South America’s Elevation Map:
- Consider the scale: Choose a map with a suitable scale for your specific needs. A larger scale map will provide more detail, while a smaller scale map will show a broader overview.
- Pay attention to contour lines: Understand how contour lines represent elevation changes. Closer spacing indicates steeper slopes, while wider spacing suggests gentle gradients.
- Look for key features: Identify prominent features on the map, such as mountain ranges, rivers, and lakes, to gain a better understanding of the terrain.
- Use online tools: Utilize online mapping platforms to explore interactive elevation maps and analyze data more effectively.
- Combine with other data: Integrate the elevation map with other data sources, such as climate data, population density, or land cover, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion:
South America’s elevation map is a valuable tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, its impact on biodiversity, climate, and human activities. By providing a visual representation of altitude, it helps researchers, planners, and policymakers make informed decisions regarding resource management, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness. As we continue to explore and understand this complex continent, the elevation map will remain an essential tool for navigating its intricate landscapes and uncovering its hidden treasures.
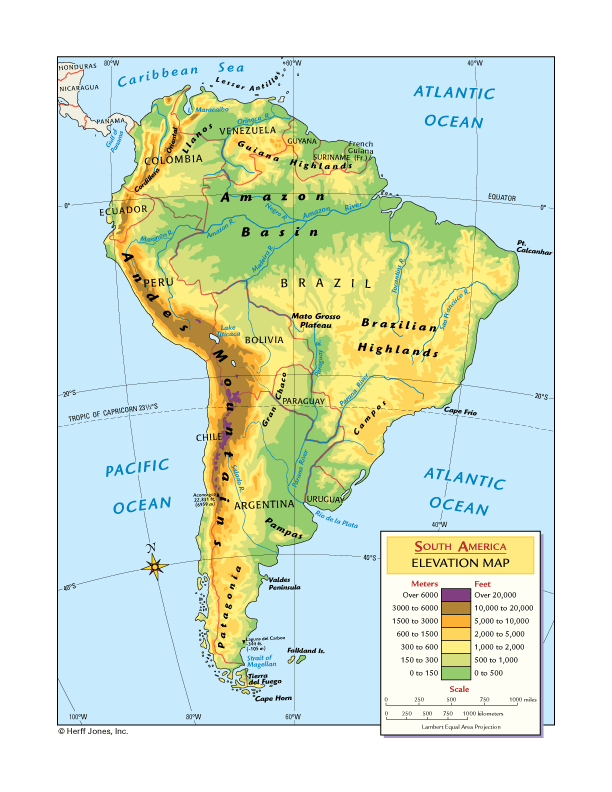


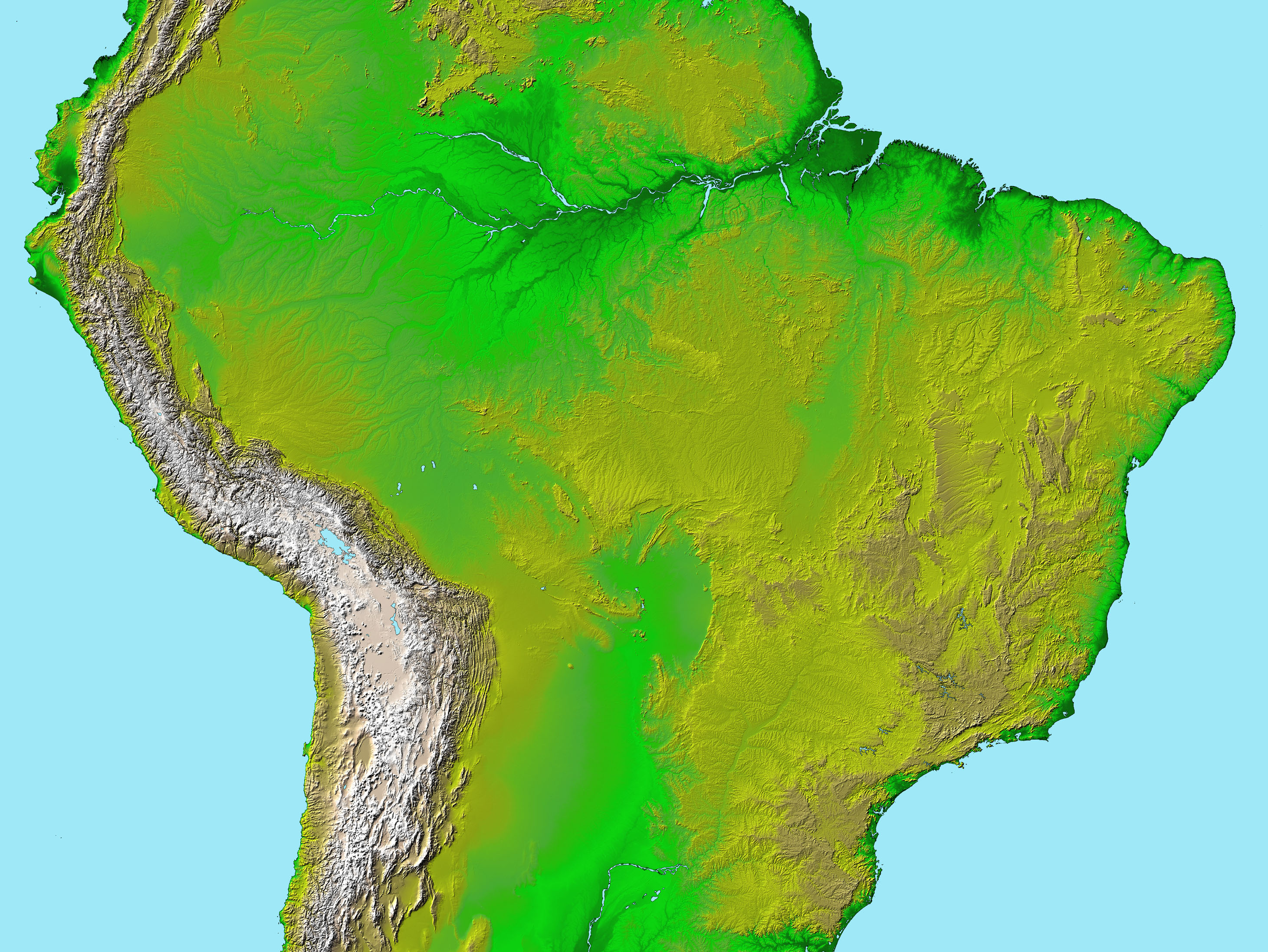

![[OC] Elevation of South America : dataisbeautiful](https://i.redd.it/bdtuqvdbqqd91.jpg)

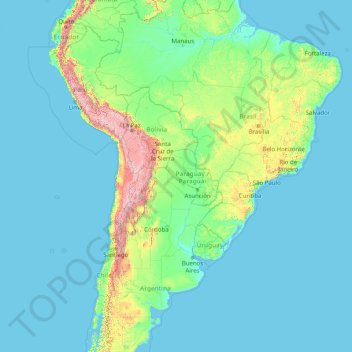
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Altitudes of South America: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!