Unveiling the Cradle of Civilization: A Geographical Exploration of Sumer
Related Articles: Unveiling the Cradle of Civilization: A Geographical Exploration of Sumer
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Cradle of Civilization: A Geographical Exploration of Sumer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Cradle of Civilization: A Geographical Exploration of Sumer

The Sumerian civilization, nestled in the fertile plains of Mesopotamia, holds a unique place in human history. It is widely recognized as the first urban civilization, laying the foundation for many of the societal structures and advancements we take for granted today. Understanding the geographical landscape of Sumer is crucial to appreciating the rise and fall of this remarkable civilization.
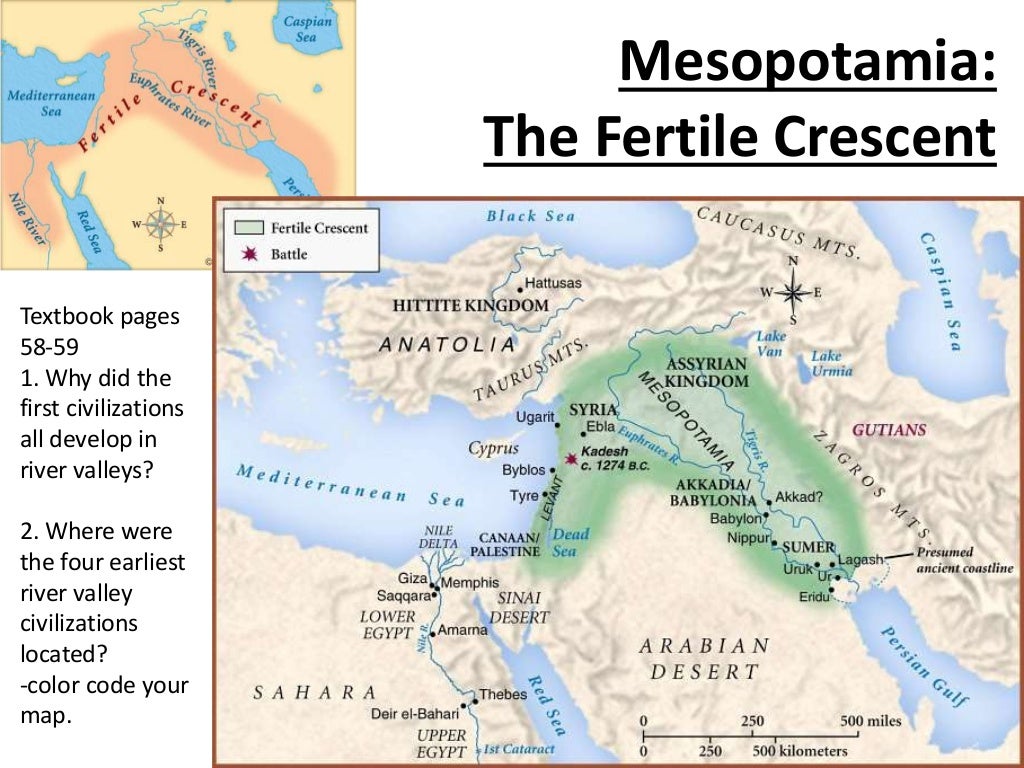
The Land of the Two Rivers:
Sumer was situated in southern Mesopotamia, a region bordered by the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. These two mighty waterways, known as the "land of the two rivers," played a pivotal role in shaping Sumerian life. The rivers provided a constant source of water for irrigation, agriculture, and transportation, allowing the Sumerians to flourish in an otherwise arid environment.
The Fertile Crescent:
The region where Sumer thrived is also known as the Fertile Crescent, a crescent-shaped area extending from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. This region, characterized by its fertile land and abundant water sources, became a cradle of civilization, giving rise to numerous ancient empires, including Sumer.
The City-States of Sumer:
Sumer was not a unified kingdom but rather a collection of independent city-states, each with its own distinct culture, government, and religious beliefs. These city-states, including Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagash, and Nippur, were centers of trade, agriculture, and cultural innovation.
A Geographical Map of Sumerian Civilization:
1. The City of Ur:
Located on the Euphrates River, Ur was a major center of trade and religious activity. It was home to the famous ziggurat dedicated to the moon god Nanna, and its archaeological remains offer valuable insights into Sumerian architecture, art, and social structures.
2. The City of Uruk:
Uruk, situated on the Euphrates River, is considered one of the oldest cities in the world. It was renowned for its monumental architecture, including the Great Ziggurat of Uruk and the White Temple. The city’s archaeological excavations have revealed evidence of early writing, irrigation systems, and complex social organization.
3. The City of Kish:
Kish, located near the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, was an important political and religious center in ancient Sumer. It was known for its skilled artisans and its role in the development of early Mesopotamian law.
4. The City of Lagash:
Lagash, situated on the Euphrates River, was a powerful city-state known for its sophisticated irrigation system and its impressive temple complexes. The city’s rulers, including Gudea, left behind a rich legacy of art and literature.
5. The City of Nippur:
Nippur, located near the Euphrates River, was the religious center of Sumer, home to the temple of Enlil, the god of air and storms. The city was a hub of scholarship and religious learning, and its archaeological remains have yielded valuable information about Sumerian mythology and cosmology.
The Importance of Geography in Sumerian Civilization:
Sumer’s unique geographical location played a crucial role in the development of its civilization. The fertile land, abundant water resources, and proximity to trade routes allowed for the growth of agriculture, trade, and cultural exchange. The rivers provided transportation, irrigation, and a source of sustenance, enabling the Sumerians to develop a complex society.
The Challenges of Sumerian Geography:
Despite its advantages, Sumer’s geography also posed challenges. The region was prone to floods, droughts, and conflicts with neighboring civilizations. The Sumerians had to develop sophisticated irrigation systems to manage the unpredictable water flow, and they constantly faced threats from other empires vying for control of the fertile land.
The Legacy of Sumerian Geography:
The geographical landscape of Sumer continues to influence the region today. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers remain vital waterways, supporting agriculture and transportation. The archaeological remains of Sumerian cities provide valuable insights into the origins of urban civilization, reminding us of the enduring legacy of this ancient civilization.
FAQs about Sumerian Civilization and its Geography:
1. What were the main geographical features of Sumer?
Sumer was situated in southern Mesopotamia, a region bordered by the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. These rivers were crucial for irrigation, agriculture, and transportation.
2. What were the major cities of Sumer?
The major cities of Sumer included Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagash, and Nippur. Each city had its own distinct culture, government, and religious beliefs.
3. How did geography influence Sumerian civilization?
The fertile land, abundant water resources, and proximity to trade routes allowed for the growth of agriculture, trade, and cultural exchange. The rivers provided transportation, irrigation, and a source of sustenance, enabling the Sumerians to develop a complex society.
4. What were the challenges faced by Sumerian civilization due to its geography?
The region was prone to floods, droughts, and conflicts with neighboring civilizations. The Sumerians had to develop sophisticated irrigation systems to manage the unpredictable water flow, and they constantly faced threats from other empires vying for control of the fertile land.
5. How does the geography of Sumer continue to influence the region today?
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers remain vital waterways, supporting agriculture and transportation. The archaeological remains of Sumerian cities provide valuable insights into the origins of urban civilization, reminding us of the enduring legacy of this ancient civilization.
Tips for Studying Sumerian Civilization and its Geography:
1. Utilize maps and geographical resources:
Visualizing the location and layout of Sumerian cities and their surrounding landscape can greatly enhance understanding. Use maps, aerial photographs, and other geographical resources to gain a clearer picture of the region.
2. Explore archaeological sites and museums:
Visiting archaeological sites and museums showcasing Sumerian artifacts provides a tangible connection to the civilization’s past. Examine the architecture, art, and artifacts to gain insights into Sumerian life and culture.
3. Read historical accounts and scholarly works:
Researching Sumerian history and culture through written sources, including ancient texts, archaeological reports, and scholarly books, provides a comprehensive understanding of the civilization’s development and achievements.
4. Connect geography to social and cultural aspects:
Analyze how the geographical landscape shaped Sumerian society, economy, and cultural practices. Explore the relationship between the environment and the development of irrigation systems, agriculture, trade, and religious beliefs.
5. Draw comparisons with other ancient civilizations:
Comparing Sumerian civilization with other ancient civilizations, such as Egypt or the Indus Valley Civilization, can highlight similarities and differences in their geographical contexts, social structures, and cultural achievements.
Conclusion:
The geographical landscape of Sumer played a pivotal role in the rise and fall of this remarkable civilization. The fertile land, abundant water resources, and proximity to trade routes fostered innovation and cultural exchange, while the challenges of floods, droughts, and conflicts with neighboring civilizations tested the resilience of the Sumerian people. Understanding the geography of Sumer allows us to appreciate the unique contributions of this ancient civilization, which laid the foundation for many of the advancements we enjoy today. By studying the geography of Sumer, we gain a deeper understanding of the origins of urban civilization and the enduring influence of this ancient world on our present.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Cradle of Civilization: A Geographical Exploration of Sumer. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!