Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of the United States and Canada Physical Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of the United States and Canada Physical Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of the United States and Canada Physical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of the United States and Canada Physical Map
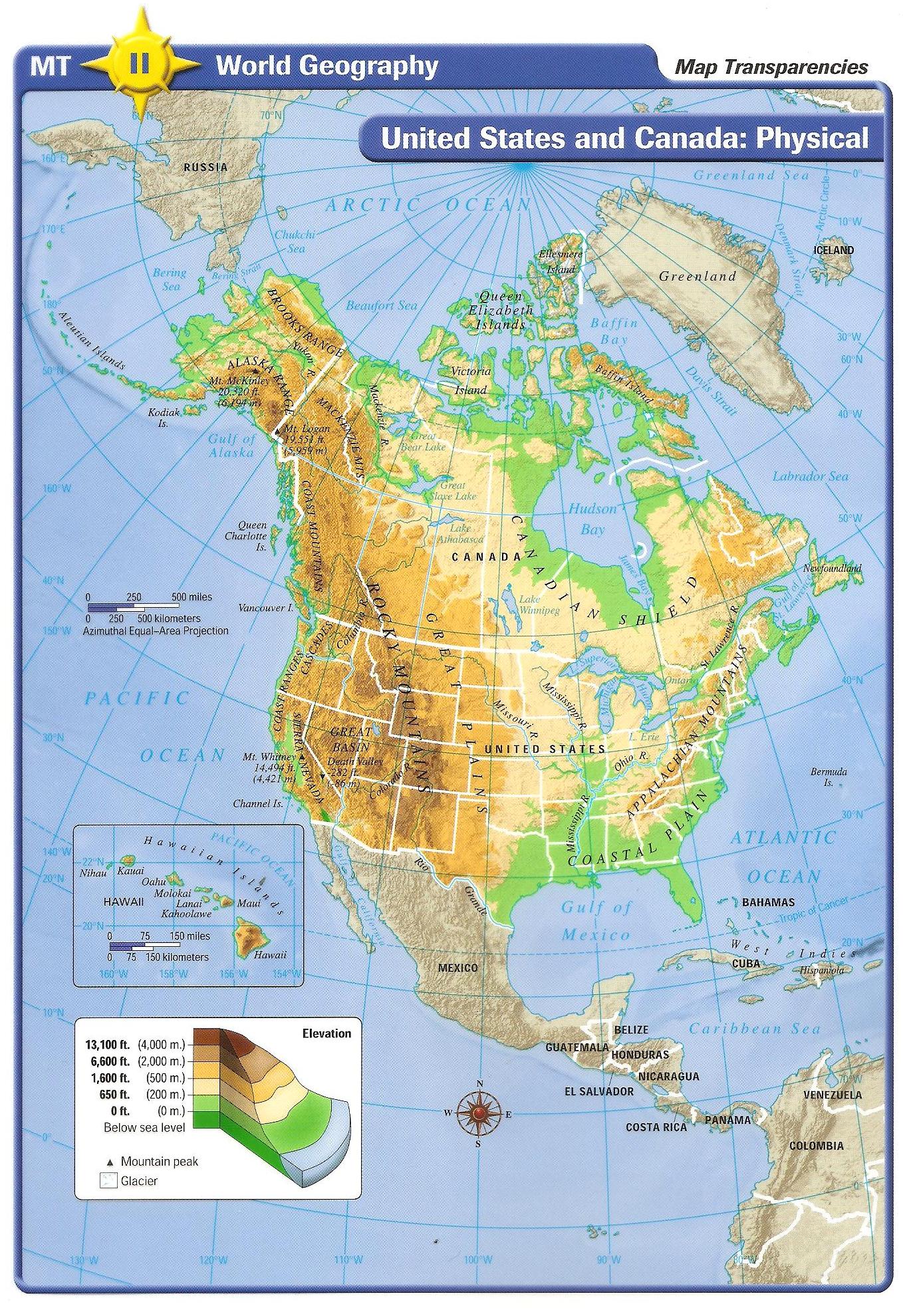
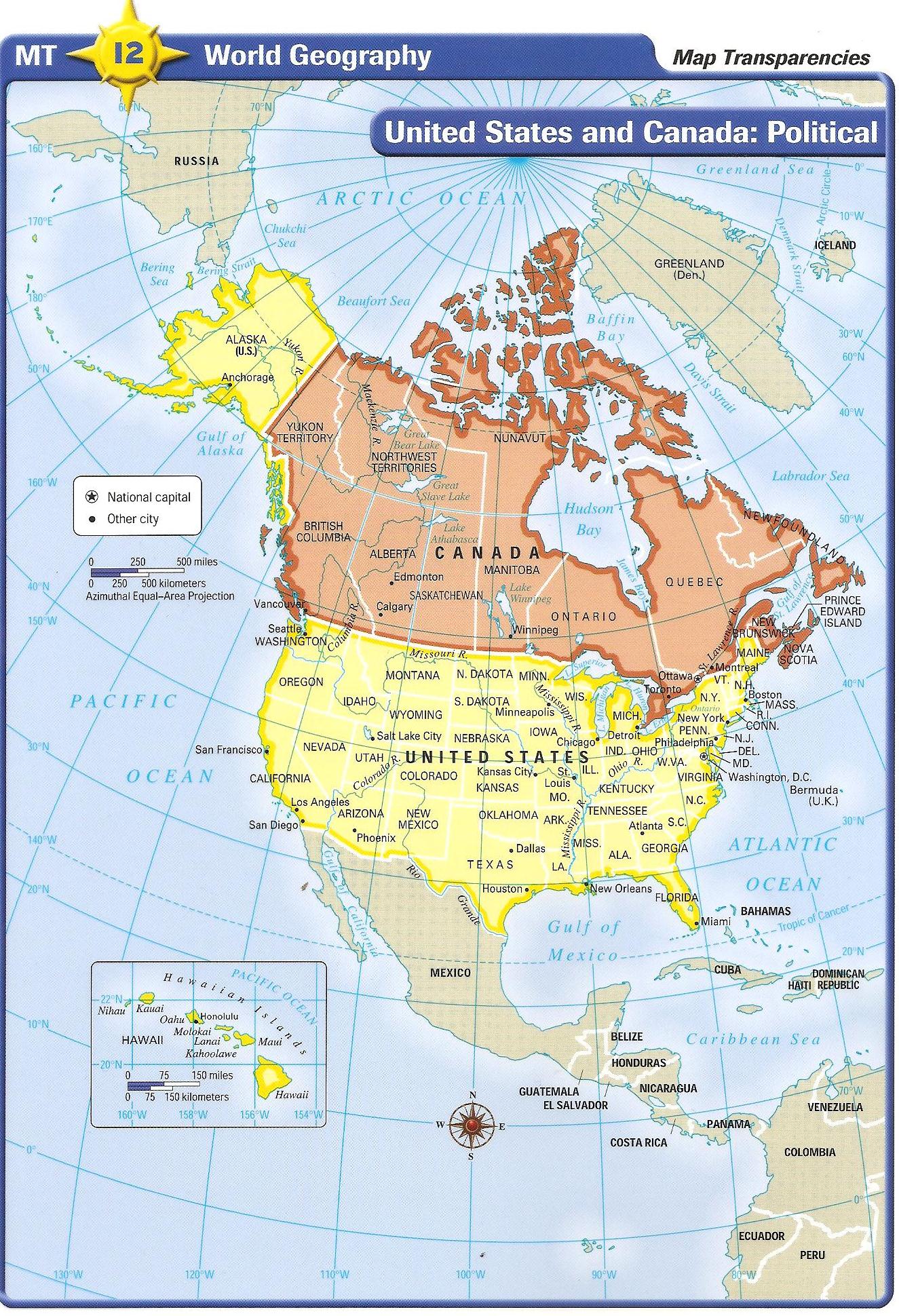
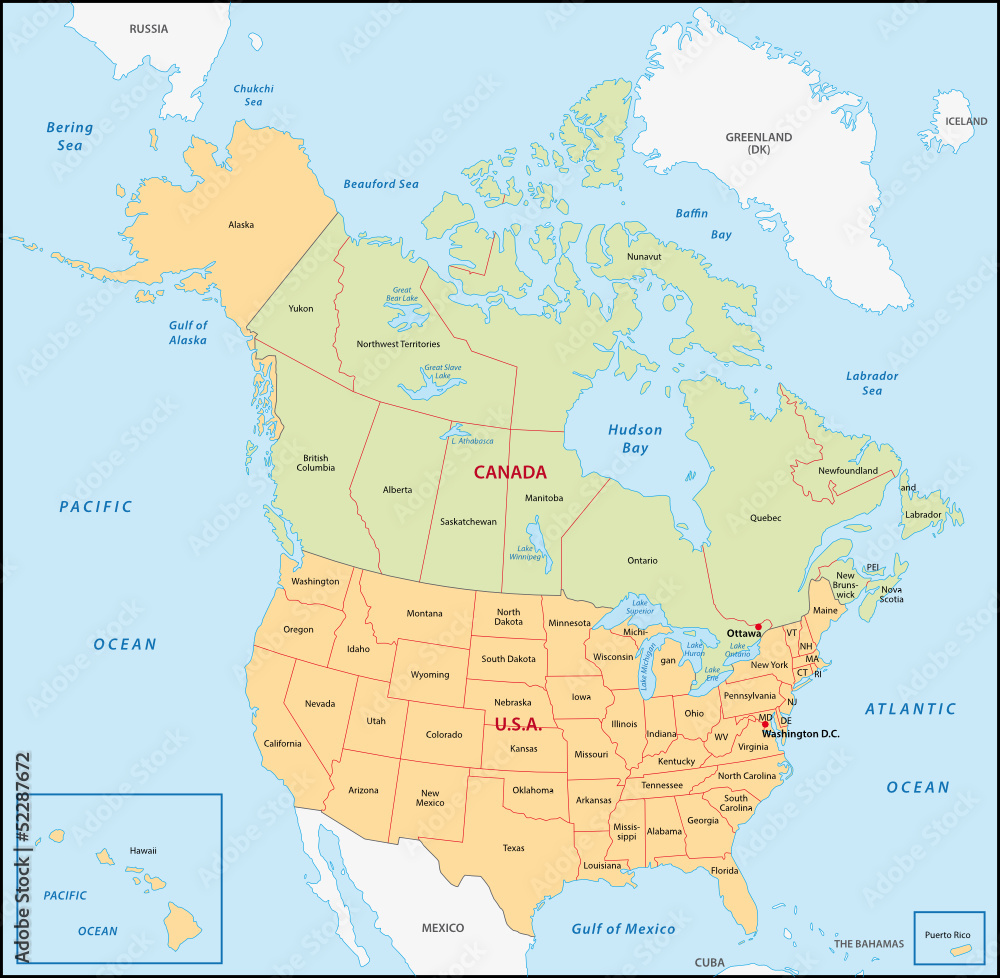
The North American continent, home to the United States and Canada, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, sculpted by geological forces over eons. Understanding the physical geography of this vast region is crucial for comprehending its natural resources, climate patterns, and the unique challenges and opportunities presented by its varied terrain. This exploration delves into the intricate details of the United States and Canada physical map, highlighting its key features and their impact on human life.
A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Physical Features
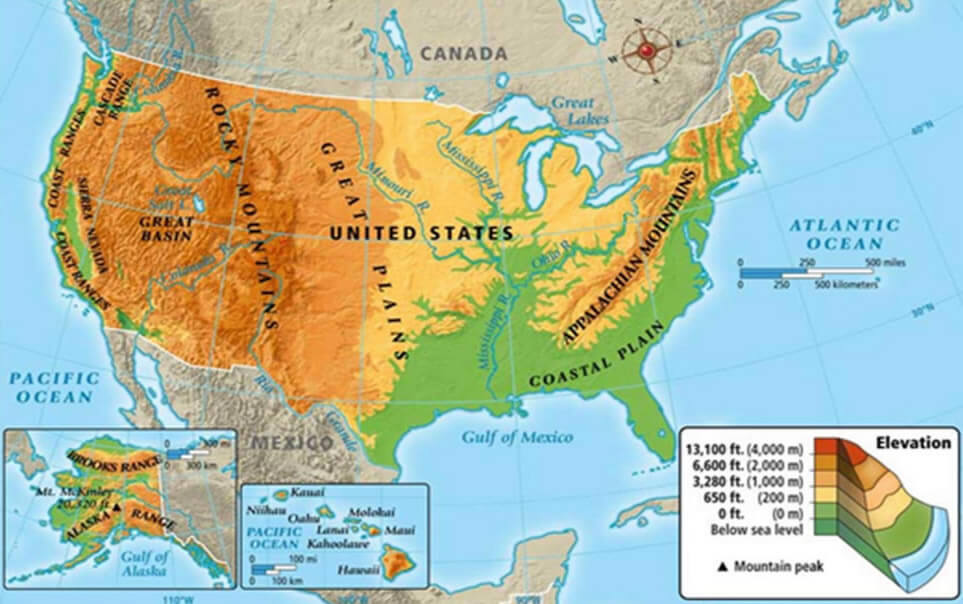
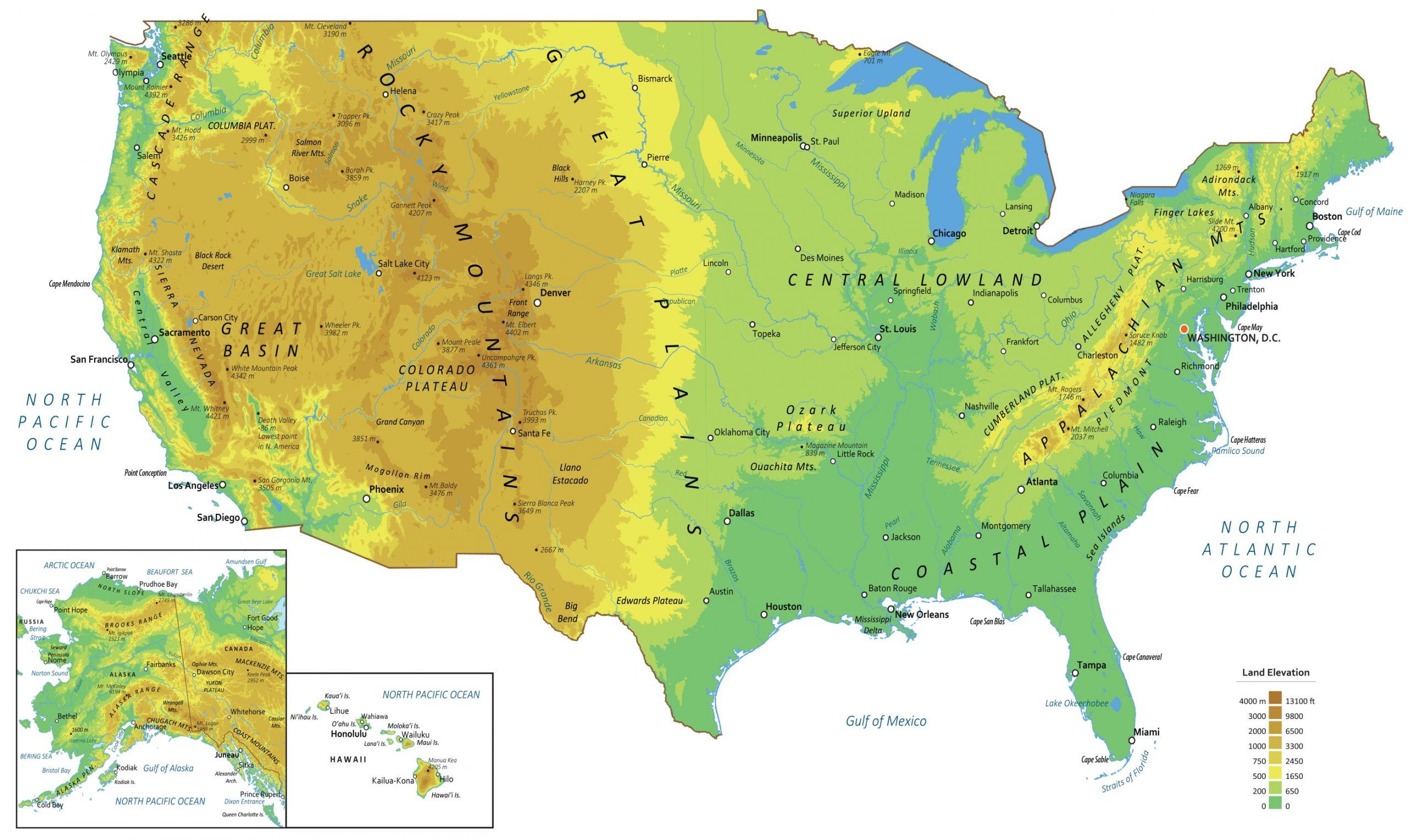
The United States and Canada physical map reveals a fascinating interplay of mountains, plains, plateaus, and coastlines.
Mountains: Backbone of the Continent
The Rocky Mountains, a majestic chain stretching from northern British Columbia to New Mexico, form the continental divide, separating the waters flowing eastward to the Atlantic Ocean from those flowing westward to the Pacific. This formidable mountain range, with its towering peaks and deep valleys, has played a pivotal role in shaping the climate and ecology of the region.
The Appalachian Mountains, a much older range, run along the eastern edge of North America, from Newfoundland to Alabama. While less imposing than the Rockies, they are nonetheless a significant geographical feature, influencing the climate and creating fertile valleys for agriculture.
Plains: Vast and Expansive
The Great Plains, a vast expanse of flat, grassy land stretching from the foothills of the Rockies to the Mississippi River, are a defining feature of the North American interior. This region, once dominated by nomadic tribes, is now a major agricultural hub, producing a significant portion of the continent’s food supply.
Plateaus: Elevated Landscapes
The Colorado Plateau, located in the southwestern United States, is a high, arid region characterized by canyons, mesas, and buttes. Its unique geological formations, most notably the Grand Canyon, are a testament to the power of erosion over millennia.
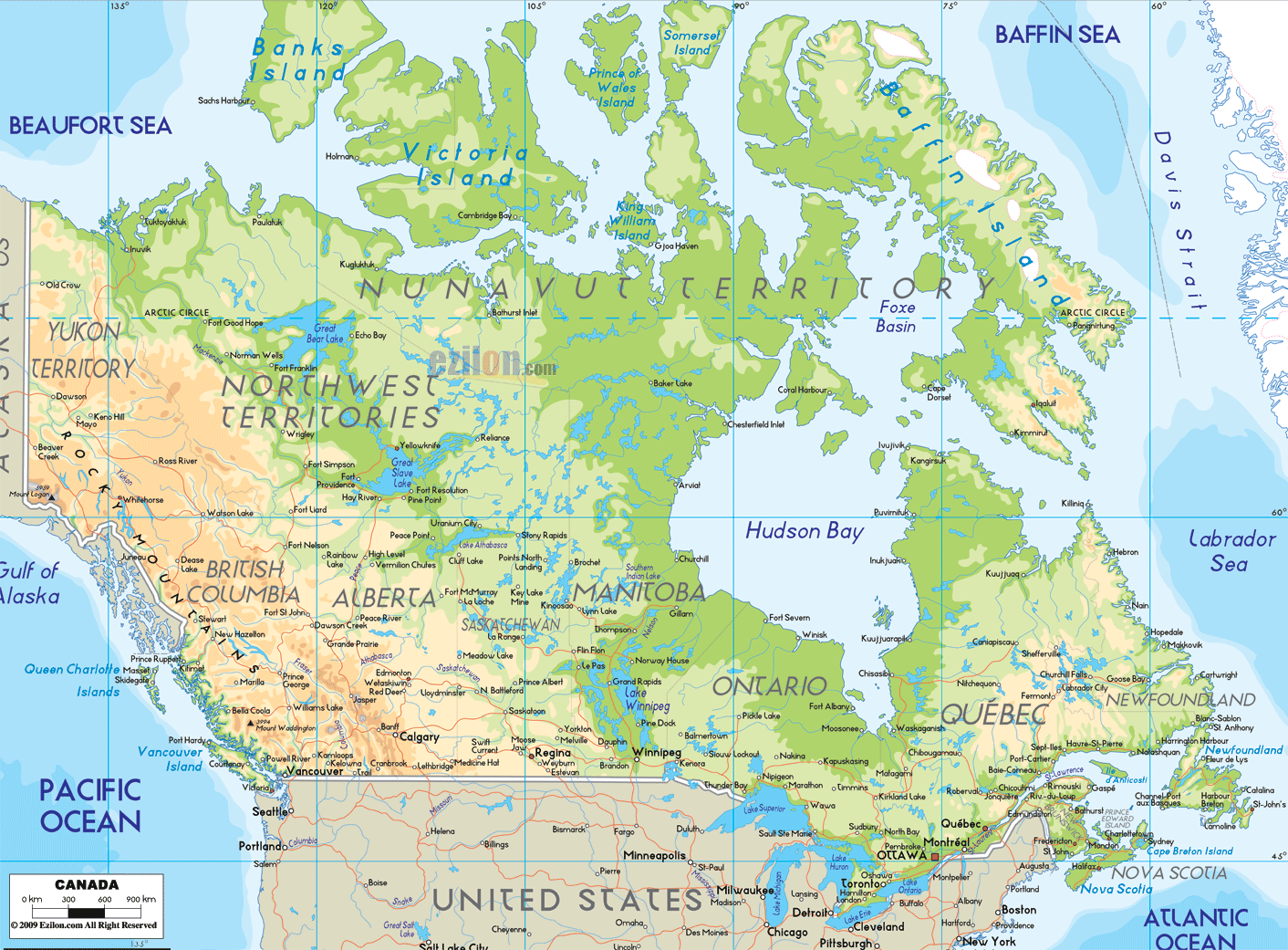
The Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of ancient, rugged terrain, covers much of central and eastern Canada. This region, rich in mineral resources, is sparsely populated but holds immense ecological significance.
Coastlines: Gateway to the World
The Atlantic Coast, with its long, sandy beaches and numerous bays, has been a vital trade route and a center of human settlement for centuries. The Pacific Coast, with its rugged cliffs, deep inlets, and volcanic mountains, offers breathtaking scenery and diverse ecosystems.
Waterways: Veins of the Continent
The Mississippi River, the longest river in North America, flows southward from its source in Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico. This vital waterway has served as a transportation artery for centuries, facilitating trade and connecting communities across the vast continent.
The Great Lakes, a chain of five massive freshwater lakes, straddle the border between the United States and Canada. These lakes, a vital source of drinking water and transportation, are also home to a diverse array of wildlife.
Climate: A Mosaic of Patterns
The physical geography of the United States and Canada creates a diverse array of climate patterns, ranging from the frigid Arctic to the humid subtropics.
Continental Climate: Extremes of Temperature
The interior of the continent, particularly the Great Plains, experiences a continental climate characterized by hot summers and cold winters. This climate, with its wide temperature swings, is conducive to certain types of agriculture, but also poses challenges for human habitation.
Maritime Climate: Moderate Temperatures
The coastal regions of the United States and Canada, particularly those along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts, experience a maritime climate, characterized by moderate temperatures and high humidity. This climate, influenced by the moderating effects of the oceans, supports a diverse array of plant and animal life.
Mountain Climate: Altitude and Precipitation
The mountainous regions of the continent, including the Rockies and the Appalachians, experience a mountain climate, characterized by cooler temperatures and higher precipitation at higher elevations. This climate supports a variety of ecosystems, from forests and grasslands to alpine meadows and glaciers.
Human Impact: Shaping the Landscape
The physical geography of the United States and Canada has profoundly influenced human settlement patterns, economic activities, and cultural development.
Agriculture: A Vital Industry
The fertile plains of the United States and Canada have made agriculture a cornerstone of their economies. From the wheat fields of the Great Plains to the fruit orchards of the Pacific Northwest, agriculture has shaped the landscape and provided sustenance for millions.
Resource Extraction: Harnessing Natural Wealth
The vast natural resources of the continent, including minerals, fossil fuels, and timber, have driven economic growth and industrial development. Mining, oil and gas extraction, and forestry are key industries, shaping the landscape and contributing to the economies of both countries.
Urbanization: Growth and Change
The physical geography of the United States and Canada has also influenced the growth and development of cities. Coastal cities, such as New York City and Los Angeles, have flourished as centers of trade and commerce. Inland cities, such as Chicago and Toronto, have developed as transportation hubs and manufacturing centers.
Conservation and Sustainability: Protecting the Future
The physical geography of the United States and Canada presents both opportunities and challenges for environmental conservation. The vast forests, wetlands, and wilderness areas are vital for biodiversity and ecosystem services. However, these ecosystems are also facing threats from pollution, habitat loss, and climate change.
Understanding the Physical Map: A Key to Knowledge
The United States and Canada physical map is not merely a collection of lines and colors; it is a window into the complex interplay of geological forces, climate patterns, and human activity. By understanding the physical geography of this region, we gain a deeper appreciation for its natural beauty, its challenges, and its potential for a sustainable future.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Physical Map
1. What are the major mountain ranges in the United States and Canada?
The major mountain ranges include the Rocky Mountains, the Appalachian Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range, and the Coast Mountains.
2. What are the key differences between the Atlantic and Pacific Coastlines?
The Atlantic Coast is characterized by long, sandy beaches and numerous bays, while the Pacific Coast is more rugged, with cliffs, inlets, and volcanic mountains.
3. How does the physical geography of the United States and Canada influence its climate?
The continent’s physical features, including mountains, plains, and coastlines, create a diverse range of climate patterns, from continental to maritime to mountain climates.
4. What are the major waterways in the United States and Canada?
The major waterways include the Mississippi River, the Great Lakes, the St. Lawrence River, and the Columbia River.
5. How has the physical geography of the United States and Canada shaped its economy?
The continent’s natural resources, including minerals, fossil fuels, and fertile land, have driven economic growth in industries such as agriculture, mining, and forestry.
Tips for Understanding the Physical Map
- Utilize online resources: Numerous websites and interactive maps provide detailed information about the physical geography of the United States and Canada.
- Explore geographic databases: Websites like Google Earth and ArcGIS offer comprehensive data and visualizations of the continent’s physical features.
- Read books and articles: Numerous books and articles delve into the specific aspects of the physical geography of the United States and Canada, providing in-depth knowledge.
- Travel and experience: Visiting different regions of the continent firsthand provides a unique perspective on the physical geography and its impact on human life.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Landscape and Life
The United States and Canada physical map is a testament to the power of nature and the resilience of human spirit. From the towering peaks of the Rockies to the vast expanse of the Great Plains, this region offers a diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding its physical geography is essential for appreciating its natural beauty, its challenges, and its potential for a sustainable future. By embracing the knowledge gleaned from the physical map, we can better understand the interconnectedness of our world and work towards a future where humanity and nature coexist in harmony.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of the United States and Canada Physical Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!