Unveiling the Secrets of La Niña: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of La Niña: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of La Niña: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of La Niña: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Maps
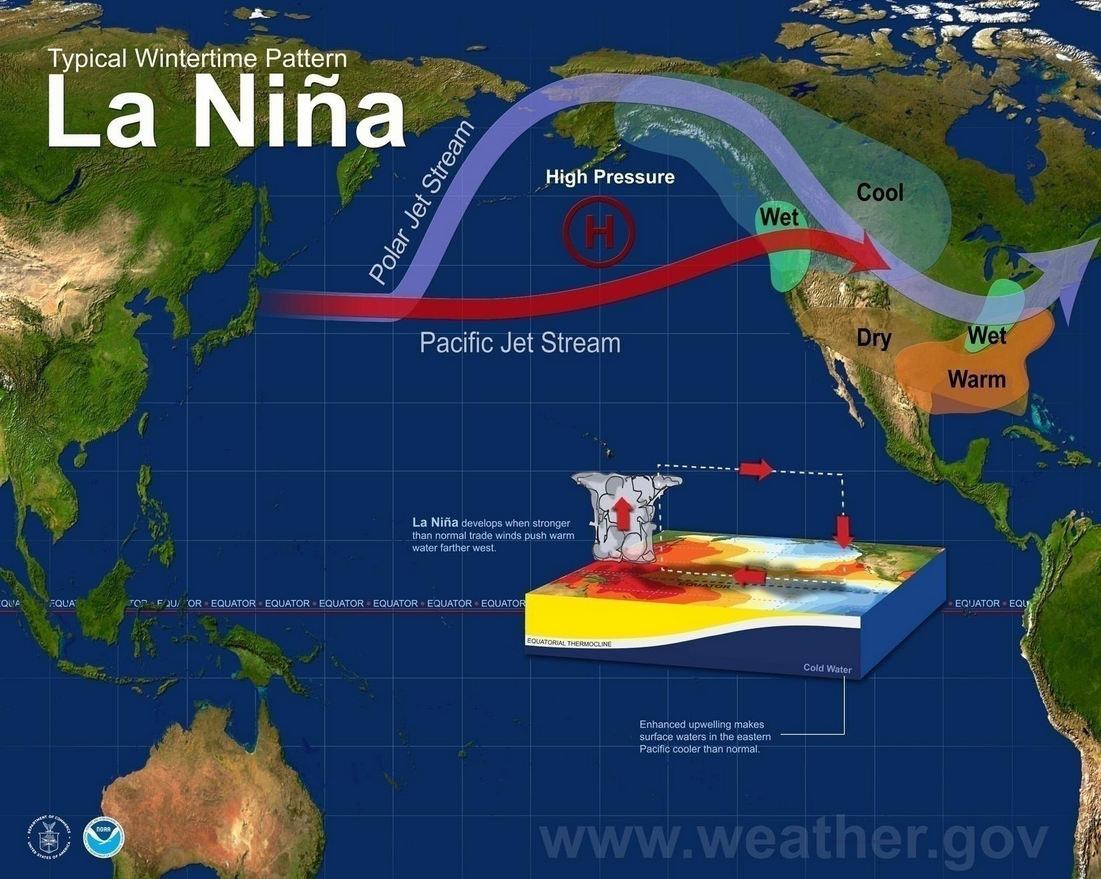
La Niña, a recurring climate pattern characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, exerts a significant influence on global weather patterns. While its effects are felt worldwide, understanding its intricacies requires delving into the intricate interplay of atmospheric and oceanic processes. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to deciphering La Niña maps, highlighting their importance in forecasting weather conditions and understanding the impact on various regions across the globe.
Understanding La Niña: A Deep Dive into the Phenomenon
La Niña, often referred to as the "cool phase" of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, is a natural climate pattern that occurs every few years. Its origins lie in the complex interplay of ocean currents, atmospheric pressure, and wind patterns in the Pacific Ocean.
The Role of Ocean Currents and Atmospheric Pressure
The Pacific Ocean’s vast expanse is home to intricate currents that transport heat and influence global weather patterns. During La Niña, trade winds strengthen, pushing warm surface waters westward. This westward movement creates a pool of cooler-than-average water in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific, leading to a decrease in sea surface temperatures.
Simultaneously, atmospheric pressure patterns shift. The high-pressure zone in the eastern Pacific intensifies, while the low-pressure zone in the western Pacific weakens. This pressure gradient further enhances the trade winds, amplifying the westward flow of warm surface waters.
The Impact of La Niña on Global Weather Patterns
La Niña’s influence extends far beyond the Pacific Ocean, impacting weather patterns across the globe. The cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific trigger a chain reaction of atmospheric changes, affecting rainfall, temperature, and wind patterns in various regions.
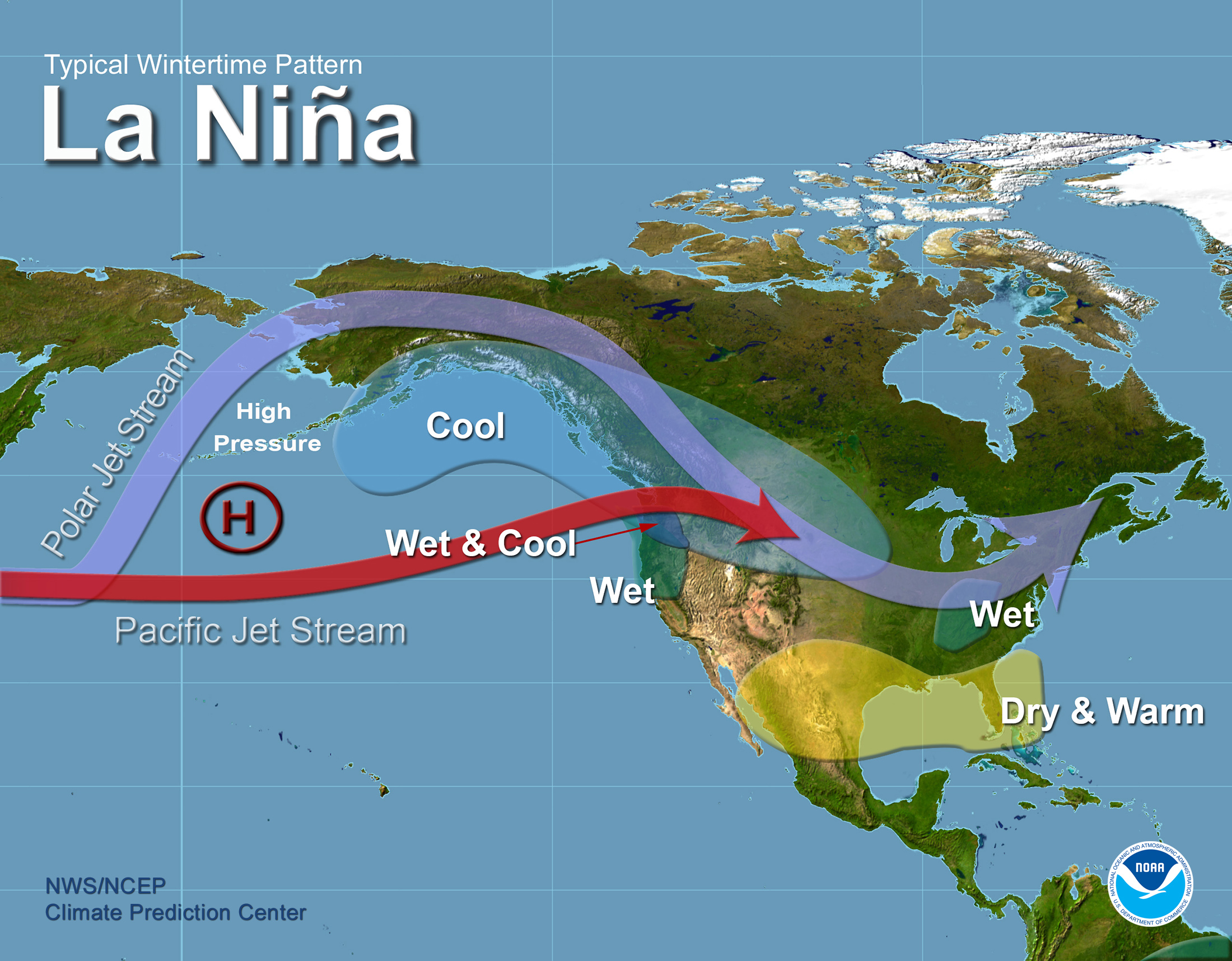
Impacts in the Americas:
- North America: La Niña typically brings drier and warmer conditions to the southern United States, while the northern regions experience colder and snowier winters. The Pacific Northwest often sees increased rainfall.
- South America: La Niña can lead to increased rainfall in the Amazon rainforest, while the southern regions experience drier conditions.
Impacts in Asia and Oceania:
- Southeast Asia: La Niña often results in drier conditions, potentially leading to droughts in Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
- Australia: The eastern and southeastern regions of Australia experience increased rainfall and a higher risk of flooding during La Niña events.
- South Asia: La Niña can enhance the monsoon season in India, leading to heavier rainfall.
Impacts in Africa and Europe:
- Africa: La Niña can influence rainfall patterns across the continent, potentially leading to droughts in some regions and increased rainfall in others.
- Europe: La Niña can contribute to colder winters in northern Europe, while warmer temperatures are observed in southern Europe.
Deciphering La Niña Maps: A Visual Guide to Understanding the Phenomenon
La Niña maps, also known as ENSO maps, provide a visual representation of the sea surface temperature anomalies in the Pacific Ocean. These maps play a crucial role in understanding the evolution of La Niña events and predicting their impact on global weather patterns.
Key Elements of La Niña Maps:
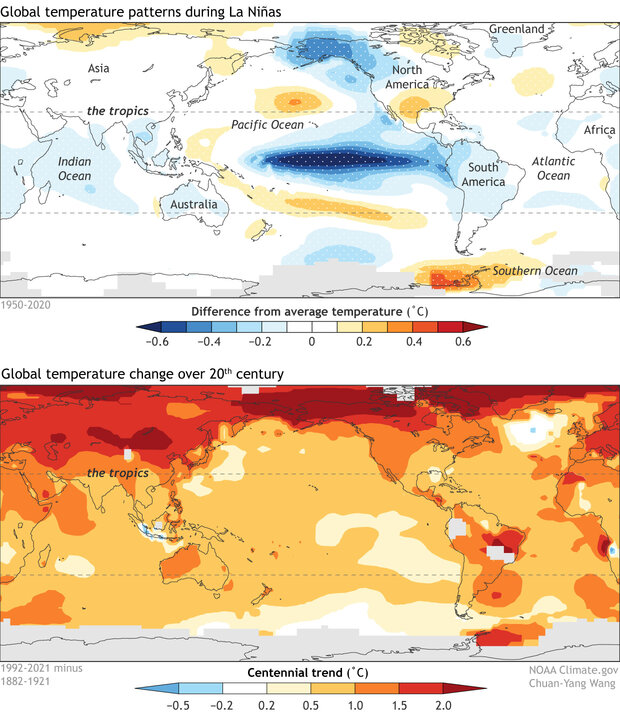
- Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies: The map depicts the deviation of sea surface temperatures from their long-term average. Areas shaded in blue indicate cooler-than-average temperatures, while areas shaded in red indicate warmer-than-average temperatures.
- Contour Lines: Contour lines connect points with the same sea surface temperature anomaly, providing a visual representation of the spatial distribution of the anomalies.
- Time Series Data: La Niña maps often include time series data, showing the evolution of sea surface temperature anomalies over time. This data helps scientists track the development and decay of La Niña events.
- Spatial Coverage: La Niña maps typically cover the entire Pacific Ocean, from the coast of South America to the western Pacific. This allows scientists to assess the extent and intensity of the La Niña event.
Interpreting La Niña Maps: A Guide to Understanding the Data
Analyzing La Niña maps requires an understanding of the key elements discussed above. By observing the spatial distribution of sea surface temperature anomalies and the temporal evolution of the event, scientists can gain insights into the strength and duration of La Niña events.
Identifying La Niña Events:
- Strong La Niña: Characterized by widespread and persistent cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific.
- Moderate La Niña: Exhibits cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures, but with a smaller spatial extent or shorter duration.
- Weak La Niña: Shows less pronounced cooling in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific.
Predicting Weather Patterns:
La Niña maps serve as valuable tools for predicting weather patterns in various regions. By analyzing the spatial distribution and intensity of the anomalies, scientists can forecast potential changes in rainfall, temperature, and wind patterns.
The Importance of La Niña Maps: Forecasting and Mitigation
La Niña maps play a crucial role in various fields, enabling informed decision-making and mitigation strategies.
Forecasting and Planning:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on La Niña maps to anticipate potential changes in rainfall and temperature, allowing them to adjust planting schedules, irrigation practices, and crop selection.
- Water Management: Water resource managers use La Niña maps to forecast potential changes in water availability, aiding in water allocation and drought mitigation efforts.
- Disaster Preparedness: La Niña maps help emergency management agencies anticipate potential weather-related disasters, such as floods, droughts, and wildfires, enabling them to develop preparedness plans and allocate resources effectively.
Mitigation and Adaptation:
- Climate Change Adaptation: La Niña maps contribute to understanding the potential impacts of climate change on weather patterns, informing adaptation strategies for vulnerable communities.
- Resource Management: La Niña maps assist in managing resources, such as water and energy, to mitigate the potential impacts of La Niña events.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about La Niña Maps
Q1: How often does La Niña occur?
La Niña events occur every few years, with an average cycle length of 2-7 years. However, their frequency and intensity can vary.
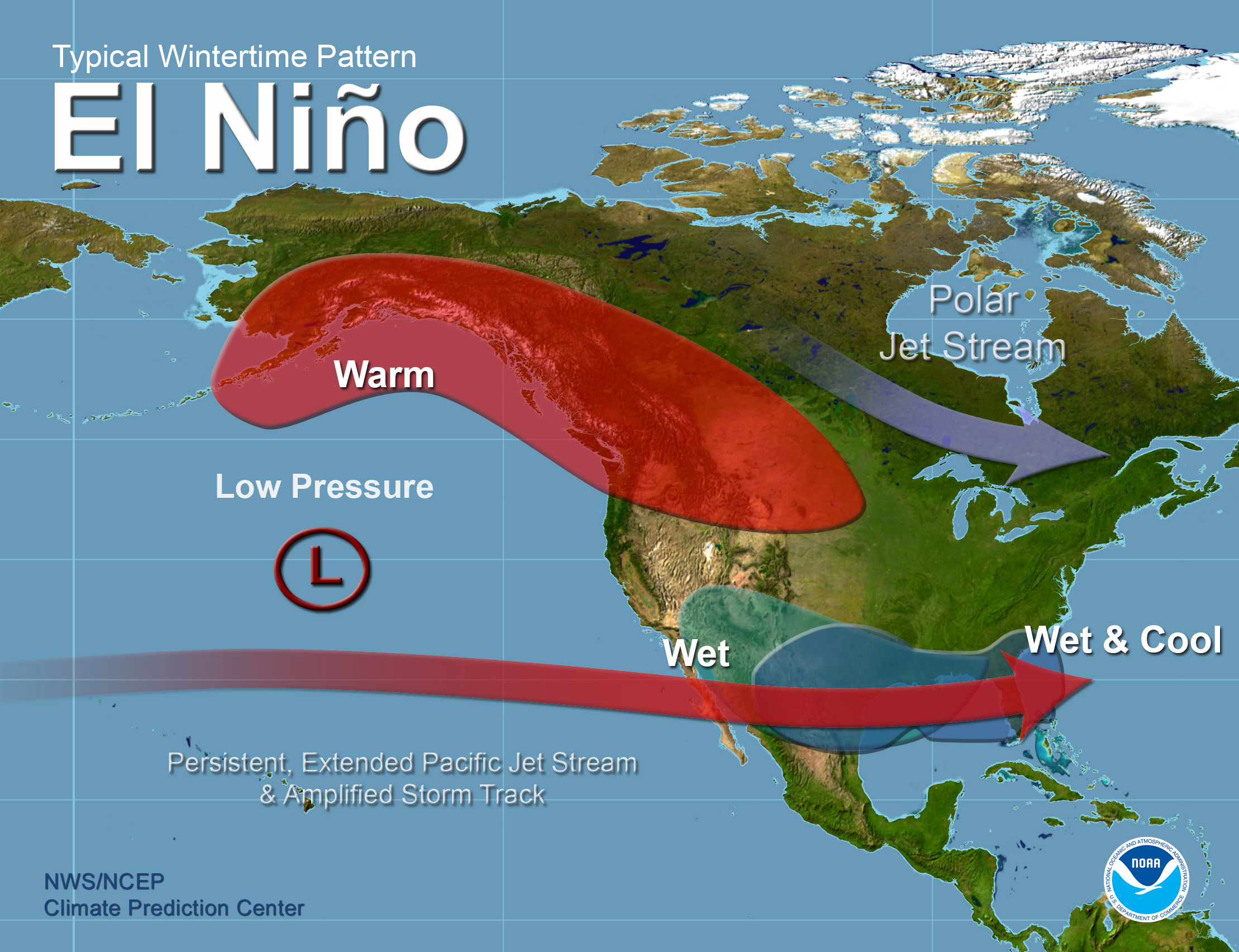
Q2: What are the main differences between La Niña and El Niño?
While both La Niña and El Niño are part of the ENSO cycle, they are characterized by opposite changes in sea surface temperatures. La Niña features cooler-than-average temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific, while El Niño exhibits warmer-than-average temperatures in the same region.
Q3: How do La Niña maps differ from El Niño maps?
La Niña maps depict cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific, while El Niño maps show warmer-than-average temperatures in the same region. The spatial distribution and intensity of the anomalies can vary depending on the specific event.
Q4: Can La Niña maps predict the exact weather conditions in a particular location?
While La Niña maps provide valuable insights into potential weather patterns, they cannot predict exact conditions at specific locations. The impact of La Niña events can vary depending on local factors, such as topography and proximity to large bodies of water.
Q5: Are La Niña maps always accurate?
La Niña maps provide a valuable tool for understanding and predicting weather patterns, but they are not always perfectly accurate. The complexity of the climate system and the inherent variability of weather patterns can lead to uncertainties in forecasting.
Tips for Using La Niña Maps Effectively:
- Consult Multiple Sources: Refer to multiple La Niña maps and forecasts from reputable sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the event.
- Consider Local Factors: Remember that La Niña’s impact can vary depending on local factors, such as topography and proximity to large bodies of water.
- Stay Updated: Monitor La Niña maps and forecasts regularly to stay informed about the evolution of the event and its potential impacts.
- Plan and Adapt: Use La Niña maps to inform your planning and adaptation strategies, particularly in sectors sensitive to weather changes.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Secrets of La Niña Maps
La Niña maps provide a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the impacts of this complex climate pattern. By deciphering the intricate interplay of ocean currents, atmospheric pressure, and wind patterns, scientists can gain valuable insights into the evolution and influence of La Niña events. These maps serve as a vital resource for various sectors, enabling informed decision-making, resource management, and mitigation strategies to address the challenges posed by this recurring climate pattern.
Understanding La Niña maps is not merely a scientific endeavor but a crucial step towards building resilience and adapting to a changing climate. By harnessing the knowledge gleaned from these maps, we can navigate the complex interplay of weather patterns and mitigate the potential risks associated with La Niña events.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of La Niña: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!